Kunde Yang
Angle-distance decomposition based on deep learning for active sonar detection
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Underwater target detection using active sonar constitutes a critical research area in marine sciences and engineering. However, traditional signal processing methods face significant challenges in complex underwater environments due to noise, reverberation, and interference. To address these issues, this paper presents a deep learning-based active sonar target detection method that decomposes the detection process into separate angle and distance estimation tasks. Active sonar target detection employs deep learning models to predict target distance and angle, with the final target position determined by integrating these estimates. Limited underwater acoustic data hinders effective model training, but transfer learning and simulation offer practical solutions to this challenge. Experimental results verify that the method achieves effective and robust performance under challenging conditions.
A Robust ADMM-Based Optimization Algorithm For Underwater Acoustic Channel Estimation
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:Accurate estimation of the Underwater acoustic (UWA) is a key part of underwater communications, especially for coherent systems. The severe multipath effects and large delay spreads make the estimation problem large-scale. The non-stationary, non-Gaussian, and impulsive nature of ocean ambient noise poses further obstacles to the design of estimation algorithms. Under the framework of compressed sensing (CS), this work addresses the issue of robust channel estimation when measurements are contaminated by impulsive noise. A first-order algorithm based on alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) is proposed. Numerical simulations of time-varying channel estimation are performed to show its improved performance in highly impulsive noise environments.
LMD: A Learnable Mask Network to Detect Adversarial Examples for Speaker Verification
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:Although the security of automatic speaker verification (ASV) is seriously threatened by recently emerged adversarial attacks, there have been some countermeasures to alleviate the threat. However, many defense approaches not only require the prior knowledge of the attackers but also possess weak interpretability. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose an attacker-independent and interpretable method, named learnable mask detector (LMD), to separate adversarial examples from the genuine ones. It utilizes score variation as an indicator to detect adversarial examples, where the score variation is the absolute discrepancy between the ASV scores of an original audio recording and its transformed audio synthesized from its masked complex spectrogram. A core component of the score variation detector is to generate the masked spectrogram by a neural network. The neural network needs only genuine examples for training, which makes it an attacker-independent approach. Its interpretability lies that the neural network is trained to minimize the score variation of the targeted ASV, and maximize the number of the masked spectrogram bins of the genuine training examples. Its foundation is based on the observation that, masking out the vast majority of the spectrogram bins with little speaker information will inevitably introduce a large score variation to the adversarial example, and a small score variation to the genuine example. Experimental results with 12 attackers and two representative ASV systems show that our proposed method outperforms five state-of-the-art baselines. The extensive experimental results can also be a benchmark for the detection-based ASV defenses.
Symmetric Saliency-based Adversarial Attack To Speaker Identification
Oct 30, 2022



Abstract:Adversarial attack approaches to speaker identification either need high computational cost or are not very effective, to our knowledge. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose a novel generation-network-based approach, called symmetric saliency-based encoder-decoder (SSED), to generate adversarial voice examples to speaker identification. It contains two novel components. First, it uses a novel saliency map decoder to learn the importance of speech samples to the decision of a targeted speaker identification system, so as to make the attacker focus on generating artificial noise to the important samples. It also proposes an angular loss function to push the speaker embedding far away from the source speaker. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SSED yields the state-of-the-art performance, i.e. over 97% targeted attack success rate and a signal-to-noise level of over 39 dB on both the open-set and close-set speaker identification tasks, with a low computational cost.
IF equation: a feature extractor for high-concentration time-frequency representation
Nov 23, 2021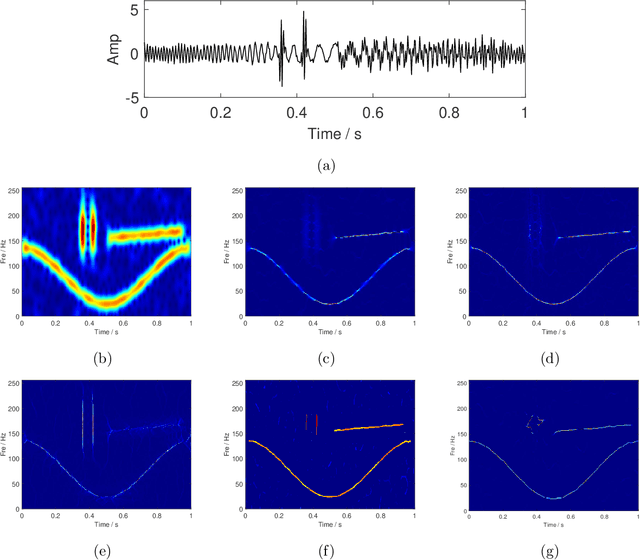

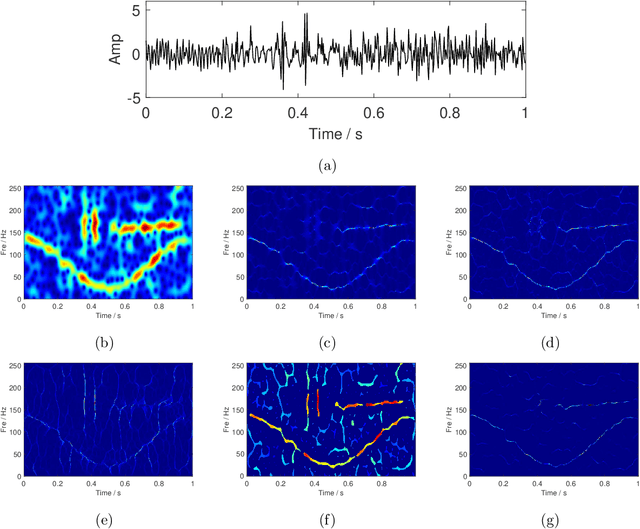
Abstract:High-concentration time-frequency (TF) representation provides a valuable tool for characterizing multi-component non-stationary signals. In our previous work, we proposed using an instantaneous frequency (IF) equation to sharpen the TF distribution and its effectiveness has been verified in experiments. In this paper, we systematically discuss why the IF equation-based TF analysis methods work and how to use the IF equation to improve the TF sharpness. By theory analysis, many popular TF post-processing methods, such as the synchroextracting transform, the multi-synchrosqueezing transform, and the time extracting transform, fall into the IF equation-based category. A comparison of the IF equation-based method with the popular synchrosqueezing transform is made. Numerical examples of the theoretical derivations are presented to illustrate the performance of the proposed IF equation-based TF analysis method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge