Dang Van Thin
ComOM at VLSP 2023: A Dual-Stage Framework with BERTology and Unified Multi-Task Instruction Tuning Model for Vietnamese Comparative Opinion Mining
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:The ComOM shared task aims to extract comparative opinions from product reviews in Vietnamese language. There are two sub-tasks, including (1) Comparative Sentence Identification (CSI) and (2) Comparative Element Extraction (CEE). The first task is to identify whether the input is a comparative review, and the purpose of the second task is to extract the quintuplets mentioned in the comparative review. To address this task, our team proposes a two-stage system based on fine-tuning a BERTology model for the CSI task and unified multi-task instruction tuning for the CEE task. Besides, we apply the simple data augmentation technique to increase the size of the dataset for training our model in the second stage. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms the other competitors and has achieved the top score on the official private test.
Span Labeling Approach for Vietnamese and Chinese Word Segmentation
Oct 01, 2021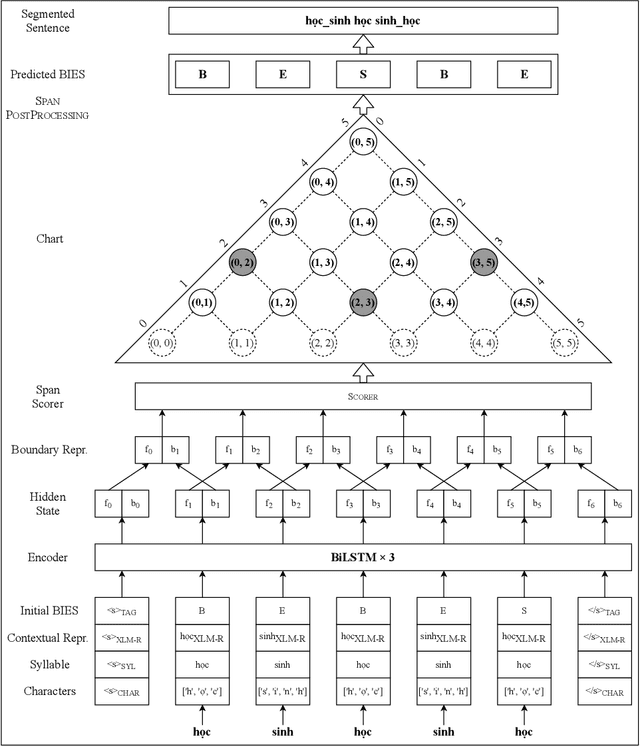
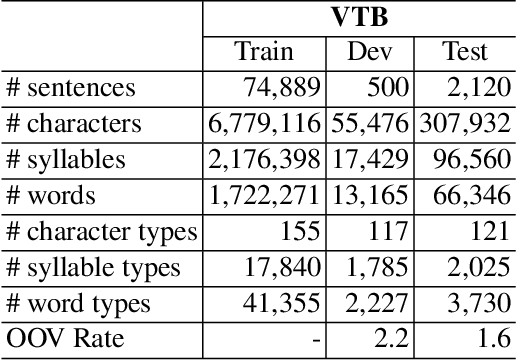
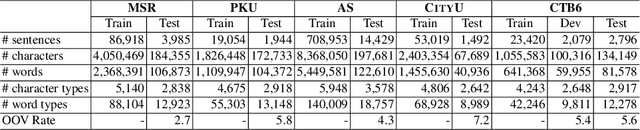
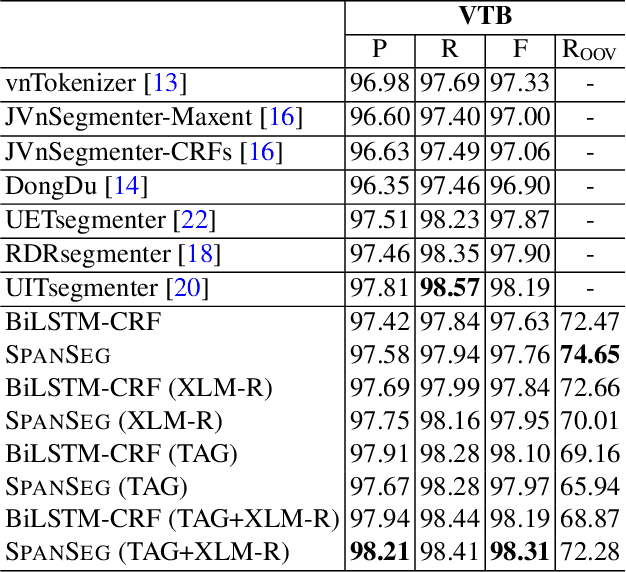
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a span labeling approach to model n-gram information for Vietnamese word segmentation, namely SPAN SEG. We compare the span labeling approach with the conditional random field by using encoders with the same architecture. Since Vietnamese and Chinese have similar linguistic phenomena, we evaluated the proposed method on the Vietnamese treebank benchmark dataset and five Chinese benchmark datasets. Through our experimental results, the proposed approach SpanSeg achieves higher performance than the sequence tagging approach with the state-of-the-art F-score of 98.31% on the Vietnamese treebank benchmark, when they both apply the contextual pre-trained language model XLM-RoBERTa and the predicted word boundary information. Besides, we do fine-tuning experiments for the span labeling approach on BERT and ZEN pre-trained language model for Chinese with fewer parameters, faster inference time, and competitive or higher F-scores than the previous state-of-the-art approach, word segmentation with word-hood memory networks, on five Chinese benchmarks.
Investigating Monolingual and Multilingual BERTModels for Vietnamese Aspect Category Detection
Mar 17, 2021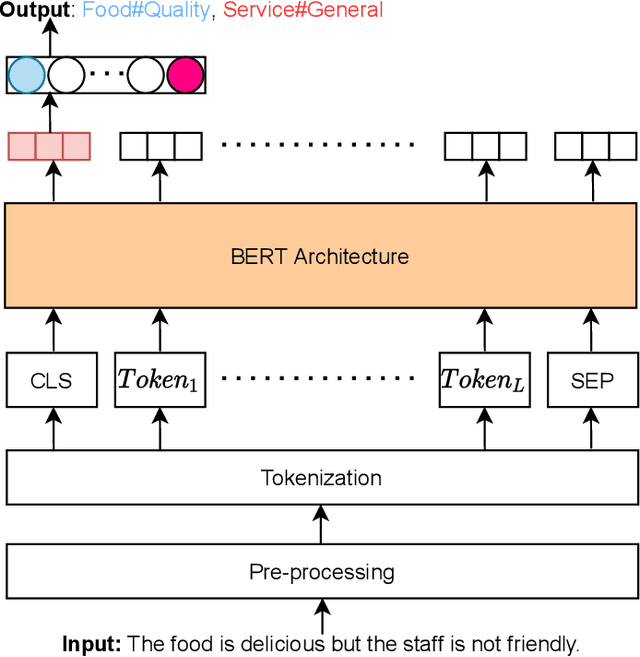

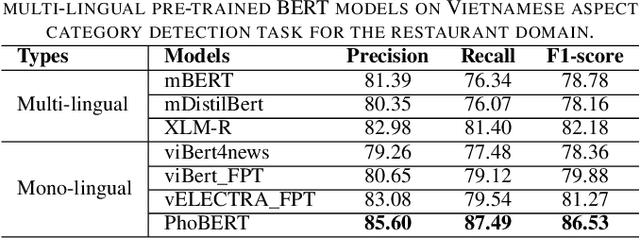
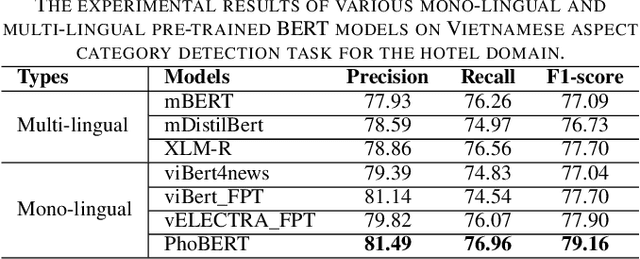
Abstract:Aspect category detection (ACD) is one of the challenging tasks in the Aspect-based sentiment Analysis problem. The purpose of this task is to identify the aspect categories mentioned in user-generated reviews from a set of pre-defined categories. In this paper, we investigate the performance of various monolingual pre-trained language models compared with multilingual models on the Vietnamese aspect category detection problem. We conduct the experiments on two benchmark datasets for the restaurant and hotel domain. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness of the monolingual PhoBERT model than others on two datasets. We also evaluate the performance of the multilingual model based on the combination of whole SemEval-2016 datasets in other languages with the Vietnamese dataset. To the best of our knowledge, our research study is the first attempt at performing various available pre-trained language models on aspect category detection task and utilize the datasets from other languages based on multilingual models.
Vietnamese Word Segmentation with SVM: Ambiguity Reduction and Suffix Capture
Jun 14, 2020

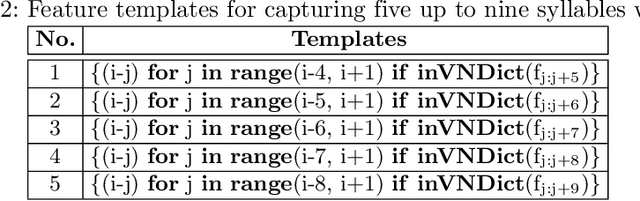

Abstract:In this paper, we approach Vietnamese word segmentation as a binary classification by using the Support Vector Machine classifier. We inherit features from prior works such as n-gram of syllables, n-gram of syllable types, and checking conjunction of adjacent syllables in the dictionary. We propose two novel ways to feature extraction, one to reduce the overlap ambiguity and the other to increase the ability to predict unknown words containing suffixes. Different from UETsegmenter and RDRsegmenter, two state-of-the-art Vietnamese word segmentation methods, we do not employ the longest matching algorithm as an initial processing step or any post-processing technique. According to experimental results on benchmark Vietnamese datasets, our proposed method obtained a better F1-score than the prior state-of-the-art methods UETsegmenter, and RDRsegmenter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge