Kazuki Inoue
Understanding Fake Faces
Sep 22, 2018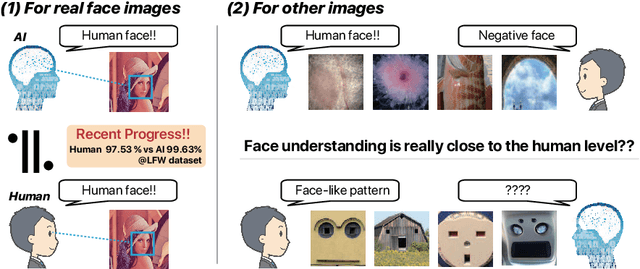


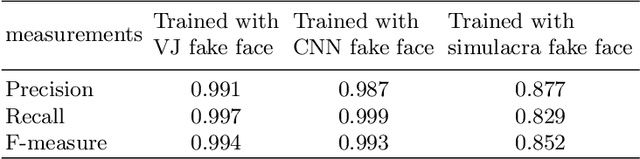
Abstract:Face recognition research is one of the most active topics in computer vision (CV), and deep neural networks (DNN) are now filling the gap between human-level and computer-driven performance levels in face verification algorithms. However, although the performance gap appears to be narrowing in terms of accuracy-based expectations, a curious question has arisen; specifically, "Face understanding of AI is really close to that of human?" In the present study, in an effort to confirm the brain-driven concept, we conduct image-based detection, classification, and generation using an in-house created fake face database. This database has two configurations: (i) false positive face detections produced using both the Viola Jones (VJ) method and convolutional neural networks (CNN), and (ii) simulacra that have fundamental characteristics that resemble faces but are completely artificial. The results show a level of suggestive knowledge that indicates the continuing existence of a gap between the capabilities of recent vision-based face recognition algorithms and human-level performance. On a positive note, however, we have obtained knowledge that will advance the progress of face-understanding models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge