Keran Ye
Deformable Multibody Modeling for Model Predictive Control in Legged Locomotion with Embodied Compliance
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:The paper presents a method to stabilize dynamic gait for a legged robot with embodied compliance. Our approach introduces a unified description for rigid and compliant bodies to approximate their deformation and a formulation for deformable multibody systems. We develop the centroidal composite predictive deformed inertia (CCPDI) tensor of a deformable multibody system and show how to integrate it with the standard-of-practice model predictive controller (MPC). Simulation shows that the resultant control framework can stabilize trot stepping on a quadrupedal robot with both rigid and compliant spines under the same MPC configurations. Compared to standard MPC, the developed CCPDI-enabled MPC distributes the ground reactive forces closer to the heuristics for body balance, and it is thus more likely to stabilize the gaits of the compliant robot. A parametric study shows that our method preserves some level of robustness within a suitable envelope of key parameter values.
Design and Central Pattern Generator Control of a New Transformable Wheel-Legged Robot
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a new wheel-legged robot and develops motion controllers based on central pattern generators (CPGs) for the robot to navigate over a range of terrains. A transformable leg-wheel design is considered and characterized in terms of key locomotion characteristics as a function of the design. Kinematic analysis is conducted based on a generalized four-bar mechanism driven by a coaxial hub arrangement. The analysis is used to inform the design of a central pattern generator to control the robot by mapping oscillator states to wheel-leg trajectories and implementing differential steering within the oscillator network. Three oscillator models are used as the basis of the CPGs, and their performance is compared over a range of inputs. The CPG-based controller is used to drive the developed robot prototype on level ground and over obstacles. Additional simulated tests are performed for uneven terrain negotiation and obstacle climbing. Results demonstrate the effectiveness of CPG control in transformable wheel-legged robots.
A Novel Lockable Spring-loaded Prismatic Spine to Support Agile Quadrupedal Locomotion
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces a way to systematically investigate the effect of compliant prismatic spines in quadrupedal robot locomotion. We develop a novel spring-loaded lockable spine module, together with a new Spinal Compliance-Integrated Quadruped (SCIQ) platform for both empirical and numerical research. Individual spine tests reveal beneficial spinal characteristics like a degressive spring, and validate the efficacy of a proposed compact locking/unlocking mechanism for the spine. Benchmark vertical jumping and landing tests with our robot show comparable jumping performance between the rigid and compliant spines. An observed advantage of the compliant spine module is that it can alleviate more challenging landing conditions by absorbing impact energy and dissipating the remainder via feet slipping through much in cat-like stretching fashion.
Evaluation of Legged Robot Landing Capability Under Aggressive Linear and Angular Velocities
Feb 24, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a method to evaluate the capability of aggressive legged robot landing under significant touchdown linear and angular velocities upon impact. Our approach builds upon the Planar Inverted Pendulum with Flywheel (PIPF) model and introduces a landing framework for the first stance step on a non-dimensional basis. We develop a nonlinear framework with iterative constrained trajectory optimization to stabilize the first stance step prior to N-step Capturability analysis. Performance maps across many different initial conditions reveal approximately linear boundaries as well as the effect of inertia, body incidence angle and leg attacking angle on the boundary shape. Our method also yields the engineering insight that body inertia affects the performance map the most, hence its optimization can be prioritized when the target is to improve robot landing efficacy.
Modeling and Trajectory Optimization for Standing Long Jumping of a Quadruped with A Preloaded Elastic Prismatic Spine
Sep 01, 2021
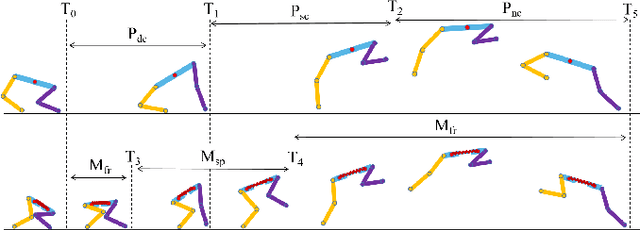


Abstract:This paper presents a novel methodology to model and optimize trajectories of a quadrupedal robot with spinal compliance to improve standing jump performance compared to quadrupeds with a rigid spine. We introduce an elastic model for a prismatic robotic spine that is actively preloaded and mechanically lock-enabled at initial and maximum length, and develop a constrained trajectory optimization method to co-optimize the elastic parameters and motion trajectories toward enhanced jumping distance. Results reveal that a less stiff spring is likely to facilitate jumping performance not as a direct propelling source but as a means to unleash more motor power for propelling by trading-off overall energy efficiency. We also visualize the impact of spring coefficients on the overall optimization routine from energetic perspectives to identify the suitable parameter region.
A Portable Agricultural Robot for Continuous Apparent Soil ElectricalConductivity Measurements to Improve Irrigation Practices
Jul 20, 2021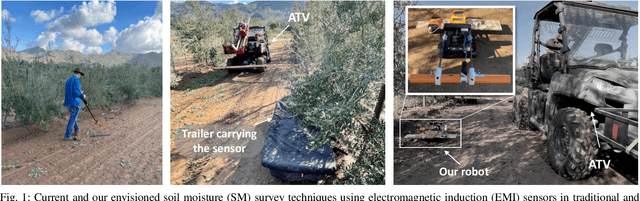
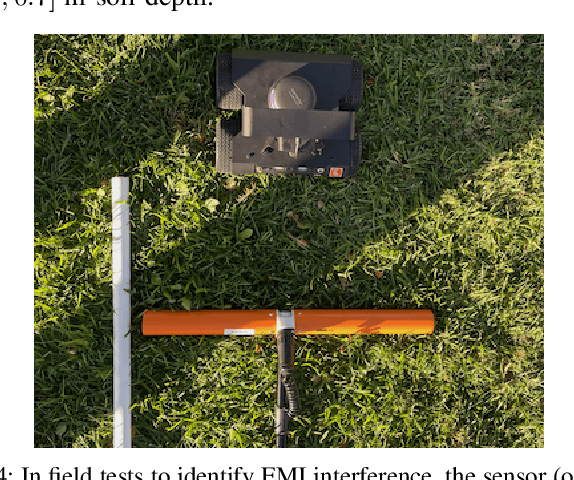
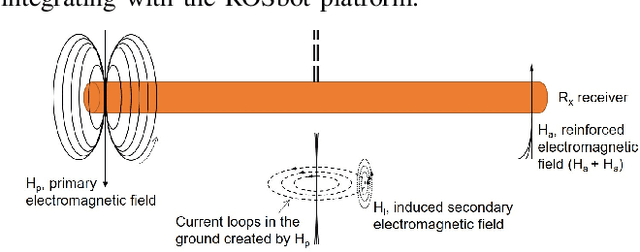
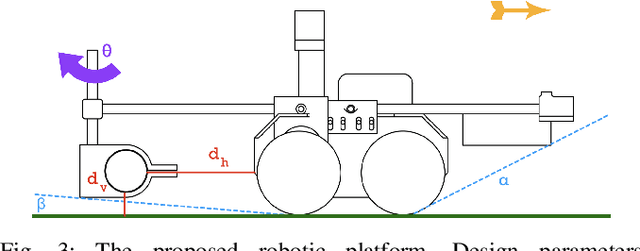

Abstract:Near-ground sensing data, such as geospatial measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity (ECa), are used in precision agriculture to improve farming practices and increase crop yield. Near-ground sensors provide valuable information, yet, the process of collecting, assessing, and interpreting measurements requires significant human labor. Automating parts of this process via the use of mobile robots can help decrease labor burden, and increase the accuracy and frequency of data collections, and overall increase the adoption and use of ECa measurement technology. This paper introduces a roboticized means to autonomously perform geospatial ECa measurements and map soil moisture content in micro-irrigated orchard systems. We retrofit a small wheeled mobile robot with a small electromagnetic induction sensor by studying and taking into consideration the effect of the robot body to the sensor's readings, and develop a software stack to enable autonomous logging of geo-referenced measurements. The proposed roboticized ECa measurement method is evaluated by mapping a 50m x 30m field against the baseline of human-conducted measurements obtained by walking the sensor in the same field and following the same path. Experimental testing reveals that our approach yields roboticized measurements comparable to human-conducted ones, despite the robot's small form factor.
Development and Testing of a Novel Automated Insect Capture Module for Sample Collection and Transfer
Aug 29, 2020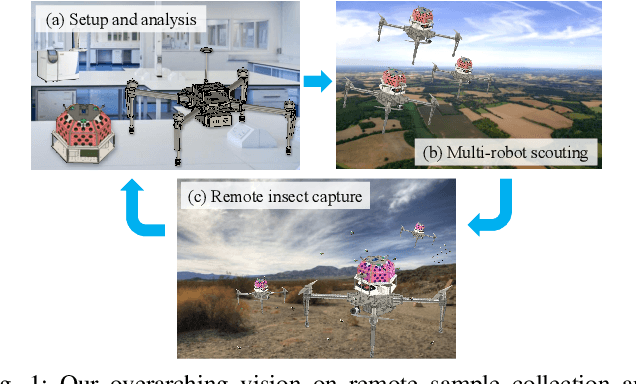
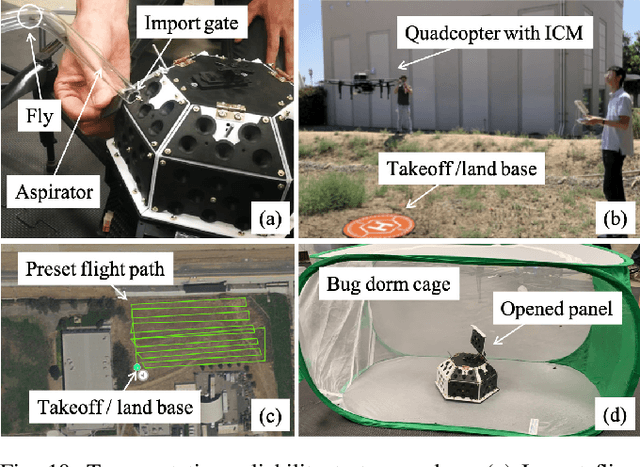
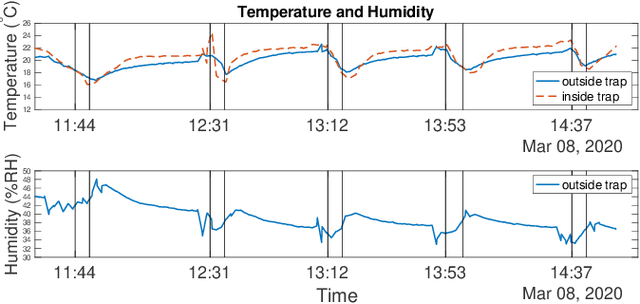
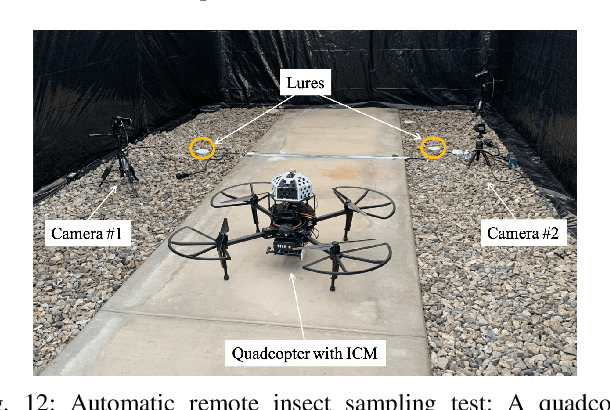
Abstract:There exists an urgent need for efficient tools in disease surveillance to help model and predict the spread of disease. The transmission of insect-borne diseases poses a serious concern to public health officials and the medical and research community at large. In the modeling of this spread, we face bottlenecks in (1) the frequency at which we are able to sample insect vectors in environments that are prone to propagating disease, (2) manual labor needed to set up and retrieve surveillance devices like traps, and (3) the return time in analyzing insect samples and determining if an infectious disease is spreading in a region. To help address these bottlenecks, we present in this paper the design, fabrication, and testing of a novel automated insect capture module (ICM) or trap that aims to improve the rate of transferring samples collected from the environment via aerial robots. The ICM features an ultraviolet light attractant, passive capture mechanism, panels which can open and close for access to insects, and a small onboard computer for automated operation and data logging. At the same time, the ICM is designed to be accessible; it is small-scale, lightweight and low-cost, and can be integrated with commercially available aerial robots. Indoor and outdoor experimentation validates ICM's feasibility in insect capturing and safe transportation. The device can help bring us one step closer toward achieving fully autonomous and scalable epidemiology by leveraging autonomous robots technology to aid the medical and research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge