Linh-Bao Vo
Joint Chinese Word Segmentation and Part-of-speech Tagging via Two-stage Span Labeling
Dec 17, 2021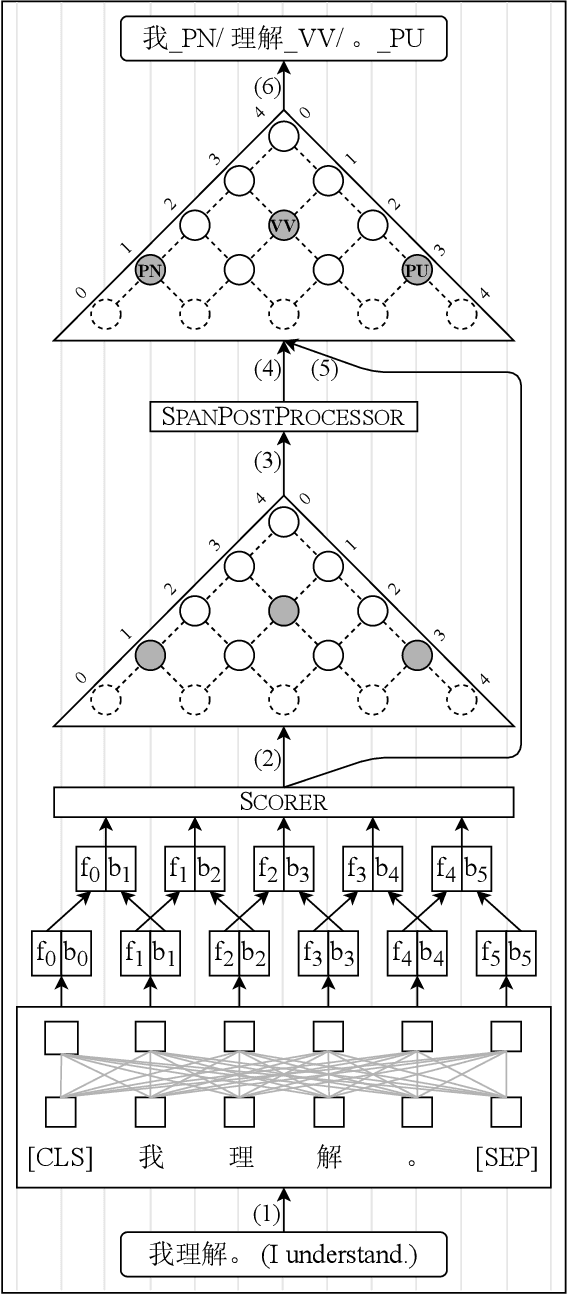
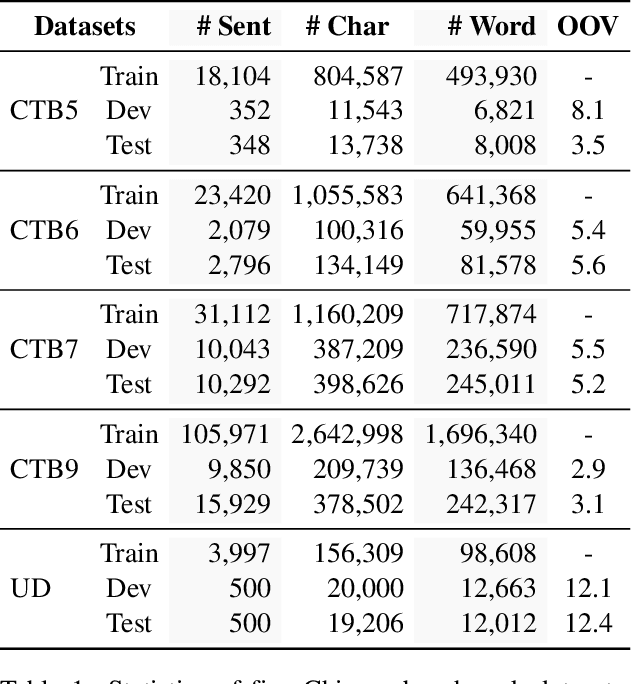
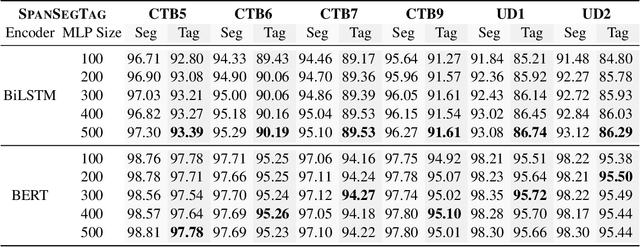
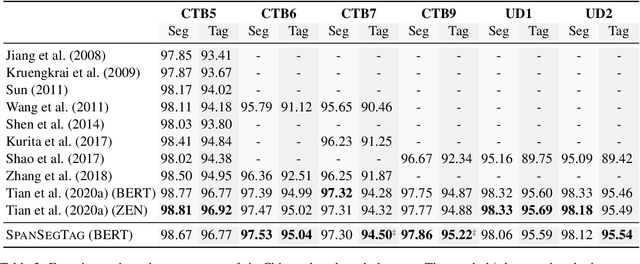
Abstract:Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging are necessary tasks in terms of computational linguistics and application of natural language processing. Many re-searchers still debate the demand for Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging in the deep learning era. Nevertheless, resolving ambiguities and detecting unknown words are challenging problems in this field. Previous studies on joint Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging mainly follow the character-based tagging model focusing on modeling n-gram features. Unlike previous works, we propose a neural model named SpanSegTag for joint Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging following the span labeling in which the probability of each n-gram being the word and the part-of-speech tag is the main problem. We use the biaffine operation over the left and right boundary representations of consecutive characters to model the n-grams. Our experiments show that our BERT-based model SpanSegTag achieved competitive performances on the CTB5, CTB6, and UD, or significant improvements on CTB7 and CTB9 benchmark datasets compared with the current state-of-the-art method using BERT or ZEN encoders.
Span Labeling Approach for Vietnamese and Chinese Word Segmentation
Oct 01, 2021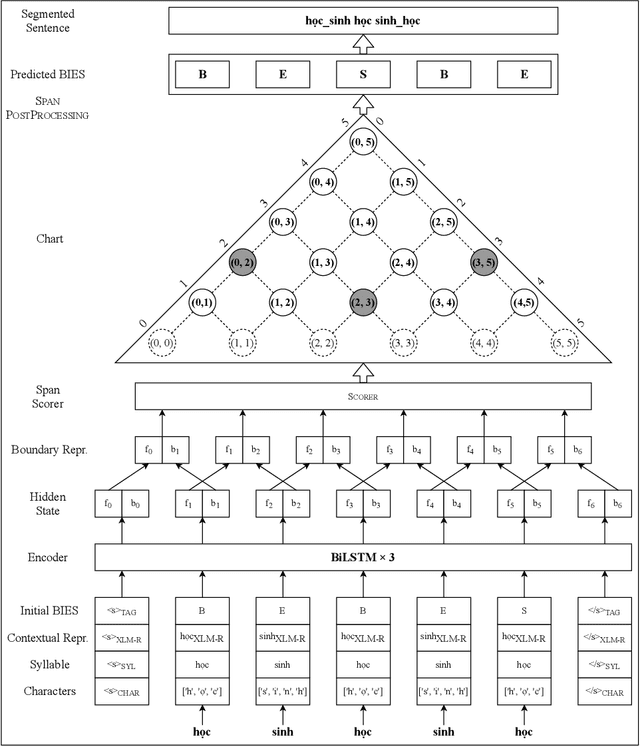
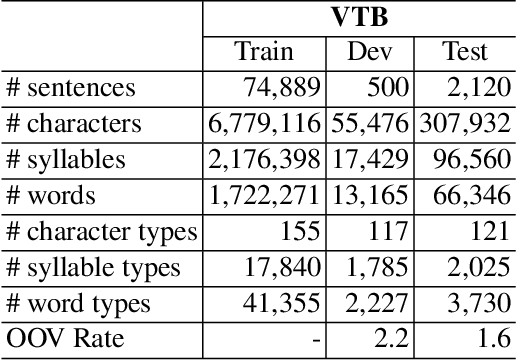
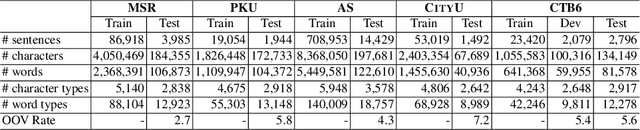
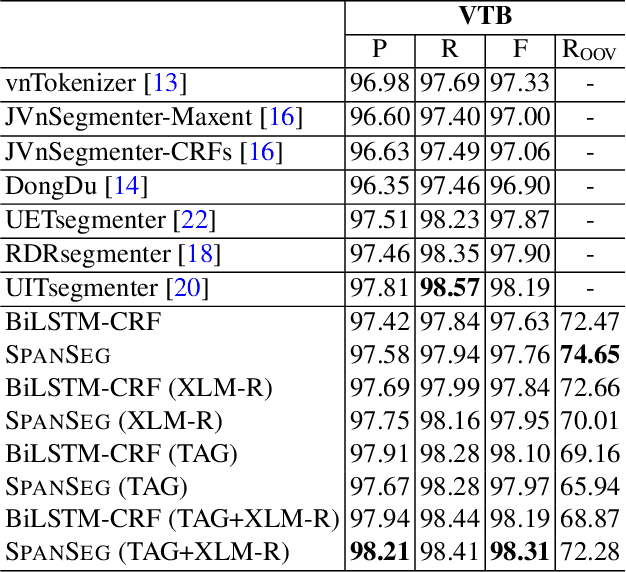
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a span labeling approach to model n-gram information for Vietnamese word segmentation, namely SPAN SEG. We compare the span labeling approach with the conditional random field by using encoders with the same architecture. Since Vietnamese and Chinese have similar linguistic phenomena, we evaluated the proposed method on the Vietnamese treebank benchmark dataset and five Chinese benchmark datasets. Through our experimental results, the proposed approach SpanSeg achieves higher performance than the sequence tagging approach with the state-of-the-art F-score of 98.31% on the Vietnamese treebank benchmark, when they both apply the contextual pre-trained language model XLM-RoBERTa and the predicted word boundary information. Besides, we do fine-tuning experiments for the span labeling approach on BERT and ZEN pre-trained language model for Chinese with fewer parameters, faster inference time, and competitive or higher F-scores than the previous state-of-the-art approach, word segmentation with word-hood memory networks, on five Chinese benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge