Kustaa Hietala
Uncertainty-aware deep learning methods for robust diabetic retinopathy classification
Feb 02, 2022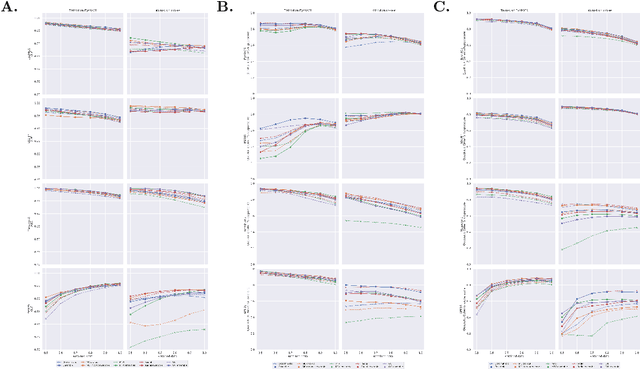
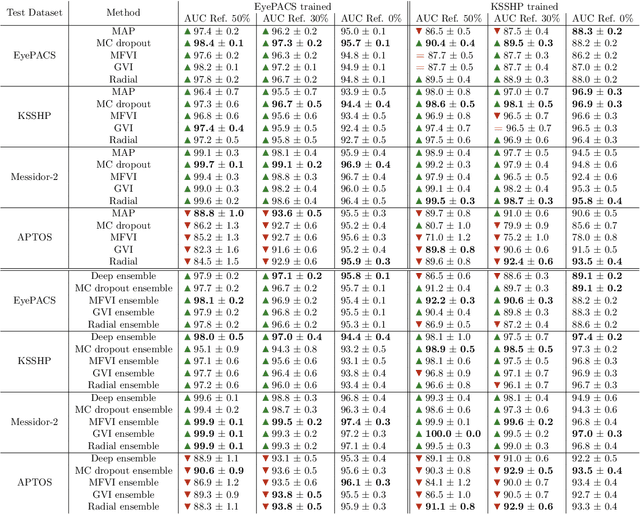
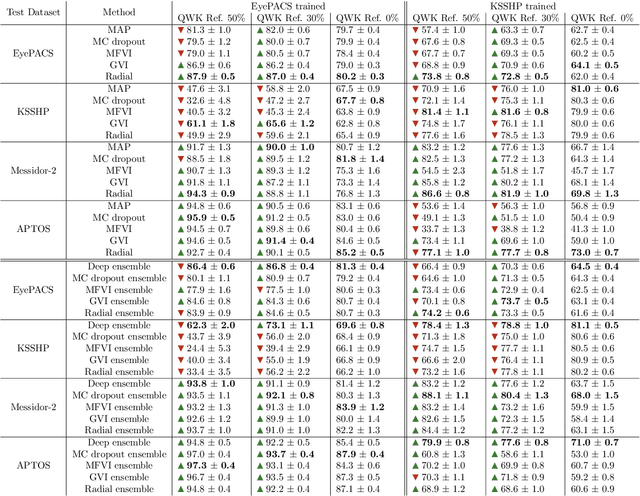
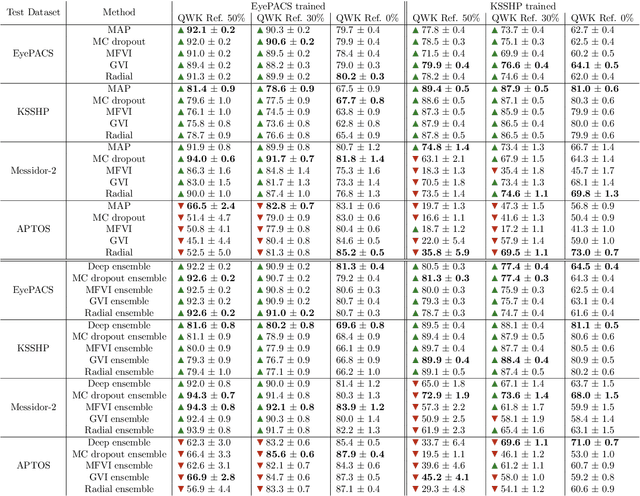
Abstract:Automatic classification of diabetic retinopathy from retinal images has been widely studied using deep neural networks with impressive results. However, there is a clinical need for estimation of the uncertainty in the classifications, a shortcoming of modern neural networks. Recently, approximate Bayesian deep learning methods have been proposed for the task but the studies have only considered the binary referable/non-referable diabetic retinopathy classification applied to benchmark datasets. We present novel results by systematically investigating a clinical dataset and a clinically relevant 5-class classification scheme, in addition to benchmark datasets and the binary classification scheme. Moreover, we derive a connection between uncertainty measures and classifier risk, from which we develop a new uncertainty measure. We observe that the previously proposed entropy-based uncertainty measure generalizes to the clinical dataset on the binary classification scheme but not on the 5-class scheme, whereas our new uncertainty measure generalizes to the latter case.
Deep Learning Fundus Image Analysis for Diabetic Retinopathy and Macular Edema Grading
Apr 16, 2019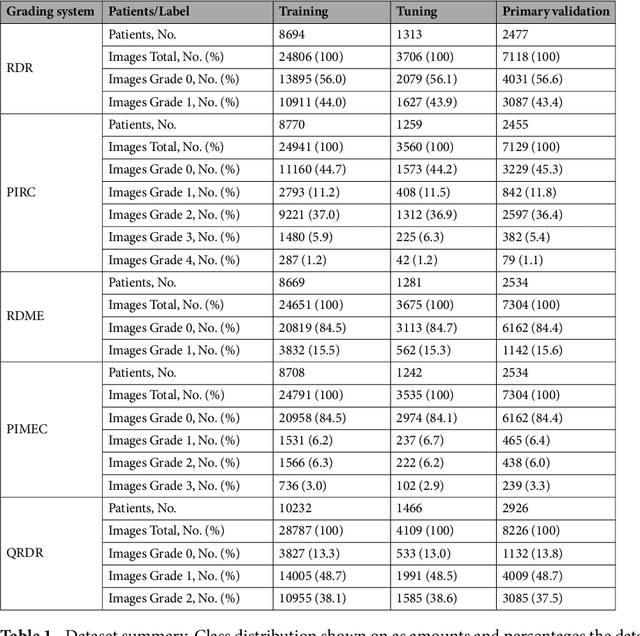
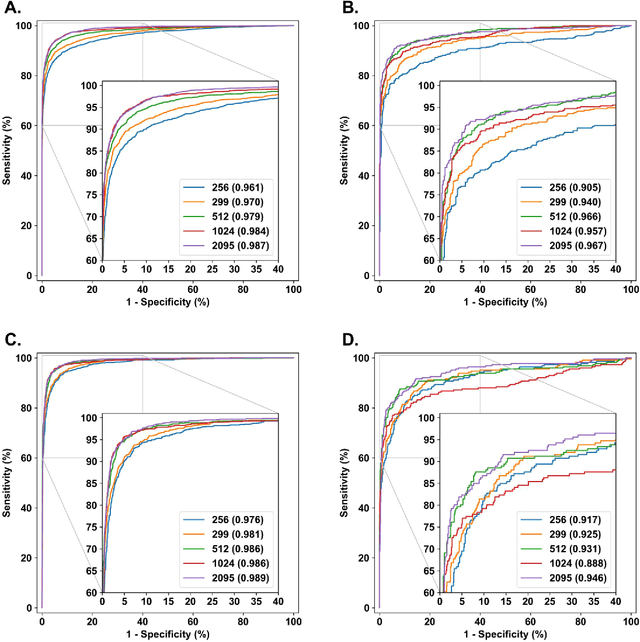
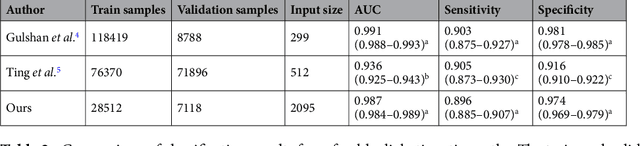
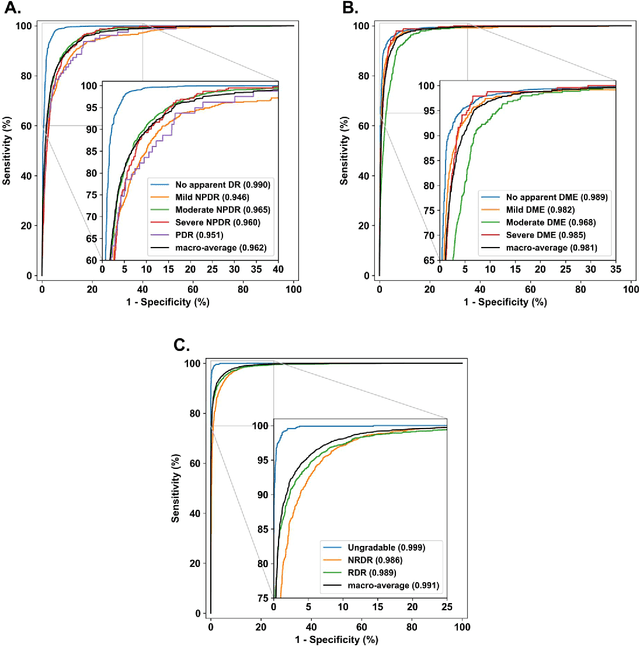
Abstract:Diabetes is a globally prevalent disease that can cause visible microvascular complications such as diabetic retinopathy and macular edema in the human eye retina, the images of which are today used for manual disease screening. This labor-intensive task could greatly benefit from automatic detection using deep learning technique. Here we present a deep learning system that identifies referable diabetic retinopathy comparably or better than presented in the previous studies, although we use only a small fraction of images (<1/4) in training but are aided with higher image resolutions. We also provide novel results for five different screening and clinical grading systems for diabetic retinopathy and macular edema classification, including results for accurately classifying images according to clinical five-grade diabetic retinopathy and four-grade diabetic macular edema scales. These results suggest, that a deep learning system could increase the cost-effectiveness of screening while attaining higher than recommended performance, and that the system could be applied in clinical examinations requiring finer grading.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge