Lorenz Wendlinger
Robust Generalizable Heterogeneous Legal Link Prediction
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Recent work has applied link prediction to large heterogeneous legal citation networks \new{with rich meta-features}. We find that this approach can be improved by including edge dropout and feature concatenation for the learning of more robust representations, which reduces error rates by up to 45%. We also propose an approach based on multilingual node features with an improved asymmetric decoder for compatibility, which allows us to generalize and extend the prediction to more, geographically and linguistically disjoint, data from New Zealand. Our adaptations also improve inductive transferability between these disjoint legal systems.
On the Suitability of pre-trained foundational LLMs for Analysis in German Legal Education
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:We show that current open-source foundational LLMs possess instruction capability and German legal background knowledge that is sufficient for some legal analysis in an educational context. However, model capability breaks down in very specific tasks, such as the classification of "Gutachtenstil" appraisal style components, or with complex contexts, such as complete legal opinions. Even with extended context and effective prompting strategies, they cannot match the Bag-of-Words baseline. To combat this, we introduce a Retrieval Augmented Generation based prompt example selection method that substantially improves predictions in high data availability scenarios. We further evaluate the performance of pre-trained LLMs on two standard tasks for argument mining and automated essay scoring and find it to be more adequate. Throughout, pre-trained LLMs improve upon the baseline in scenarios with little or no labeled data with Chain-of-Thought prompting further helping in the zero-shot case.
SUDS: A Strategy for Unsupervised Drift Sampling
Nov 05, 2024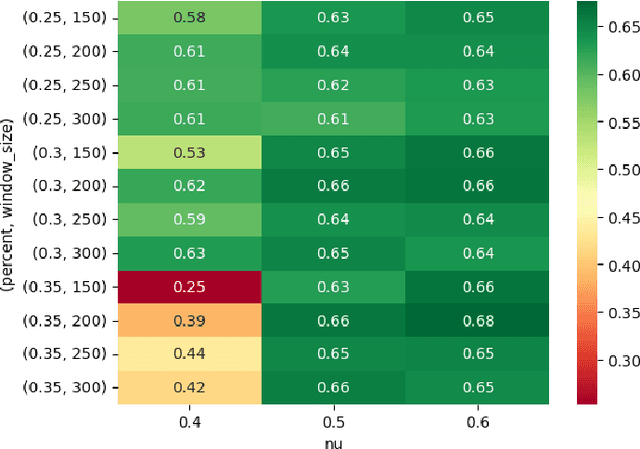
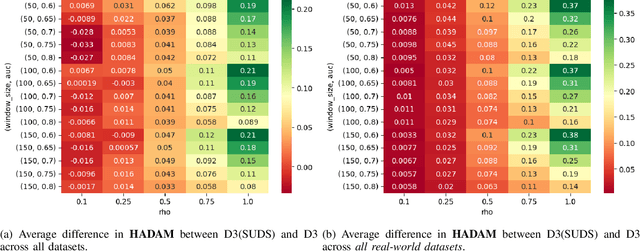
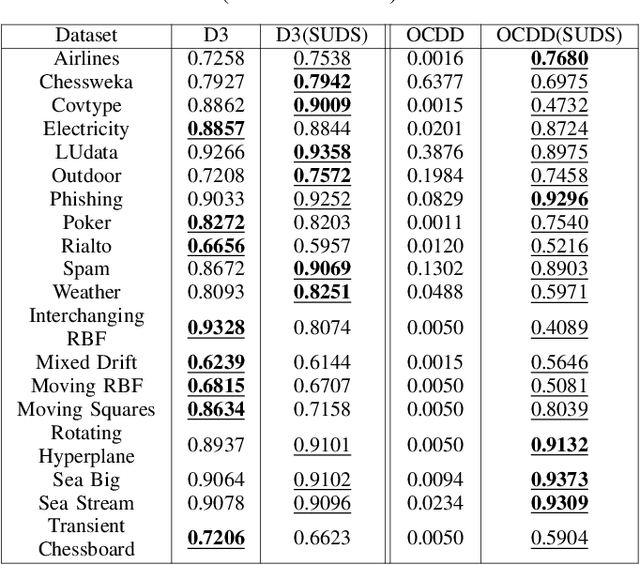
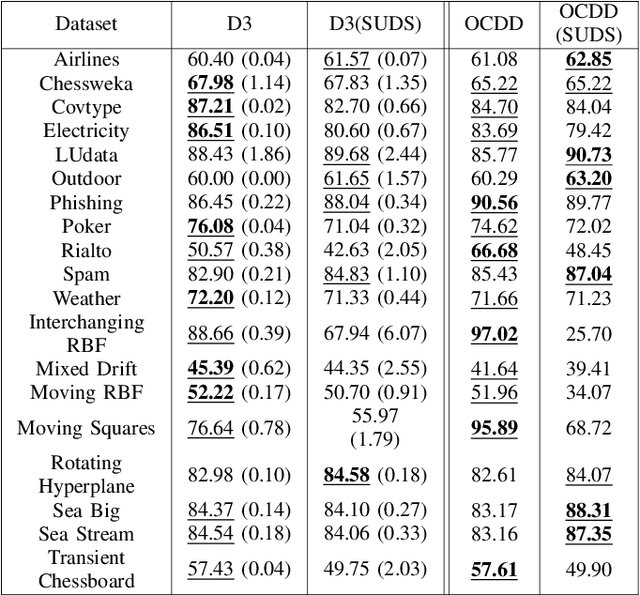
Abstract:Supervised machine learning often encounters concept drift, where the data distribution changes over time, degrading model performance. Existing drift detection methods focus on identifying these shifts but often overlook the challenge of acquiring labeled data for model retraining after a shift occurs. We present the Strategy for Drift Sampling (SUDS), a novel method that selects homogeneous samples for retraining using existing drift detection algorithms, thereby enhancing model adaptability to evolving data. SUDS seamlessly integrates with current drift detection techniques. We also introduce the Harmonized Annotated Data Accuracy Metric (HADAM), a metric that evaluates classifier performance in relation to the quantity of annotated data required to achieve the stated performance, thereby taking into account the difficulty of acquiring labeled data. Our contributions are twofold: SUDS combines drift detection with strategic sampling to improve the retraining process, and HADAM provides a metric that balances classifier performance with the amount of labeled data, ensuring efficient resource utilization. Empirical results demonstrate the efficacy of SUDS in optimizing labeled data use in dynamic environments, significantly improving the performance of machine learning applications in real-world scenarios. Our code is open source and available at https://github.com/cfellicious/SUDS/
DriftGAN: Using historical data for Unsupervised Recurring Drift Detection
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:In real-world applications, input data distributions are rarely static over a period of time, a phenomenon known as concept drift. Such concept drifts degrade the model's prediction performance, and therefore we require methods to overcome these issues. The initial step is to identify concept drifts and have a training method in place to recover the model's performance. Most concept drift detection methods work on detecting concept drifts and signalling the requirement to retrain the model. However, in real-world cases, there could be concept drifts that recur over a period of time. In this paper, we present an unsupervised method based on Generative Adversarial Networks(GAN) to detect concept drifts and identify whether a specific concept drift occurred in the past. Our method reduces the time and data the model requires to get up to speed for recurring drifts. Our key results indicate that our proposed model can outperform the current state-of-the-art models in most datasets. We also test our method on a real-world use case from astrophysics, where we detect the bow shock and magnetopause crossings with better results than the existing methods in the domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge