Lukas Zhornyak
HashEncoding: Autoencoding with Multiscale Coordinate Hashing
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:We present HashEncoding, a novel autoencoding architecture that leverages a non-parametric multiscale coordinate hash function to facilitate a per-pixel decoder without convolutions. By leveraging the space-folding behaviour of hashing functions, HashEncoding allows for an inherently multiscale embedding space that remains much smaller than the original image. As a result, the decoder requires very few parameters compared with decoders in traditional autoencoders, approaching a non-parametric reconstruction of the original image and allowing for greater generalizability. Finally, by allowing backpropagation directly to the coordinate space, we show that HashEncoding can be exploited for geometric tasks such as optical flow.
Beyond mAP: Re-evaluating and Improving Performance in Instance Segmentation with Semantic Sorting and Contrastive Flow
Jul 04, 2022
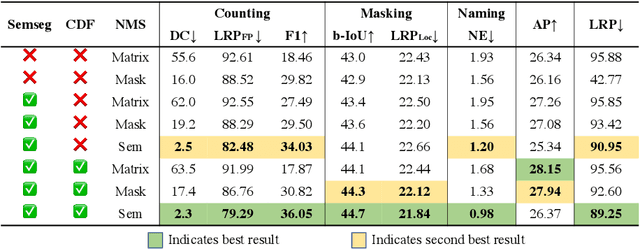
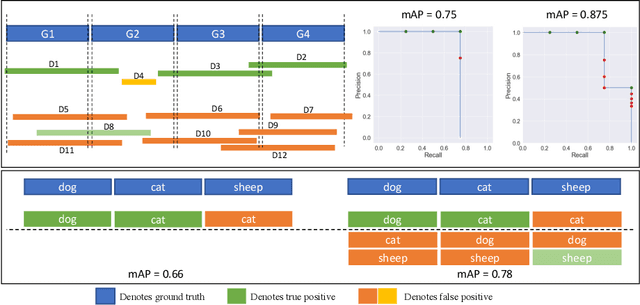
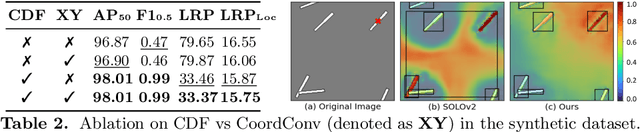
Abstract:Top-down instance segmentation methods improve mAP by hedging bets on low-confidence predictions to match a ground truth. Moreover, the query-key paradigm of top-down methods leads to the instance merging problem. An excessive number of duplicate predictions leads to the (over)counting error, and the independence of category and localization branches leads to the naming error. The de-facto mAP metric doesn't capture these errors, as we show that a trivial dithering scheme can simultaneously increase mAP with hedging errors. To this end, we propose two graph-based metrics that quantifies the amount of hedging both inter-and intra-class. We conjecture the source of the hedging problem is due to feature merging and propose a) Contrastive Flow Field to encode contextual differences between instances as a supervisory signal, and b) Semantic Sorting and NMS step to suppress duplicates and incorrectly categorized prediction. Ablations show that our method encodes contextual information better than baselines, and experiments on COCO our method simultaneously reduces merging and hedging errors compared to state-of-the-art instance segmentation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge