Khurshid Alam
Exploring 6G Potential for Industrial Digital Twinning and Swarm Intelligence in Obstacle-Rich
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:With the advent of 6G technology, the demand for efficient and intelligent systems in industrial applications has surged, driving the need for advanced solutions in target localization. Utilizing swarm robots to locate unknown targets involves navigating increasingly complex environments. Digital Twinning (DT) offers a robust solution by creating a virtual replica of the physical world, which enhances the swarm's navigation capabilities. Our framework leverages DT and integrates Swarm Intelligence to store physical map information in the cloud, enabling robots to efficiently locate unknown targets. The simulation results demonstrate that the DT framework, augmented by Swarm Intelligence, significantly improves target location efficiency in obstacle-rich environments compared to traditional methods. This research underscores the potential of combining DT and Swarm Intelligence to advance the field of robotic navigation and target localization in complex industrial settings.
Leveraging Machine Learning for Industrial Wireless Communications
May 05, 2021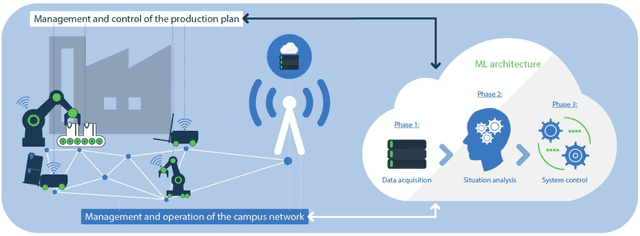
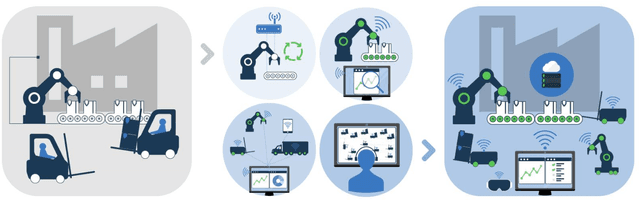
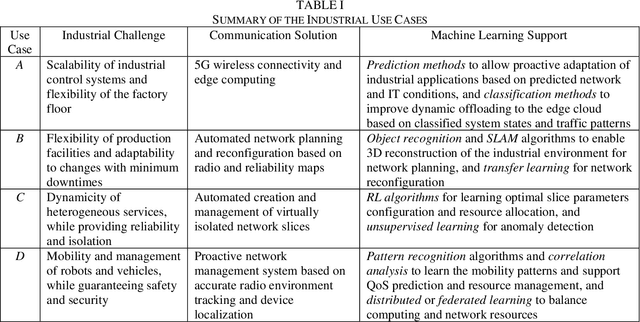
Abstract:Two main trends characterize today's communication landscape and are finding their way into industrial facilities: the rollout of 5G with its distinct support for vertical industries and the increasing success of machine learning (ML). The combination of those two technologies open the doors to many exciting industrial applications and its impact is expected to rapidly increase in the coming years, given the abundant data growth and the availability of powerful edge computers in production facilities. Unlike most previous work that has considered the application of 5G and ML in industrial environment separately, this paper highlights the potential and synergies that result from combining them. The overall vision presented here generates from the KICK project, a collaboration of several partners from the manufacturing and communication industry as well as research institutes. This unprecedented blend of 5G and ML expertise creates a unique perspective on ML-supported industrial communications and their role in facilitating industrial automation. The paper identifies key open industrial challenges that are grouped into four use cases: wireless connectivity and edge-cloud integration, flexibility in network reconfiguration, dynamicity of heterogeneous network services, and mobility of robots and vehicles. Moreover, the paper provides insights into the advantages of ML-based industrial communications and discusses current challenges of data acquisition in real systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge