Levi Corallo
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Optical Character Recognition and Transcription of Berber Signs from Images in a Low-Resource Language Amazigh
Mar 21, 2023
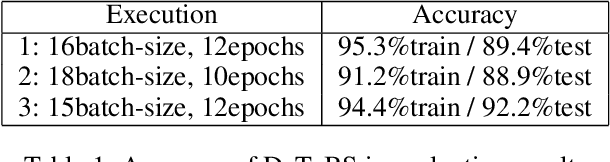


Abstract:The Berber, or Amazigh language family is a low-resource North African vernacular language spoken by the indigenous Berber ethnic group. It has its own unique alphabet called Tifinagh used across Berber communities in Morocco, Algeria, and others. The Afroasiatic language Berber is spoken by 14 million people, yet lacks adequate representation in education, research, web applications etc. For instance, there is no option of translation to or from Amazigh / Berber on Google Translate, which hosts over 100 languages today. Consequently, we do not find specialized educational apps, L2 (2nd language learner) acquisition, automated language translation, and remote-access facilities enabled in Berber. Motivated by this background, we propose a supervised approach called DaToBS for Detection and Transcription of Berber Signs. The DaToBS approach entails the automatic recognition and transcription of Tifinagh characters from signs in photographs of natural environments. This is achieved by self-creating a corpus of 1862 pre-processed character images; curating the corpus with human-guided annotation; and feeding it into an OCR model via the deployment of CNN for deep learning based on computer vision models. We deploy computer vision modeling (rather than language models) because there are pictorial symbols in this alphabet, this deployment being a novel aspect of our work. The DaToBS experimentation and analyses yield over 92 percent accuracy in our research. To the best of our knowledge, ours is among the first few works in the automated transcription of Berber signs from roadside images with deep learning, yielding high accuracy. This can pave the way for developing pedagogical applications in the Berber language, thereby addressing an important goal of outreach to underrepresented communities via AI in education.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge