Khalid Alnajjar
Threefold model for AI Readiness: A Case Study with Finnish Healthcare SMEs
Mar 15, 2025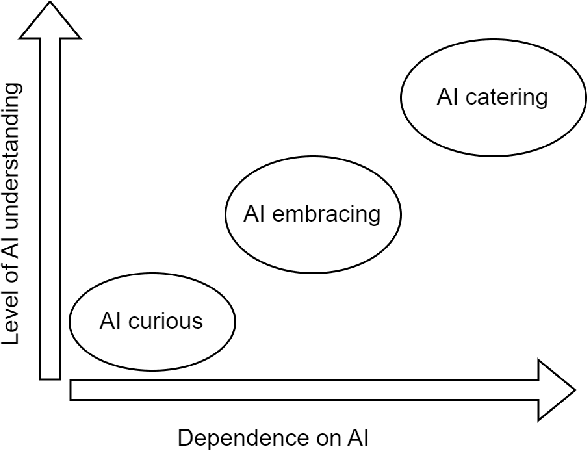
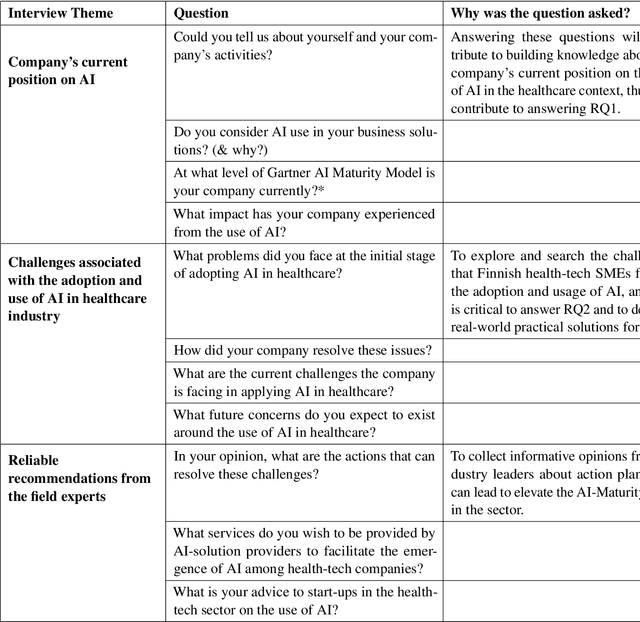
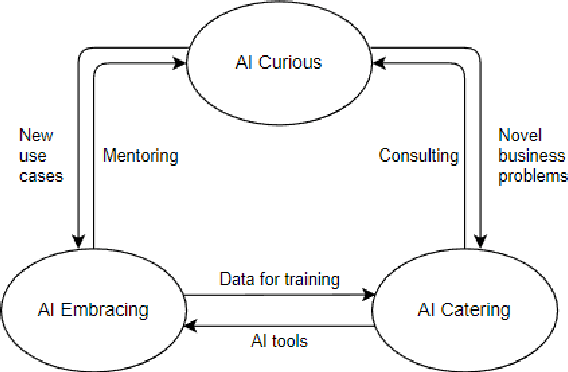
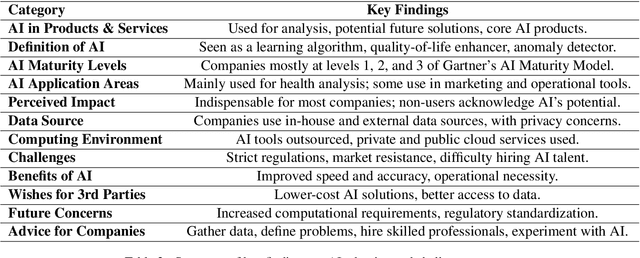
Abstract:This study examines AI adoption among Finnish healthcare SMEs through semi-structured interviews with six health-tech companies. We identify three AI engagement categories: AI-curious (exploring AI), AI-embracing (integrating AI), and AI-catering (providing AI solutions). Our proposed threefold model highlights key adoption barriers, including regulatory complexities, technical expertise gaps, and financial constraints. While SMEs recognize AI's potential, most remain in early adoption stages. We provide actionable recommendations to accelerate AI integration, focusing on regulatory reforms, talent development, and inter-company collaboration, offering valuable insights for healthcare organizations, policymakers, and researchers.
Analyzing Pokémon and Mario Streamers' Twitch Chat with LLM-based User Embeddings
Nov 17, 2024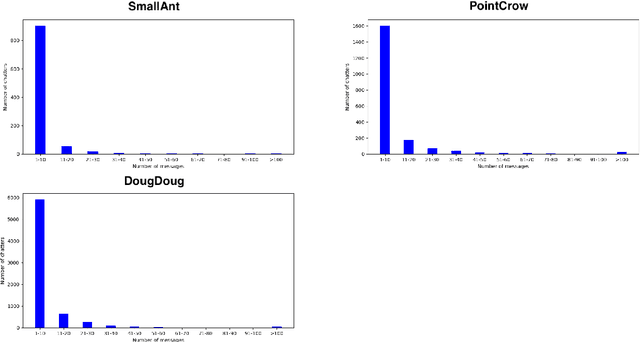
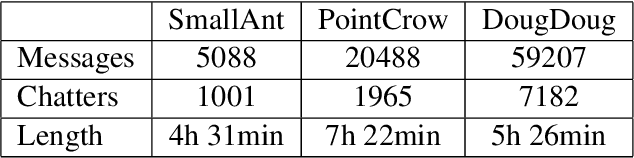
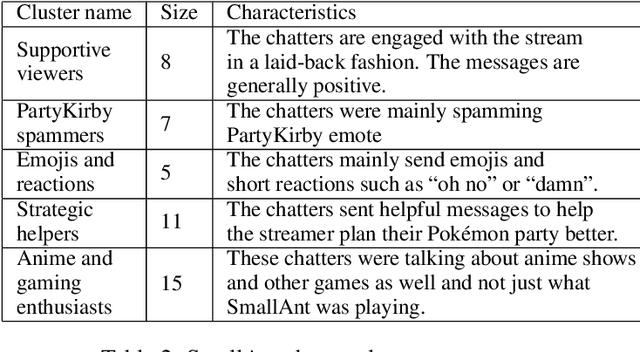
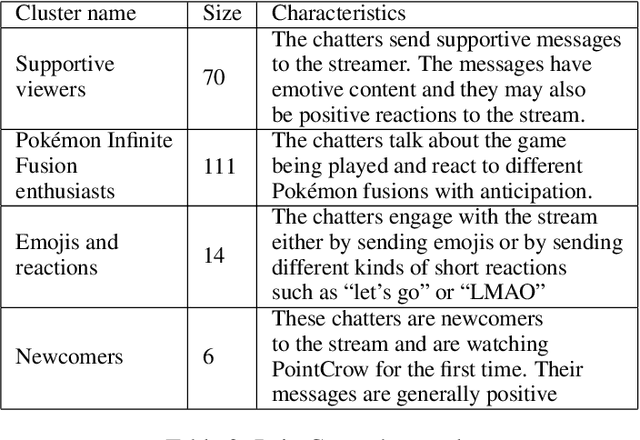
Abstract:We present a novel digital humanities method for representing our Twitch chatters as user embeddings created by a large language model (LLM). We cluster these embeddings automatically using affinity propagation and further narrow this clustering down through manual analysis. We analyze the chat of one stream by each Twitch streamer: SmallAnt, DougDoug and PointCrow. Our findings suggest that each streamer has their own type of chatters, however two categories emerge for all of the streamers: supportive viewers and emoji and reaction senders. Repetitive message spammers is a shared chatter category for two of the streamers.
Leveraging Transformer-Based Models for Predicting Inflection Classes of Words in an Endangered Sami Language
Nov 04, 2024
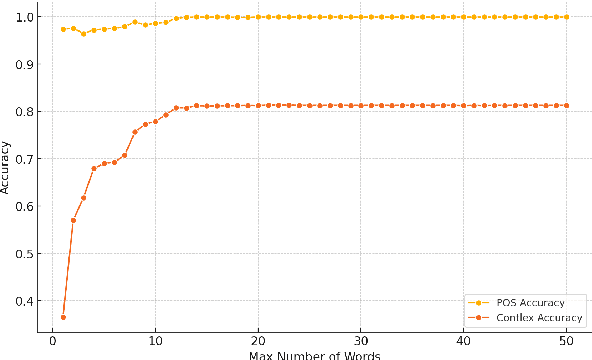

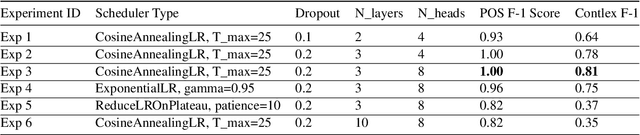
Abstract:This paper presents a methodology for training a transformer-based model to classify lexical and morphosyntactic features of Skolt Sami, an endangered Uralic language characterized by complex morphology. The goal of our approach is to create an effective system for understanding and analyzing Skolt Sami, given the limited data availability and linguistic intricacies inherent to the language. Our end-to-end pipeline includes data extraction, augmentation, and training a transformer-based model capable of predicting inflection classes. The motivation behind this work is to support language preservation and revitalization efforts for minority languages like Skolt Sami. Accurate classification not only helps improve the state of Finite-State Transducers (FSTs) by providing greater lexical coverage but also contributes to systematic linguistic documentation for researchers working with newly discovered words from literature and native speakers. Our model achieves an average weighted F1 score of 1.00 for POS classification and 0.81 for inflection class classification. The trained model and code will be released publicly to facilitate future research in endangered NLP.
Sentiment Analysis Using Aligned Word Embeddings for Uralic Languages
May 24, 2023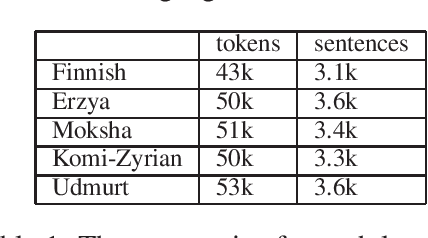
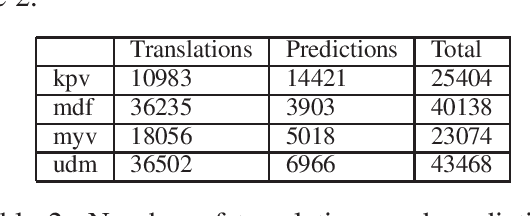
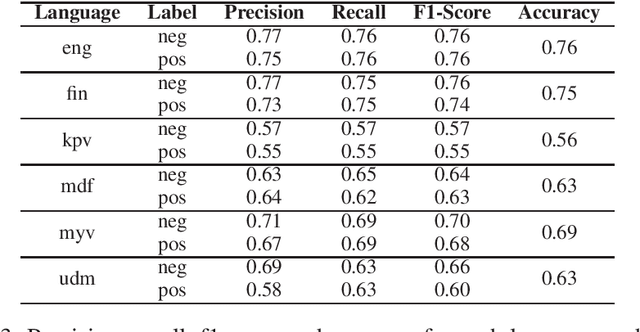
Abstract:In this paper, we present an approach for translating word embeddings from a majority language into 4 minority languages: Erzya, Moksha, Udmurt and Komi-Zyrian. Furthermore, we align these word embeddings and present a novel neural network model that is trained on English data to conduct sentiment analysis and then applied on endangered language data through the aligned word embeddings. To test our model, we annotated a small sentiment analysis corpus for the 4 endangered languages and Finnish. Our method reached at least 56\% accuracy for each endangered language. The models and the sentiment corpus will be released together with this paper. Our research shows that state-of-the-art neural models can be used with endangered languages with the only requirement being a dictionary between the endangered language and a majority language.
Ring That Bell: A Corpus and Method for Multimodal Metaphor Detection in Videos
Dec 15, 2022Abstract:We present the first openly available multimodal metaphor annotated corpus. The corpus consists of videos including audio and subtitles that have been annotated by experts. Furthermore, we present a method for detecting metaphors in the new dataset based on the textual content of the videos. The method achieves a high F1-score (62\%) for metaphorical labels. We also experiment with other modalities and multimodal methods; however, these methods did not out-perform the text-based model. In our error analysis, we do identify that there are cases where video could help in disambiguating metaphors, however, the visual cues are too subtle for our model to capture. The data is available on Zenodo.
Emotion Conditioned Creative Dialog Generation
Dec 06, 2022Abstract:We present a DialGPT based model for generating creative dialog responses that are conditioned based on one of the following emotions: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, pain, sadness and surprise. Our model is capable of producing a contextually apt response given an input sentence and a desired emotion label. Our model is capable of expressing the desired emotion with an accuracy of 0.6. The best performing emotions are neutral, fear and disgust. When measuring the strength of the expressed emotion, we find that anger, fear and disgust are expressed in the most strong fashion by the model.
Modern French Poetry Generation with RoBERTa and GPT-2
Dec 06, 2022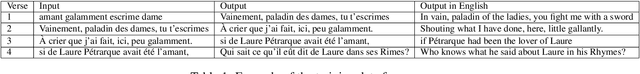

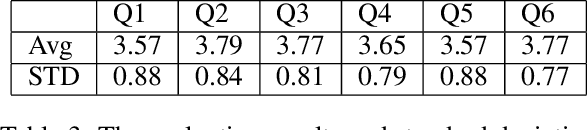
Abstract:We present a novel neural model for modern poetry generation in French. The model consists of two pretrained neural models that are fine-tuned for the poem generation task. The encoder of the model is a RoBERTa based one while the decoder is based on GPT-2. This way the model can benefit from the superior natural language understanding performance of RoBERTa and the good natural language generation performance of GPT-2. Our evaluation shows that the model can create French poetry successfully. On a 5 point scale, the lowest score of 3.57 was given by human judges to typicality and emotionality of the output poetry while the best score of 3.79 was given to understandability.
Automatic Generation of Factual News Headlines in Finnish
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:We present a novel approach to generating news headlines in Finnish for a given news story. We model this as a summarization task where a model is given a news article, and its task is to produce a concise headline describing the main topic of the article. Because there are no openly available GPT-2 models for Finnish, we will first build such a model using several corpora. The model is then fine-tuned for the headline generation task using a massive news corpus. The system is evaluated by 3 expert journalists working in a Finnish media house. The results showcase the usability of the presented approach as a headline suggestion tool to facilitate the news production process.
Video Games as a Corpus: Sentiment Analysis using Fallout New Vegas Dialog
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:We present a method for extracting a multilingual sentiment annotated dialog data set from Fallout New Vegas. The game developers have preannotated every line of dialog in the game in one of the 8 different sentiments: \textit{anger, disgust, fear, happy, neutral, pained, sad } and \textit{surprised}. The game has been translated into English, Spanish, German, French and Italian. We conduct experiments on multilingual, multilabel sentiment analysis on the extracted data set using multilingual BERT, XLMRoBERTa and language specific BERT models. In our experiments, multilingual BERT outperformed XLMRoBERTa for most of the languages, also language specific models were slightly better than multilingual BERT for most of the languages. The best overall accuracy was 54\% and it was achieved by using multilingual BERT on Spanish data. The extracted data set presents a challenging task for sentiment analysis. We have released the data, including the testing and training splits, openly on Zenodo. The data set has been shuffled for copyright reasons.
When to Laugh and How Hard? A Multimodal Approach to Detecting Humor and its Intensity
Nov 03, 2022

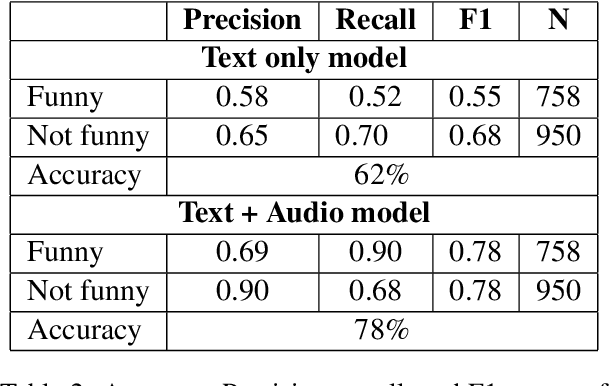
Abstract:Prerecorded laughter accompanying dialog in comedy TV shows encourages the audience to laugh by clearly marking humorous moments in the show. We present an approach for automatically detecting humor in the Friends TV show using multimodal data. Our model is capable of recognizing whether an utterance is humorous or not and assess the intensity of it. We use the prerecorded laughter in the show as annotation as it marks humor and the length of the audience's laughter tells us how funny a given joke is. We evaluate the model on episodes the model has not been exposed to during the training phase. Our results show that the model is capable of correctly detecting whether an utterance is humorous 78% of the time and how long the audience's laughter reaction should last with a mean absolute error of 600 milliseconds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge