Lukas Graf
The UmboMic: A PVDF Cantilever Microphone
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:Objective: We present the "UmboMic," a prototype piezoelectric cantilever microphone designed for future use with totally-implantable cochlear implants. Methods: The UmboMic sensor is made from polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) because of its low Young's modulus and biocompatibility. The sensor is designed to fit in the middle ear and measure the motion of the underside of the eardrum at the umbo. To maximize its performance, we developed a low noise charge amplifier in tandem with the UmboMic sensor. This paper presents the performance of the UmboMic sensor and amplifier in fresh cadaveric human temporal bones. Results: When tested in human temporal bones, the UmboMic apparatus achieves an equivalent input noise of 32.3 dB SPL over the frequency range 100 Hz to 7 kHz, good linearity, and a flat frequency response to within 10 dB from about 100 Hz to 6 kHz. Conclusion: These results demonstrate the feasibility of a PVDF-based microphone when paired with a low-noise amplifier. The reported UmboMic apparatus is comparable in performance to a conventional hearing aid microphone. Significance: The proof-of-concept UmboMic apparatus is a promising step towards creating a totally-implantable cochlear implant. A completely internal system would enhance the quality of life of cochlear implant users.
An Implantable Piezofilm Middle Ear Microphone: Performance in Human Cadaveric Temporal Bones
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:Purpose: One of the major reasons that totally implantable cochlear microphones are not readily available is the lack of good implantable microphones. An implantable microphone has the potential to provide a range of benefits over external microphones for cochlear implant users including the filtering ability of the outer ear, cosmetics, and usability in all situations. This paper presents results from experiments in human cadaveric ears of a piezofilm microphone concept under development as a possible component of a future implantable microphone system for use with cochlear implants. This microphone is referred to here as a drum microphone (DrumMic) that senses the robust and predictable motion of the umbo, the tip of the malleus. Methods: The performance was measured of five DrumMics inserted in four different human cadaveric temporal bones. Sensitivity, linearity, bandwidth, and equivalent input noise were measured during these experiments using a sound stimulus and measurement setup. Results: The sensitivity of the DrumMics was found to be tightly clustered across different microphones and ears despite differences in umbo and middle ear anatomy. The DrumMics were shown to behave linearly across a large dynamic range (46 dB SPL to 100 dB SPL) across a wide bandwidth (100 Hz to 8 kHz). The equivalent input noise (0.1-10 kHz) of the DrumMic and amplifier referenced to the ear canal was measured to be 54 dB SPL and estimated to be 46 dB SPL after accounting for the pressure gain of the outer ear. Conclusion: The results demonstrate that the DrumMic behaves robustly across ears and fabrication. The equivalent input noise performance was shown to approach that of commercial hearing aid microphones. To advance this demonstration of the DrumMic concept to a future prototype implantable in humans, work on encapsulation, biocompatibility, connectorization will be required.
Machine-Learned Prediction Equilibrium for Dynamic Traffic Assignment
Sep 14, 2021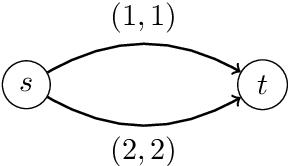
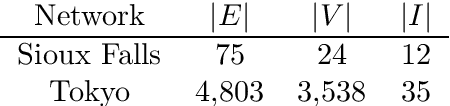
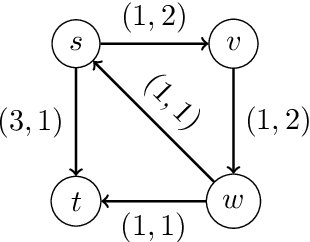
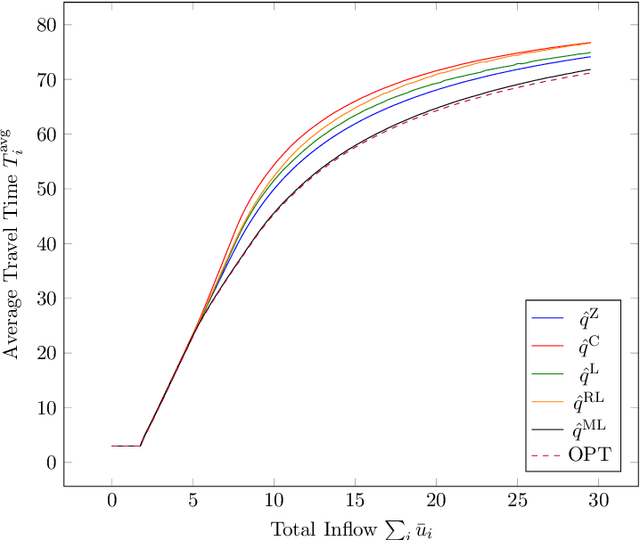
Abstract:We study a dynamic traffic assignment model, where agents base their instantaneous routing decisions on real-time delay predictions. We formulate a mathematically concise model and derive properties of the predictors that ensure a dynamic prediction equilibrium exists. We demonstrate the versatility of our framework by showing that it subsumes the well-known full information and instantaneous information models, in addition to admitting further realistic predictors as special cases. We complement our theoretical analysis by an experimental study, in which we systematically compare the induced average travel times of different predictors, including a machine-learning model trained on data gained from previously computed equilibrium flows, both on a synthetic and a real road network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge