Kurniawati Azizah
Stuttering-Aware Automatic Speech Recognition for Indonesian Language
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Automatic speech recognition systems have achieved remarkable performance on fluent speech but continue to degrade significantly when processing stuttered speech, a limitation that is particularly acute for low-resource languages like Indonesian where specialized datasets are virtually non-existent. To overcome this scarcity, we propose a data augmentation framework that generates synthetic stuttered audio by injecting repetitions and prolongations into fluent text through a combination of rule-based transformations and large language models followed by text-to-speech synthesis. We apply this synthetic data to fine-tune a pre-trained Indonesian Whisper model using transfer learning, enabling the architecture to adapt to dysfluent acoustic patterns without requiring large-scale real-world recordings. Our experiments demonstrate that this targeted synthetic exposure consistently reduces recognition errors on stuttered speech while maintaining performance on fluent segments, validating the utility of synthetic data pipelines for developing more inclusive speech technologies in under-represented languages.
Continual Learning in Machine Speech Chain Using Gradient Episodic Memory
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Continual learning for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems poses a challenge, especially with the need to avoid catastrophic forgetting while maintaining performance on previously learned tasks. This paper introduces a novel approach leveraging the machine speech chain framework to enable continual learning in ASR using gradient episodic memory (GEM). By incorporating a text-to-speech (TTS) component within the machine speech chain, we support the replay mechanism essential for GEM, allowing the ASR model to learn new tasks sequentially without significant performance degradation on earlier tasks. Our experiments, conducted on the LJ Speech dataset, demonstrate that our method outperforms traditional fine-tuning and multitask learning approaches, achieving a substantial error rate reduction while maintaining high performance across varying noise conditions. We showed the potential of our semi-supervised machine speech chain approach for effective and efficient continual learning in speech recognition.
Enhancing Indonesian Automatic Speech Recognition: Evaluating Multilingual Models with Diverse Speech Variabilities
Oct 11, 2024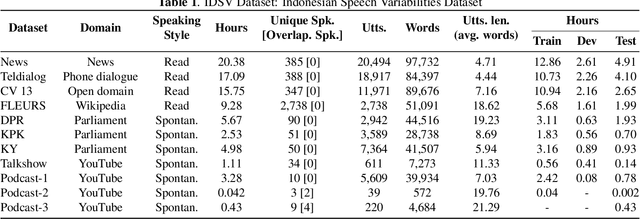
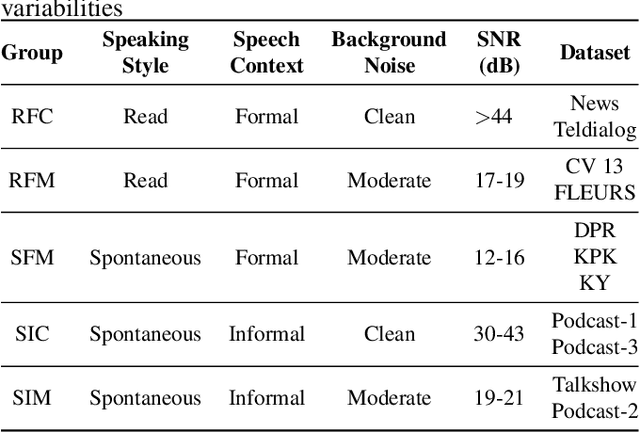
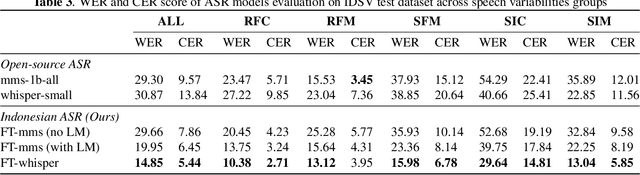
Abstract:An ideal speech recognition model has the capability to transcribe speech accurately under various characteristics of speech signals, such as speaking style (read and spontaneous), speech context (formal and informal), and background noise conditions (clean and moderate). Building such a model requires a significant amount of training data with diverse speech characteristics. Currently, Indonesian data is dominated by read, formal, and clean speech, leading to a scarcity of Indonesian data with other speech variabilities. To develop Indonesian automatic speech recognition (ASR), we present our research on state-of-the-art speech recognition models, namely Massively Multilingual Speech (MMS) and Whisper, as well as compiling a dataset comprising Indonesian speech with variabilities to facilitate our study. We further investigate the models' predictive ability to transcribe Indonesian speech data across different variability groups. The best results were achieved by the Whisper fine-tuned model across datasets with various characteristics, as indicated by the decrease in word error rate (WER) and character error rate (CER). Moreover, we found that speaking style variability affected model performance the most.
Cross-lingual Transfer Learning for Javanese Dependency Parsing
Jan 22, 2024



Abstract:While structure learning achieves remarkable performance in high-resource languages, the situation differs for under-represented languages due to the scarcity of annotated data. This study focuses on assessing the efficacy of transfer learning in enhancing dependency parsing for Javanese, a language spoken by 80 million individuals but characterized by limited representation in natural language processing. We utilized the Universal Dependencies dataset consisting of dependency treebanks from more than 100 languages, including Javanese. We propose two learning strategies to train the model: transfer learning (TL) and hierarchical transfer learning (HTL). While TL only uses a source language to pre-train the model, the HTL method uses a source language and an intermediate language in the learning process. The results show that our best model uses the HTL method, which improves performance with an increase of 10% for both UAS and LAS evaluations compared to the baseline model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge