Lingrui Li
Multi-Scale Global-Instance Prompt Tuning for Continual Test-time Adaptation in Medical Image Segmentation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Distribution shift is a common challenge in medical images obtained from different clinical centers, significantly hindering the deployment of pre-trained semantic segmentation models in real-world applications across multiple domains. Continual Test-Time Adaptation(CTTA) has emerged as a promising approach to address cross-domain shifts during continually evolving target domains. Most existing CTTA methods rely on incrementally updating model parameters, which inevitably suffer from error accumulation and catastrophic forgetting, especially in long-term adaptation. Recent prompt-tuning-based works have shown potential to mitigate the two issues above by updating only visual prompts. While these approaches have demonstrated promising performance, several limitations remain:1)lacking multi-scale prompt diversity, 2)inadequate incorporation of instance-specific knowledge, and 3)risk of privacy leakage. To overcome these limitations, we propose Multi-scale Global-Instance Prompt Tuning(MGIPT), to enhance scale diversity of prompts and capture both global- and instance-level knowledge for robust CTTA. Specifically, MGIPT consists of an Adaptive-scale Instance Prompt(AIP) and a Multi-scale Global-level Prompt(MGP). AIP dynamically learns lightweight and instance-specific prompts to mitigate error accumulation with adaptive optimal-scale selection mechanism. MGP captures domain-level knowledge across different scales to ensure robust adaptation with anti-forgetting capabilities. These complementary components are combined through a weighted ensemble approach, enabling effective dual-level adaptation that integrates both global and local information. Extensive experiments on medical image segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that our MGIPT outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving robust adaptation across continually changing target domains.
XNet v2: Fewer Limitations, Better Results and Greater Universality
Sep 02, 2024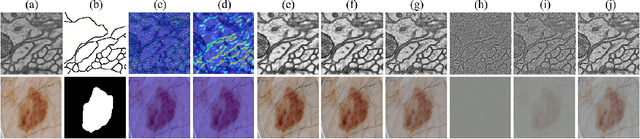
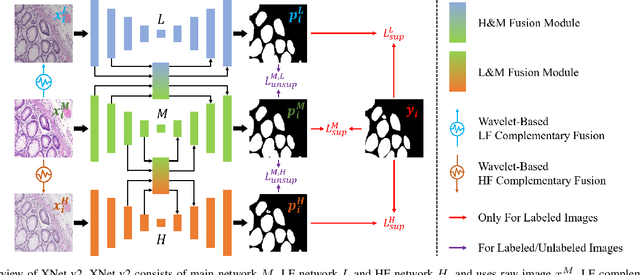
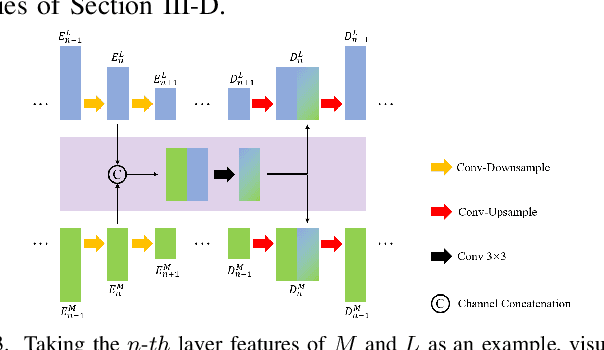
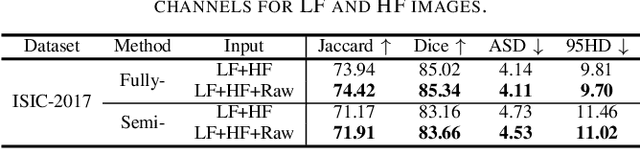
Abstract:XNet introduces a wavelet-based X-shaped unified architecture for fully- and semi-supervised biomedical segmentation. So far, however, XNet still faces the limitations, including performance degradation when images lack high-frequency (HF) information, underutilization of raw images and insufficient fusion. To address these issues, we propose XNet v2, a low- and high-frequency complementary model. XNet v2 performs wavelet-based image-level complementary fusion, using fusion results along with raw images inputs three different sub-networks to construct consistency loss. Furthermore, we introduce a feature-level fusion module to enhance the transfer of low-frequency (LF) information and HF information. XNet v2 achieves state-of-the-art in semi-supervised segmentation while maintaining competitve results in fully-supervised learning. More importantly, XNet v2 excels in scenarios where XNet fails. Compared to XNet, XNet v2 exhibits fewer limitations, better results and greater universality. Extensive experiments on three 2D and two 3D datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of XNet v2. Code is available at https://github.com/Yanfeng-Zhou/XNetv2 .
Robust Source-Free Domain Adaptation for Fundus Image Segmentation
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is a learning technique that transfers knowledge learned in the source domain from labelled training data to the target domain with only unlabelled data. It is of significant importance to medical image segmentation because of the usual lack of labelled training data. Although extensive efforts have been made to optimize UDA techniques to improve the accuracy of segmentation models in the target domain, few studies have addressed the robustness of these models under UDA. In this study, we propose a two-stage training strategy for robust domain adaptation. In the source training stage, we utilize adversarial sample augmentation to enhance the robustness and generalization capability of the source model. And in the target training stage, we propose a novel robust pseudo-label and pseudo-boundary (PLPB) method, which effectively utilizes unlabeled target data to generate pseudo labels and pseudo boundaries that enable model self-adaptation without requiring source data. Extensive experimental results on cross-domain fundus image segmentation confirm the effectiveness and versatility of our method. Source code of this study is openly accessible at https://github.com/LinGrayy/PLPB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge