Leonid Mokrushin
A Survey on the Integration of Generative AI for Critical Thinking in Mobile Networks
Apr 10, 2024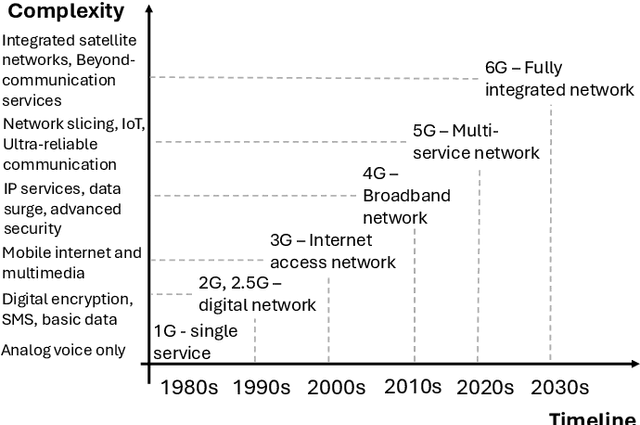
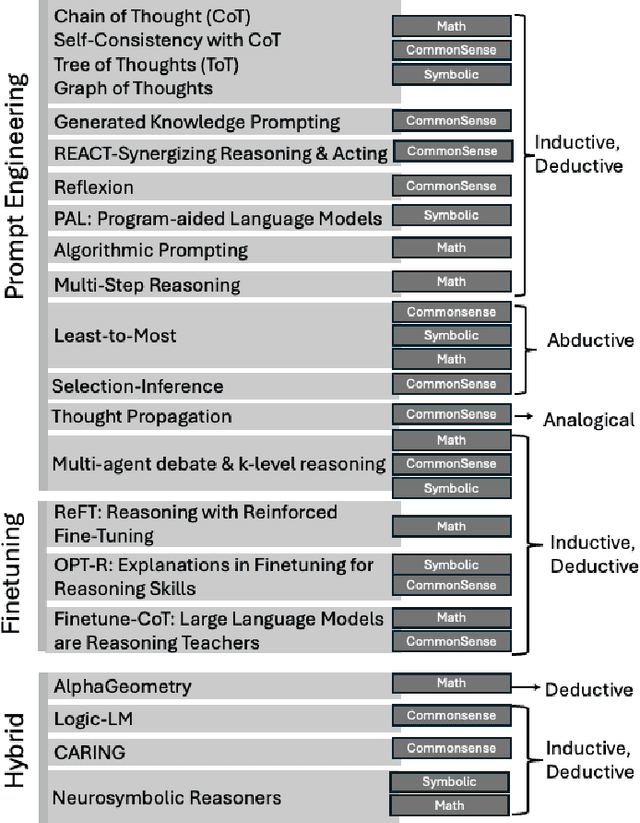
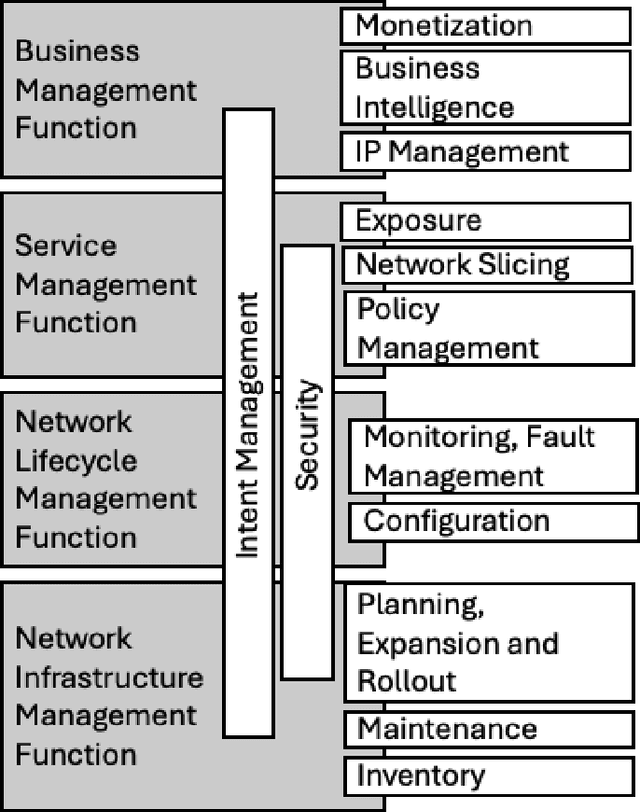
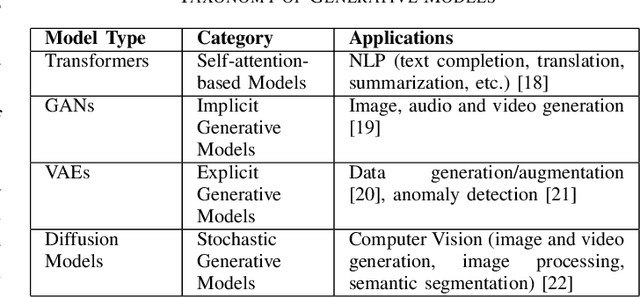
Abstract:In the near future, mobile networks are expected to broaden their services and coverage to accommodate a larger user base and diverse user needs. Thus, they will increasingly rely on artificial intelligence (AI) to manage network operation and control costs, undertaking complex decision-making roles. This shift will necessitate the application of techniques that incorporate critical thinking abilities, including reasoning and planning. Symbolic AI techniques already facilitate critical thinking based on existing knowledge. Yet, their use in telecommunications is hindered by the high cost of mostly manual curation of this knowledge and high computational complexity of reasoning tasks. At the same time, there is a spurt of innovations in industries such as telecommunications due to Generative AI (GenAI) technologies, operating independently of human-curated knowledge. However, their capacity for critical thinking remains uncertain. This paper aims to address this gap by examining the current status of GenAI algorithms with critical thinking capabilities and investigating their potential applications in telecom networks. Specifically, the aim of this study is to offer an introduction to the potential utilization of GenAI for critical thinking techniques in mobile networks, while also establishing a foundation for future research.
A Framework for Knowledge Management and Automated Reasoning Applied on Intelligent Transport Systems
Jan 11, 2017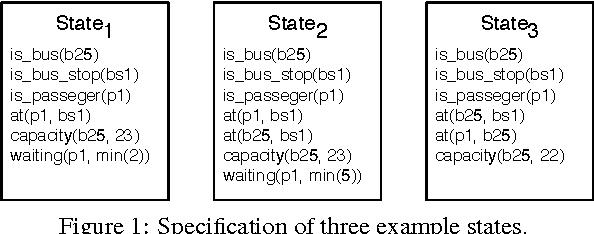
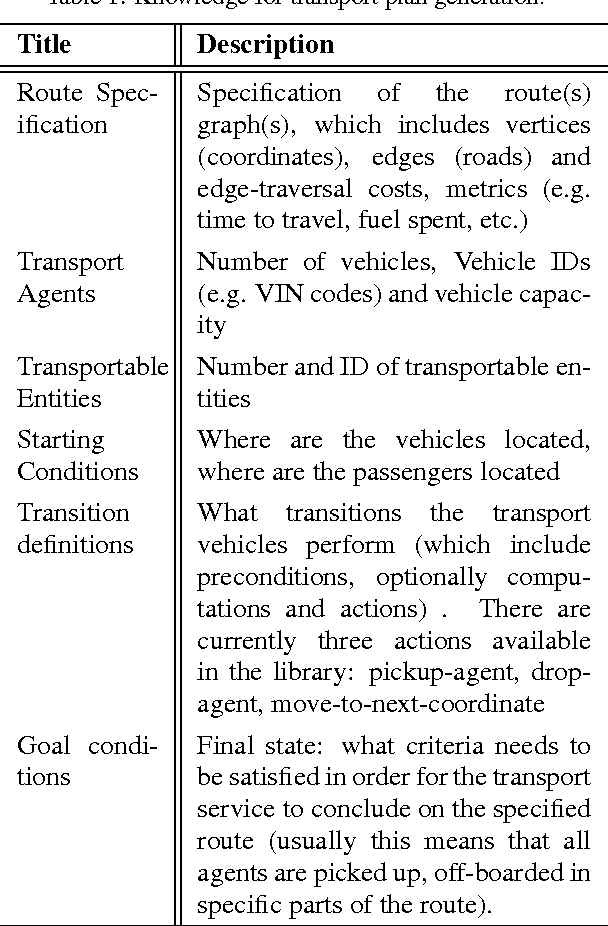
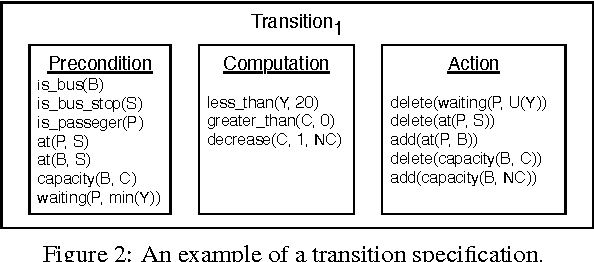
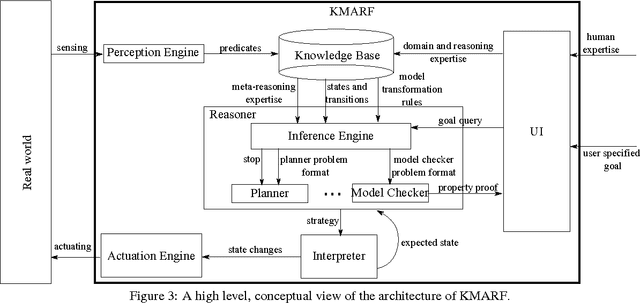
Abstract:Cyber-Physical Systems in general, and Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) in particular use heterogeneous data sources combined with problem solving expertise in order to make critical decisions that may lead to some form of actions e.g., driver notifications, change of traffic light signals and braking to prevent an accident. Currently, a major part of the decision process is done by human domain experts, which is time-consuming, tedious and error-prone. Additionally, due to the intrinsic nature of knowledge possession this decision process cannot be easily replicated or reused. Therefore, there is a need for automating the reasoning processes by providing computational systems a formal representation of the domain knowledge and a set of methods to process that knowledge. In this paper, we propose a knowledge model that can be used to express both declarative knowledge about the systems' components, their relations and their current state, as well as procedural knowledge representing possible system behavior. In addition, we introduce a framework for knowledge management and automated reasoning (KMARF). The idea behind KMARF is to automatically select an appropriate problem solver based on formalized reasoning expertise in the knowledge base, and convert a problem definition to the corresponding format. This approach automates reasoning, thus reducing operational costs, and enables reusability of knowledge and methods across different domains. We illustrate the approach on a transportation planning use case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge