Leah Chrestien
Optimize Planning Heuristics to Rank, not to Estimate Cost-to-Goal
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:In imitation learning for planning, parameters of heuristic functions are optimized against a set of solved problem instances. This work revisits the necessary and sufficient conditions of strictly optimally efficient heuristics for forward search algorithms, mainly A* and greedy best-first search, which expand only states on the returned optimal path. It then proposes a family of loss functions based on ranking tailored for a given variant of the forward search algorithm. Furthermore, from a learning theory point of view, it discusses why optimizing cost-to-goal \hstar\ is unnecessarily difficult. The experimental comparison on a diverse set of problems unequivocally supports the derived theory.
A Differentiable Loss Function for Learning Heuristics in A*
Sep 12, 2022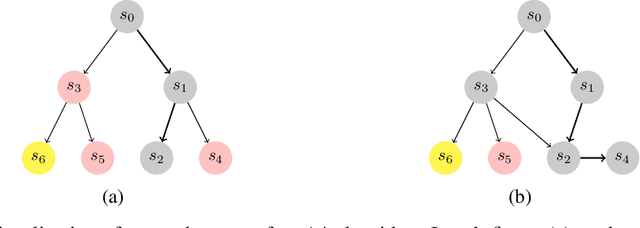
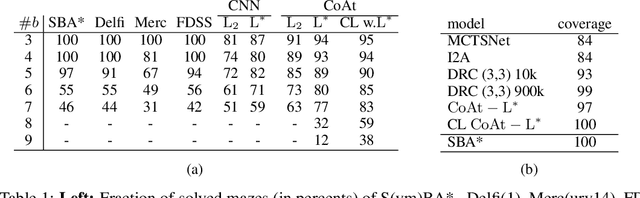
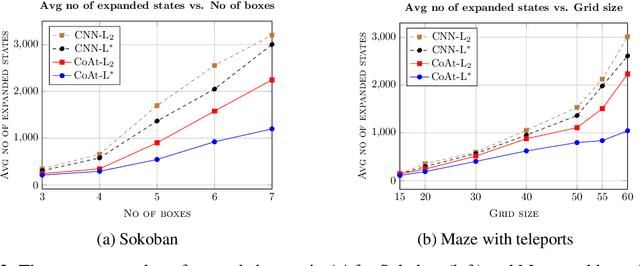
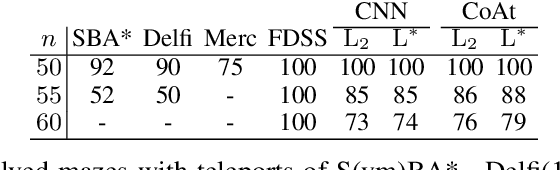
Abstract:Optimization of heuristic functions for the A* algorithm, realized by deep neural networks, is usually done by minimizing square root loss of estimate of the cost to goal values. This paper argues that this does not necessarily lead to a faster search of A* algorithm since its execution relies on relative values instead of absolute ones. As a mitigation, we propose a L* loss, which upper-bounds the number of excessively expanded states inside the A* search. The L* loss, when used in the optimization of state-of-the-art deep neural networks for automated planning in maze domains like Sokoban and maze with teleports, significantly improves the fraction of solved problems, the quality of founded plans, and reduces the number of expanded states to approximately 50%
Heuristic Search Planning with Deep Neural Networks using Imitation, Attention and Curriculum Learning
Dec 03, 2021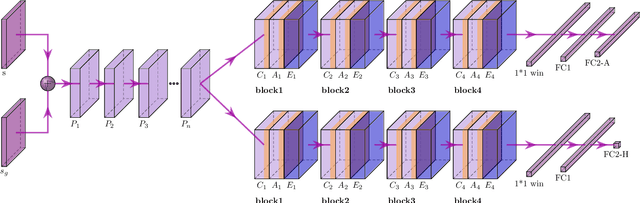
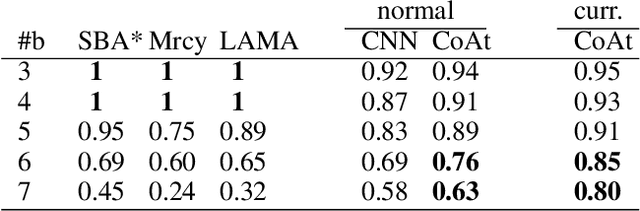
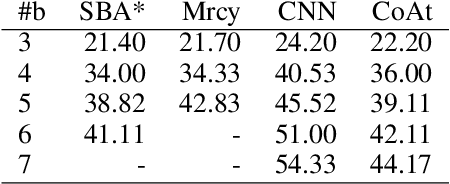
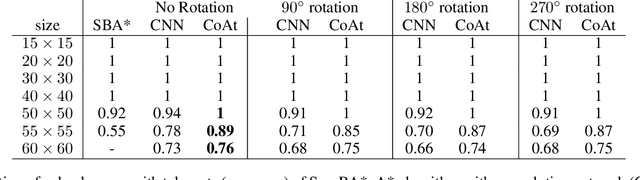
Abstract:Learning a well-informed heuristic function for hard task planning domains is an elusive problem. Although there are known neural network architectures to represent such heuristic knowledge, it is not obvious what concrete information is learned and whether techniques aimed at understanding the structure help in improving the quality of the heuristics. This paper presents a network model to learn a heuristic capable of relating distant parts of the state space via optimal plan imitation using the attention mechanism, which drastically improves the learning of a good heuristic function. To counter the limitation of the method in the creation of problems of increasing difficulty, we demonstrate the use of curriculum learning, where newly solved problem instances are added to the training set, which, in turn, helps to solve problems of higher complexities and far exceeds the performances of all existing baselines including classical planning heuristics. We demonstrate its effectiveness for grid-type PDDL domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge