Konstantin Chernyshev
Tendem: A Hybrid AI+Human Platform
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Tendem is a hybrid system where AI handles structured, repeatable work and Human Experts step in when the models fail or to verify results. Each result undergoes a comprehensive quality review before delivery to the Client. To assess Tendem's performance, we conducted a series of in-house evaluations on 94 real-world tasks, comparing it with AI-only agents and human-only workflows carried out by Upwork freelancers. The results show that Tendem consistently delivers higher-quality outputs with faster turnaround times. At the same time, its operational costs remain comparable to human-only execution. On third-party agentic benchmarks, Tendem's AI Agent (operating autonomously, without human involvement) performs near state-of-the-art on web browsing and tool-use tasks while demonstrating strong results in frontier domain knowledge and reasoning.
U-MATH: A University-Level Benchmark for Evaluating Mathematical Skills in LLMs
Dec 04, 2024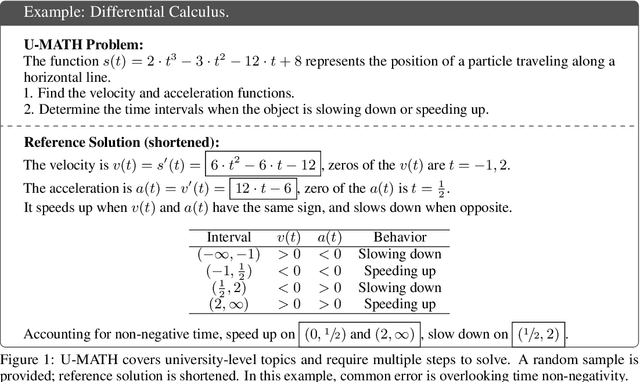
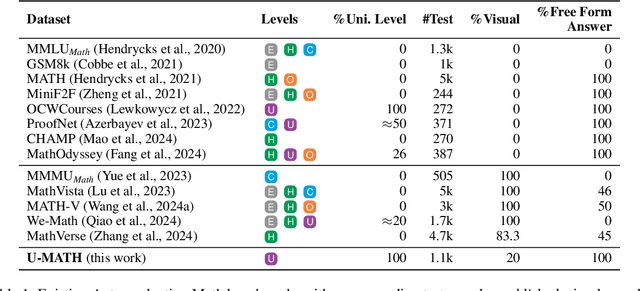
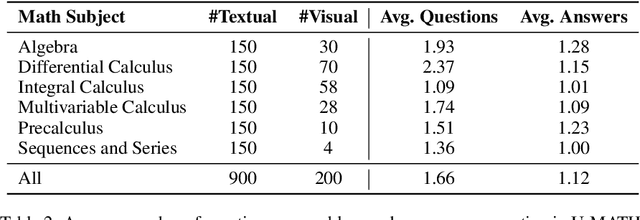
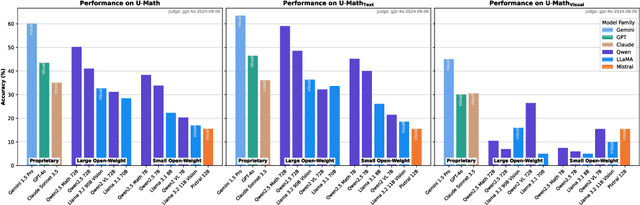
Abstract:The current evaluation of mathematical skills in LLMs is limited, as existing benchmarks are either relatively small, primarily focus on elementary and high-school problems, or lack diversity in topics. Additionally, the inclusion of visual elements in tasks remains largely under-explored. To address these gaps, we introduce U-MATH, a novel benchmark of 1,100 unpublished open-ended university-level problems sourced from teaching materials. It is balanced across six core subjects, with 20% of multimodal problems. Given the open-ended nature of U-MATH problems, we employ an LLM to judge the correctness of generated solutions. To this end, we release $\mu$-MATH, a dataset to evaluate the LLMs' capabilities in judging solutions. The evaluation of general domain, math-specific, and multimodal LLMs highlights the challenges presented by U-MATH. Our findings reveal that LLMs achieve a maximum accuracy of only 63% on text-based tasks, with even lower 45% on visual problems. The solution assessment proves challenging for LLMs, with the best LLM judge having an F1-score of 80% on $\mu$-MATH.
LCT-1 at SemEval-2023 Task 10: Pre-training and Multi-task Learning for Sexism Detection and Classification
Jun 08, 2023Abstract:Misogyny and sexism are growing problems in social media. Advances have been made in online sexism detection but the systems are often uninterpretable. SemEval-2023 Task 10 on Explainable Detection of Online Sexism aims at increasing explainability of the sexism detection, and our team participated in all the proposed subtasks. Our system is based on further domain-adaptive pre-training (Gururangan et al., 2020). Building on the Transformer-based models with the domain adaptation, we compare fine-tuning with multi-task learning and show that each subtask requires a different system configuration. In our experiments, multi-task learning performs on par with standard fine-tuning for sexism detection and noticeably better for coarse-grained sexism classification, while fine-tuning is preferable for fine-grained classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge