Luigi Biagiotti
On the Analysis of Stability, Sensitivity and Transparency in Variable Admittance Control for pHRI Enhanced by Virtual Fixtures
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:The interest in Physical Human-Robot Interaction (pHRI) has significantly increased over the last two decades thanks to the availability of collaborative robots that guarantee user safety during force exchanges. For this reason, stability concerns have been addressed extensively in the literature while proposing new control schemes for pHRI applications. Because of the nonlinear nature of robots, stability analyses generally leverage passivity concepts. On the other hand, the proposed algorithms generally consider ideal models of robot manipulators. For this reason, the primary objective of this paper is to conduct a detailed analysis of the sources of instability for a class of pHRI control schemes, namely proxy-based constrained admittance controllers, by considering parasitic effects such as transmission elasticity, motor velocity saturation, and actuation delay. Next, a sensitivity analysis supported by experimental results is carried out, in order to identify how the control parameters affect the stability of the overall system. Finally, an adaptation technique for the proxy parameters is proposed with the goal of maximizing transparency in pHRI. The proposed adaptation method is validated through both simulations and experimental tests.
Arc-Length-Based Warping for Robot Skill Synthesis from Multiple Demonstrations
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:In robotics, Learning from Demonstration (LfD) aims to transfer skills to robots by using multiple demonstrations of the same task. These demonstrations are recorded and processed to extract a consistent skill representation. This process typically requires temporal alignment through techniques such as Dynamic Time Warping (DTW). In this paper, we introduce a novel algorithm, named Spatial Sampling (SS), specifically designed for robot trajectories, that enables time-independent alignment of the trajectories by providing an arc-length parametrization of the signals. This approach eliminates the need for temporal alignment, enhancing the accuracy and robustness of skill representation. Specifically, we show that large time shifts in the demonstrated trajectories can introduce uncertainties in the synthesis of the final trajectory, which alignment in the arc-length domain can drastically reduce, in comparison with various state-of-the-art time-based signal alignment algorithms. To this end, we built a custom publicly available dataset of robot recordings to test real-world trajectories.
Optimizing Design and Control Methods for Using Collaborative Robots in Upper-Limb Rehabilitation
Jul 26, 2024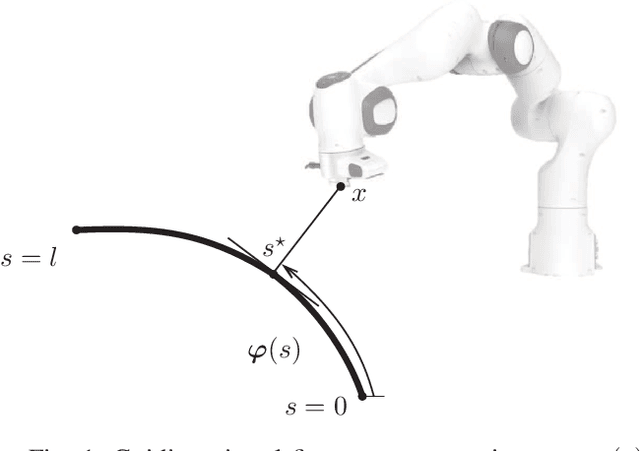
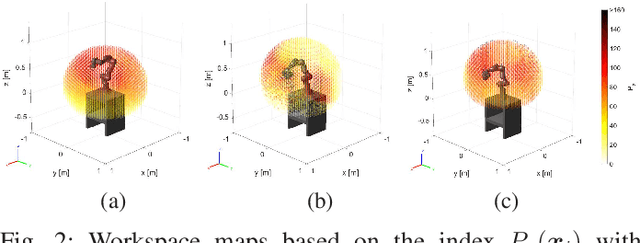
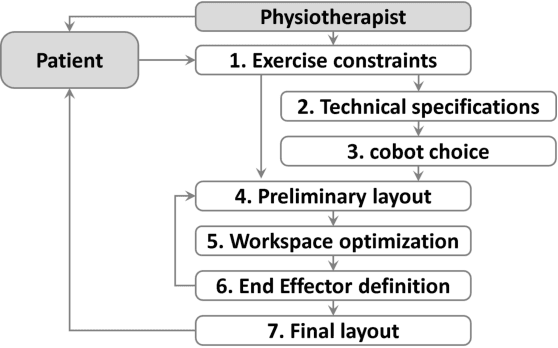
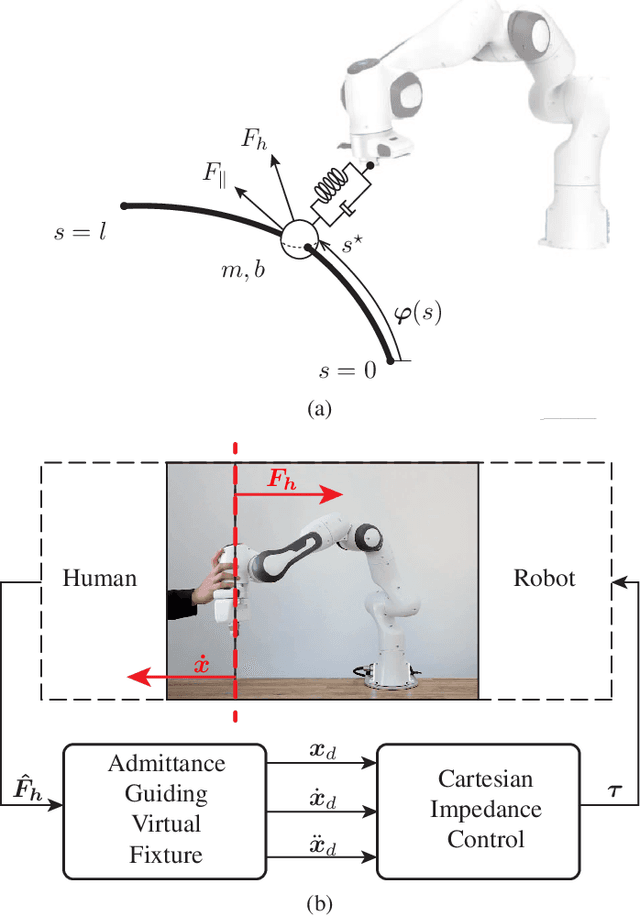
Abstract:In this paper, we address the development of a robotic rehabilitation system for the upper limbs based on collaborative end-effector solutions. The use of commercial collaborative robots offers significant advantages for this task, as they are optimized from an engineering perspective and ensure safe physical interaction with humans. However, they also come with noticeable drawbacks, such as the limited range of sizes available on the market and the standard control modes, which are primarily oriented towards industrial or service applications. To address these limitations, we propose an optimization-based design method to fully exploit the capability of the cobot in performing rehabilitation tasks. Additionally, we introduce a novel control architecture based on an admittance-type Virtual Fixture method, which constrains the motion of the robot along a prescribed path. This approach allows for an intuitive definition of the task to be performed via Programming by Demonstration and enables the system to operate both passively and actively. In passive mode, the system supports the patient during task execution with additional force, while in active mode, it opposes the motion with a braking force. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
A Minimum-Jerk Approach to Handle Singularities in Virtual Fixtures
May 06, 2024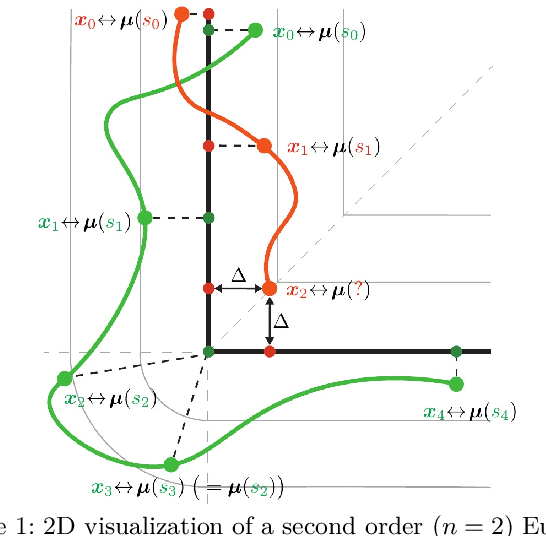


Abstract:Implementing virtual fixtures in guiding tasks constrains the movement of the robot's end effector to specific curves within its workspace. However, incorporating guiding frameworks may encounter discontinuities when optimizing the reference target position to the nearest point relative to the current robot position. This article aims to give a geometric interpretation of such discontinuities, with specific reference to the commonly adopted Gauss-Newton algorithm. The effect of such discontinuities, defined as Euclidean Distance Singularities, is experimentally proved. We then propose a solution that is based on a Linear Quadratic Tracking problem with minimum jerk command, then compare and validate the performances of the proposed framework in two different human-robot interaction scenarios.
Phase-free Dynamic Movement Primitives Applied to Kinesthetic Guidance in Robotic Co-manipulation Tasks
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:When there is a need to define and adapt a robotic task based on a reference motion, Dynamic Movement Primitives (DMP) is a standard and efficient method for encoding it. The nominal trajectory is typically obtained through a Programming by Demonstration (PbD) approach, where the robot is taught a specific task through kinesthetic guidance. Subsequently, the motion is reproduced by the manipulator in terms of both geometric path and timing law. The basic approach for modifying the duration of the execution involves adjusting a time constant characterizing the model. On the contrary, the goal of this paper is to achieve complete decoupling between the geometric information of the task, encoded into the DMP, and the phase law governing the execution, allowing them to be chosen independently. This enables the optimization of the task duration to satisfy constraints such as velocity or acceleration or even to define a phase law dependent on external inputs, such as the force applied by a user in a co-manipulation task. As an example, this mechanism will be exploited to define a rehabilitation activity where the cobot assists humans in performing various pre-planned exercises.
Optimal Feed-Forward Control for Robotic Transportation of Solid and Liquid Materials via Nonprehensile Grasp
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:In everyday life, we often find that we can maintain an object's equilibrium on a tray by adjusting its orientation. Building upon this observation and extending the method we previously proposed to suppress sloshing in a moving vessel, this paper presents a feedforward control approach for transporting objects with a robot that are not firmly grasped but simply placed on a tray. The proposed approach combines smoothing actions and end-effector re-orientation to prevent object sliding. It can be integrated into existing robotic systems as a plug-in element between the reference trajectory generator and the robot control. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods, particularly when dealing with unknown reference signals, we embed them in a direct teleoperation scheme. In this scheme, the user commands the robot carrying the tray by simply moving their hand in free space, with the hand's 3D position detected by a motion capture system. Furthermore, in the case of point-to-point motions, the same feedforward control, when fed with step inputs representing the desired goal position, dynamically generates the minimum-time reference trajectory that complies with velocity and acceleration constraints, thus avoiding sloshing and slipping. More information and accompanying videos can be found at https://sites.google.com/view/robotwaiter/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge