Ngoc-Linh Tran
Joint Chinese Word Segmentation and Part-of-speech Tagging via Two-stage Span Labeling
Dec 17, 2021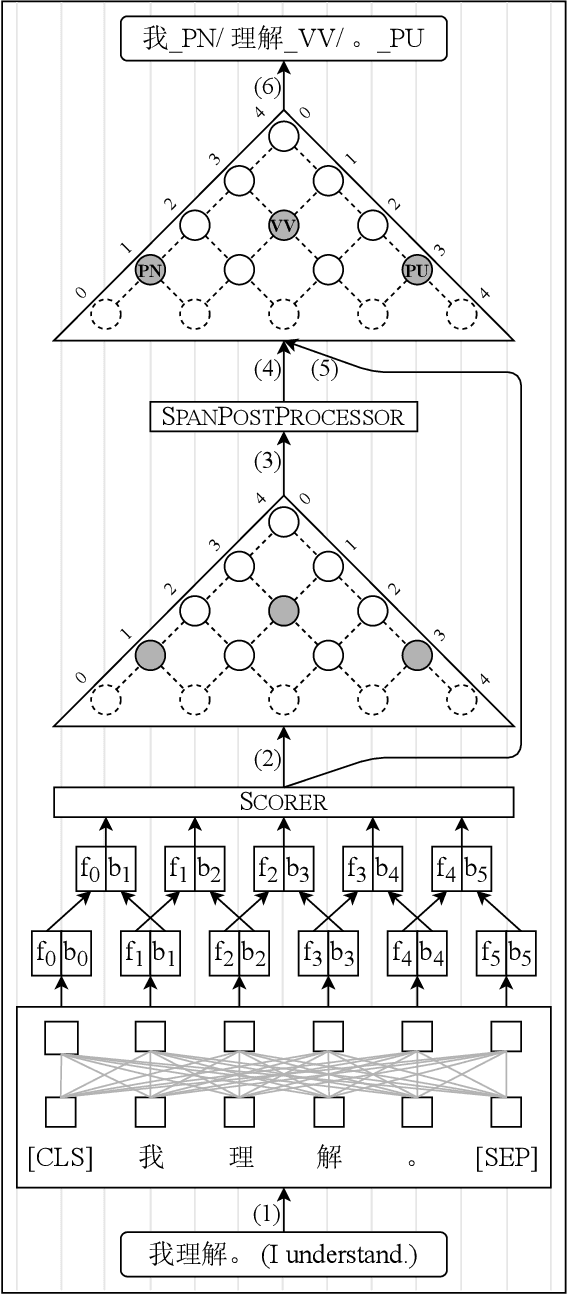
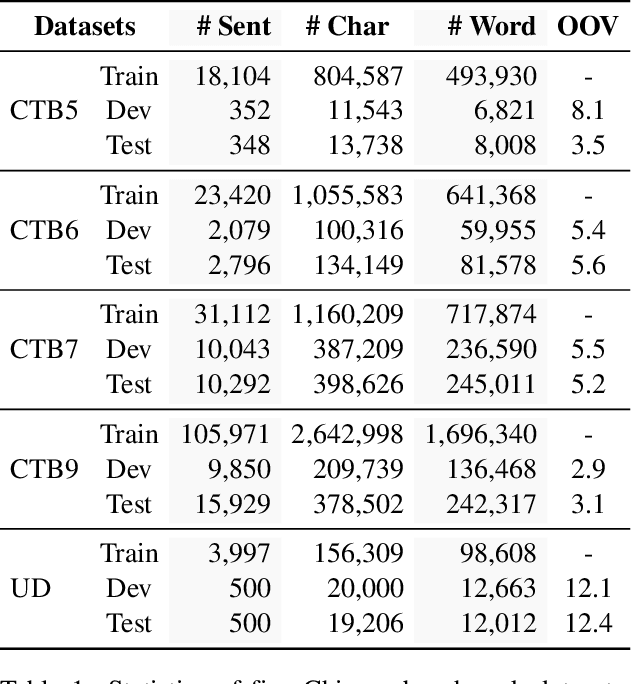
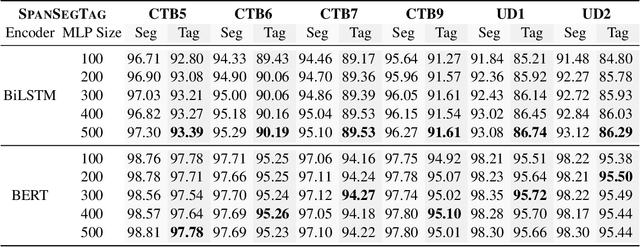
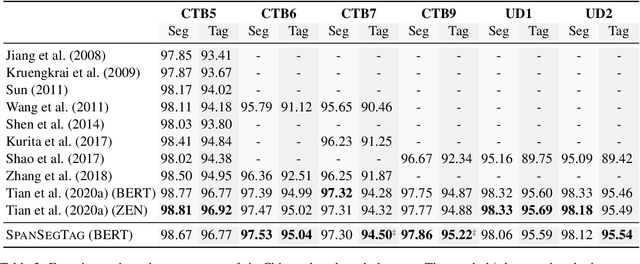
Abstract:Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging are necessary tasks in terms of computational linguistics and application of natural language processing. Many re-searchers still debate the demand for Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging in the deep learning era. Nevertheless, resolving ambiguities and detecting unknown words are challenging problems in this field. Previous studies on joint Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging mainly follow the character-based tagging model focusing on modeling n-gram features. Unlike previous works, we propose a neural model named SpanSegTag for joint Chinese word segmentation and part-of-speech tagging following the span labeling in which the probability of each n-gram being the word and the part-of-speech tag is the main problem. We use the biaffine operation over the left and right boundary representations of consecutive characters to model the n-grams. Our experiments show that our BERT-based model SpanSegTag achieved competitive performances on the CTB5, CTB6, and UD, or significant improvements on CTB7 and CTB9 benchmark datasets compared with the current state-of-the-art method using BERT or ZEN encoders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge