Luís F. Simões
Operational range bounding of spectroscopy models with anomaly detection
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Safe operation of machine learning models requires architectures that explicitly delimit their operational ranges. We evaluate the ability of anomaly detection algorithms to provide indicators correlated with degraded model performance. By placing acceptance thresholds over such indicators, hard boundaries are formed that define the model's coverage. As a use case, we consider the extraction of exoplanetary spectra from transit light curves, specifically within the context of ESA's upcoming Ariel mission. Isolation Forests are shown to effectively identify contexts where prediction models are likely to fail. Coverage/error trade-offs are evaluated under conditions of data and concept drift. The best performance is seen when Isolation Forests model projections of the prediction model's explainability SHAP values.
Multi-rendezvous Spacecraft Trajectory Optimization with Beam P-ACO
Apr 03, 2017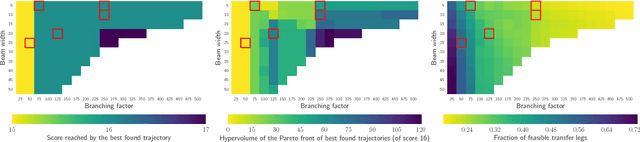
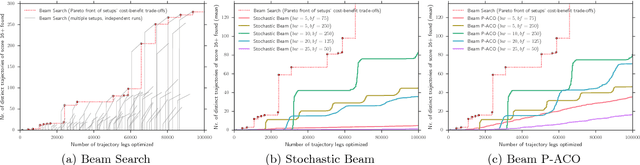
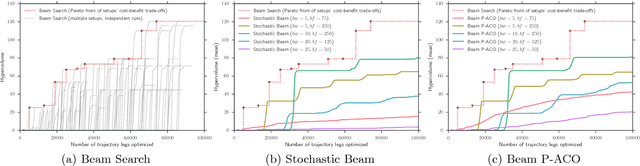
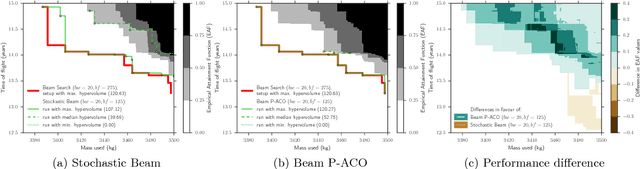
Abstract:The design of spacecraft trajectories for missions visiting multiple celestial bodies is here framed as a multi-objective bilevel optimization problem. A comparative study is performed to assess the performance of different Beam Search algorithms at tackling the combinatorial problem of finding the ideal sequence of bodies. Special focus is placed on the development of a new hybridization between Beam Search and the Population-based Ant Colony Optimization algorithm. An experimental evaluation shows all algorithms achieving exceptional performance on a hard benchmark problem. It is found that a properly tuned deterministic Beam Search always outperforms the remaining variants. Beam P-ACO, however, demonstrates lower parameter sensitivity, while offering superior worst-case performance. Being an anytime algorithm, it is then found to be the preferable choice for certain practical applications.
* Code available at https://github.com/lfsimoes/beam_paco__gtoc5
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge