Lauri Goldkind
Human services organizations and the responsible integration of AI: Considering ethics and contextualizing risk(s)
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:This paper examines the responsible integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in human services organizations (HSOs), proposing a nuanced framework for evaluating AI applications across multiple dimensions of risk. The authors argue that ethical concerns about AI deployment -- including professional judgment displacement, environmental impact, model bias, and data laborer exploitation -- vary significantly based on implementation context and specific use cases. They challenge the binary view of AI adoption, demonstrating how different applications present varying levels of risk that can often be effectively managed through careful implementation strategies. The paper highlights promising solutions, such as local large language models, that can facilitate responsible AI integration while addressing common ethical concerns. The authors propose a dimensional risk assessment approach that considers factors like data sensitivity, professional oversight requirements, and potential impact on client wellbeing. They conclude by outlining a path forward that emphasizes empirical evaluation, starting with lower-risk applications and building evidence-based understanding through careful experimentation. This approach enables organizations to maintain high ethical standards while thoughtfully exploring how AI might enhance their capacity to serve clients and communities effectively.
A resource-constrained stochastic scheduling algorithm for homeless street outreach and gleaning edible food
Mar 15, 2024

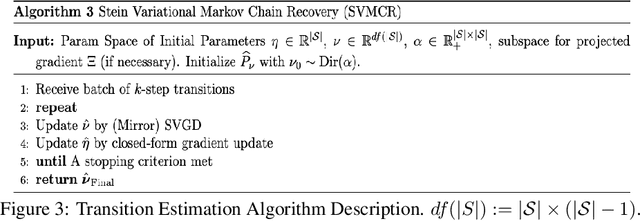
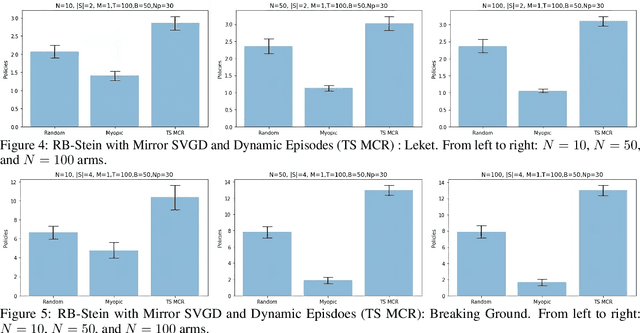
Abstract:We developed a common algorithmic solution addressing the problem of resource-constrained outreach encountered by social change organizations with different missions and operations: Breaking Ground -- an organization that helps individuals experiencing homelessness in New York transition to permanent housing and Leket -- the national food bank of Israel that rescues food from farms and elsewhere to feed the hungry. Specifically, we developed an estimation and optimization approach for partially-observed episodic restless bandits under $k$-step transitions. The results show that our Thompson sampling with Markov chain recovery (via Stein variational gradient descent) algorithm significantly outperforms baselines for the problems of both organizations. We carried out this work in a prospective manner with the express goal of devising a flexible-enough but also useful-enough solution that can help overcome a lack of sustainable impact in data science for social good.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge