Lianqiang Zhou
Hallucinating Optical Flow Features for Video Classification
May 28, 2019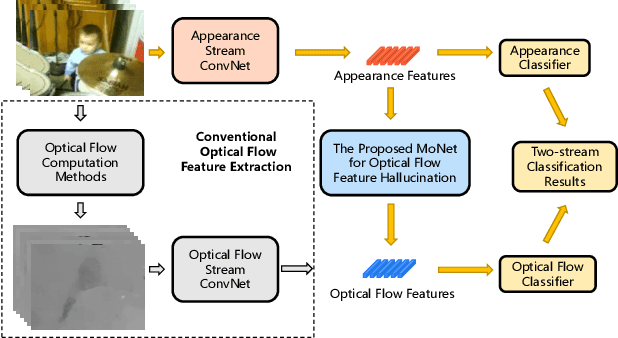
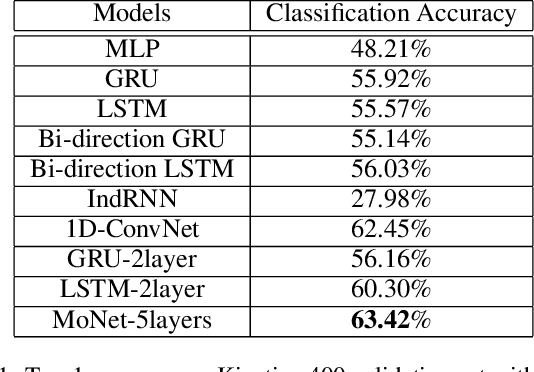
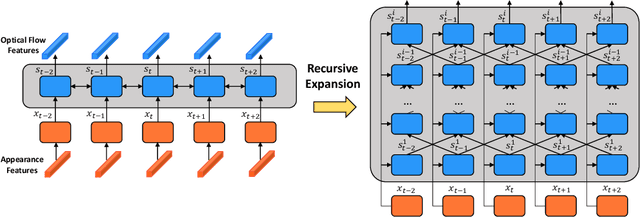
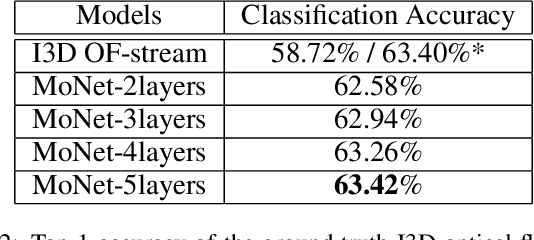
Abstract:Appearance and motion are two key components to depict and characterize the video content. Currently, the two-stream models have achieved state-of-the-art performances on video classification. However, extracting motion information, specifically in the form of optical flow features, is extremely computationally expensive, especially for large-scale video classification. In this paper, we propose a motion hallucination network, namely MoNet, to imagine the optical flow features from the appearance features, with no reliance on the optical flow computation. Specifically, MoNet models the temporal relationships of the appearance features and exploits the contextual relationships of the optical flow features with concurrent connections. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MoNet can effectively and efficiently hallucinate the optical flow features, which together with the appearance features consistently improve the video classification performances. Moreover, MoNet can help cutting down almost a half of computational and data-storage burdens for the two-stream video classification. Our code is available at: https://github.com/YongyiTang92/MoNet-Features.
Learning to Start for Sequence to Sequence Architecture
Aug 19, 2016



Abstract:The sequence to sequence architecture is widely used in the response generation and neural machine translation to model the potential relationship between two sentences. It typically consists of two parts: an encoder that reads from the source sentence and a decoder that generates the target sentence word by word according to the encoder's output and the last generated word. However, it faces to the cold start problem when generating the first word as there is no previous word to refer. Existing work mainly use a special start symbol </s>to generate the first word. An obvious drawback of these work is that there is not a learnable relationship between words and the start symbol. Furthermore, it may lead to the error accumulation for decoding when the first word is incorrectly generated. In this paper, we proposed a novel approach to learning to generate the first word in the sequence to sequence architecture rather than using the start symbol. Experimental results on the task of response generation of short text conversation show that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art approach in both of the automatic and manual evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge