Leon Guertler
TextArena
Apr 15, 2025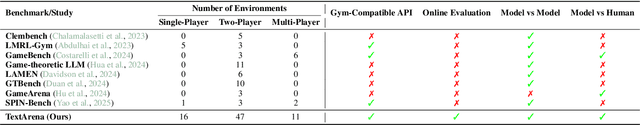
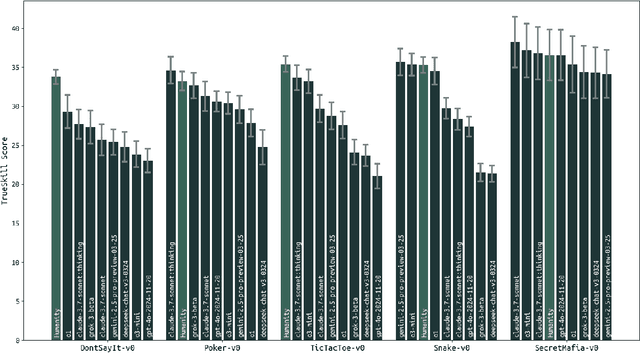
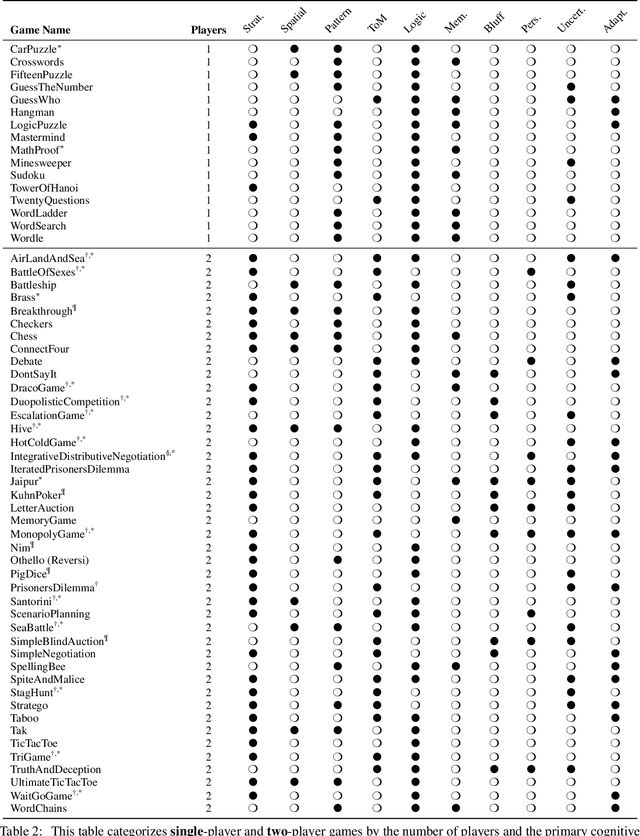

Abstract:TextArena is an open-source collection of competitive text-based games for training and evaluation of agentic behavior in Large Language Models (LLMs). It spans 57+ unique environments (including single-player, two-player, and multi-player setups) and allows for easy evaluation of model capabilities via an online-play system (against humans and other submitted models) with real-time TrueSkill scores. Traditional benchmarks rarely assess dynamic social skills such as negotiation, theory of mind, and deception, creating a gap that TextArena addresses. Designed with research, community and extensibility in mind, TextArena emphasizes ease of adding new games, adapting the framework, testing models, playing against the models, and training models. Detailed documentation of environments, games, leaderboard, and examples are available on https://github.com/LeonGuertler/TextArena and https://www.textarena.ai/.
STLM Engineering Report: Dropout
Sep 09, 2024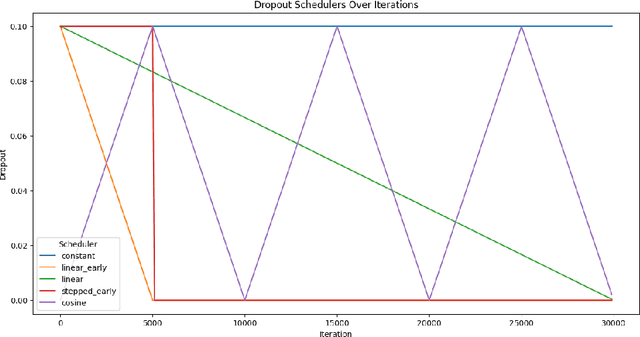
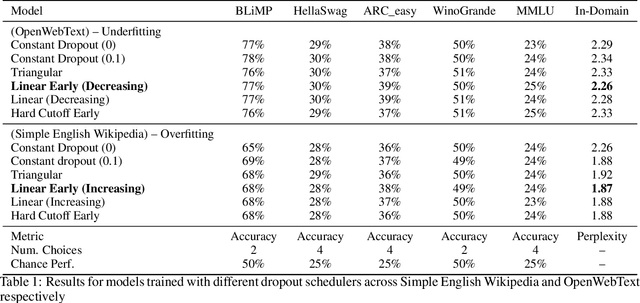
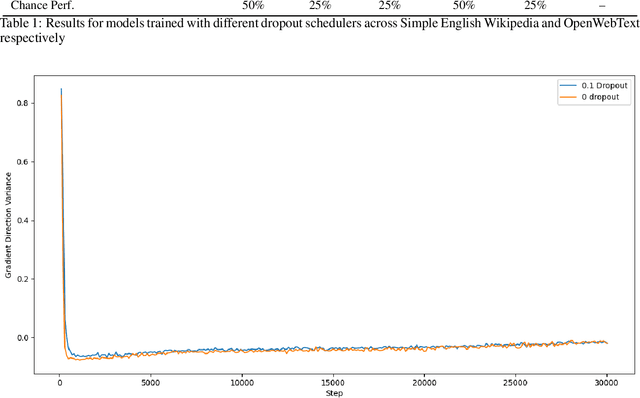
Abstract:In this work we explore the relevance of dropout for modern language models, particularly in the context of models on the scale of <100M parameters. We explore it's relevance firstly in the regime of improving the sample efficiency of models given small, high quality datasets, and secondly in the regime of improving the quality of its fit on larger datasets where models may underfit. We find that concordant with conventional wisdom, dropout remains effective in the overfitting scenario, and that furthermore it may have some relevance for improving the fit of models even in the case of excess data, as suggested by previous research. In the process we find that the existing explanation for the mechanism behind this performance gain is not applicable in the case of language modelling.
Super Tiny Language Models
May 23, 2024Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has led to significant improvements in natural language processing but also poses challenges due to their high computational and energy demands. This paper introduces a series of research efforts focused on Super Tiny Language Models (STLMs), which aim to deliver high performance with significantly reduced parameter counts. We explore innovative techniques such as byte-level tokenization with a pooling mechanism, weight tying, and efficient training strategies. These methods collectively reduce the parameter count by $90\%$ to $95\%$ compared to traditional models while maintaining competitive performance. This series of papers will explore into various subproblems, including tokenizer-free models, self-play based training, and alternative training objectives, targeting models with 10M, 50M, and 100M parameters. Our ultimate goal is to make high-performance language models more accessible and practical for a wide range of applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge