Li Miao
RAFIC: Retrieval-Augmented Few-shot Image Classification
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:Few-shot image classification is the task of classifying unseen images to one of N mutually exclusive classes, using only a small number of training examples for each class. The limited availability of these examples (denoted as K) presents a significant challenge to classification accuracy in some cases. To address this, we have developed a method for augmenting the set of K with an addition set of A retrieved images. We call this system Retrieval-Augmented Few-shot Image Classification (RAFIC). Through a series of experiments, we demonstrate that RAFIC markedly improves performance of few-shot image classification across two challenging datasets. RAFIC consists of two main components: (a) a retrieval component which uses CLIP, LAION-5B, and faiss, in order to efficiently retrieve images similar to the supplied images, and (b) retrieval meta-learning, which learns to judiciously utilize the retrieved images. Code and data is available at github.com/amirziai/rafic.
Quantum Generative Modeling of Sequential Data with Trainable Token Embedding
Nov 08, 2023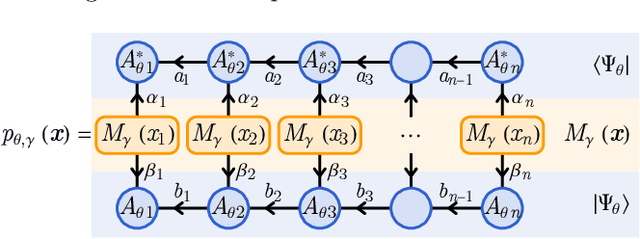
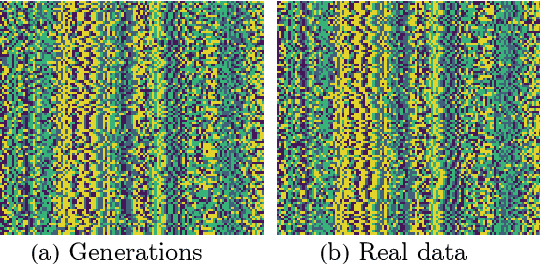
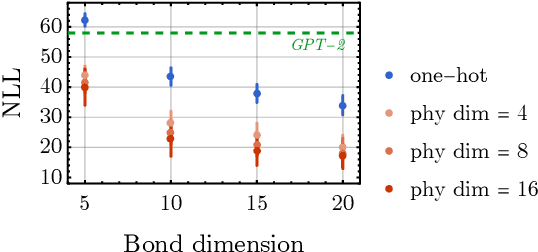
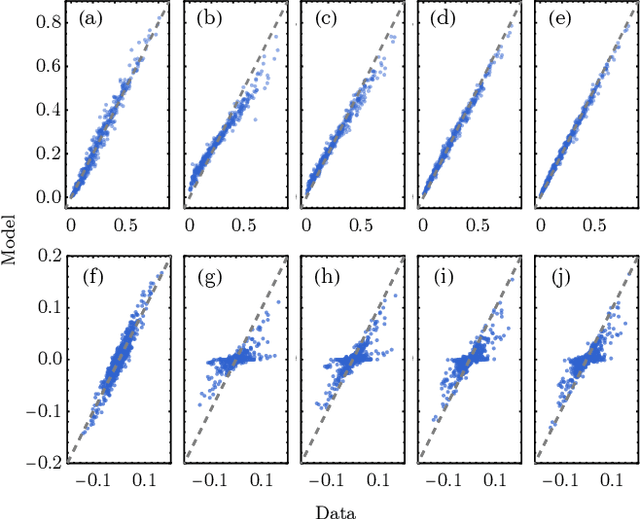
Abstract:Generative models are a class of machine learning models that aim to learn the underlying probability distribution of data. Unlike discriminative models, generative models focus on capturing the data's inherent structure, allowing them to generate new samples that resemble the original data. To fully exploit the potential of modeling probability distributions using quantum physics, a quantum-inspired generative model known as the Born machines have shown great advancements in learning classical and quantum data over matrix product state(MPS) framework. The Born machines support tractable log-likelihood, autoregressive and mask sampling, and have shown outstanding performance in various unsupervised learning tasks. However, much of the current research has been centered on improving the expressive power of MPS, predominantly embedding each token directly by a corresponding tensor index. In this study, we generalize the embedding method into trainable quantum measurement operators that can be simultaneously honed with MPS. Our study indicated that combined with trainable embedding, Born machines can exhibit better performance and learn deeper correlations from the dataset.
Multilingual Transformer Language Model for Speech Recognition in Low-resource Languages
Sep 08, 2022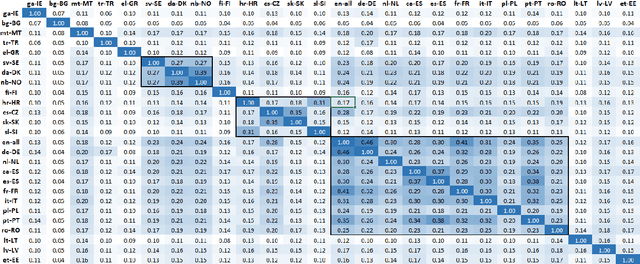
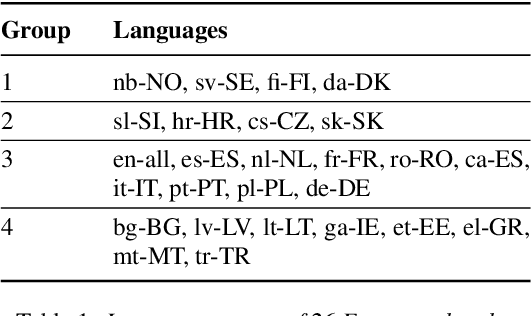
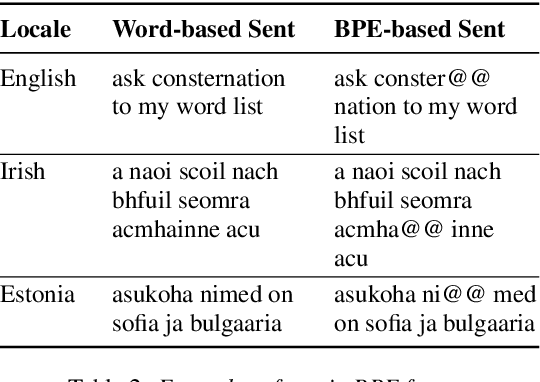
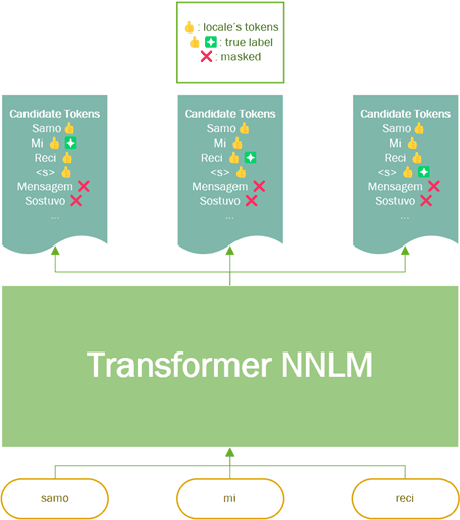
Abstract:It is challenging to train and deploy Transformer LMs for hybrid speech recognition 2nd pass re-ranking in low-resource languages due to (1) data scarcity in low-resource languages, (2) expensive computing costs for training and refreshing 100+ monolingual models, and (3) hosting inefficiency considering sparse traffic. In this study, we present a new way to group multiple low-resource locales together and optimize the performance of Multilingual Transformer LMs in ASR. Our Locale-group Multilingual Transformer LMs outperform traditional multilingual LMs along with reducing maintenance costs and operating expenses. Further, for low-resource but high-traffic locales where deploying monolingual models is feasible, we show that fine-tuning our locale-group multilingual LMs produces better monolingual LM candidates than baseline monolingual LMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge