Kazuki Higashi
Functional Eigen-Grasping Using Approach Heatmaps
Jan 22, 2024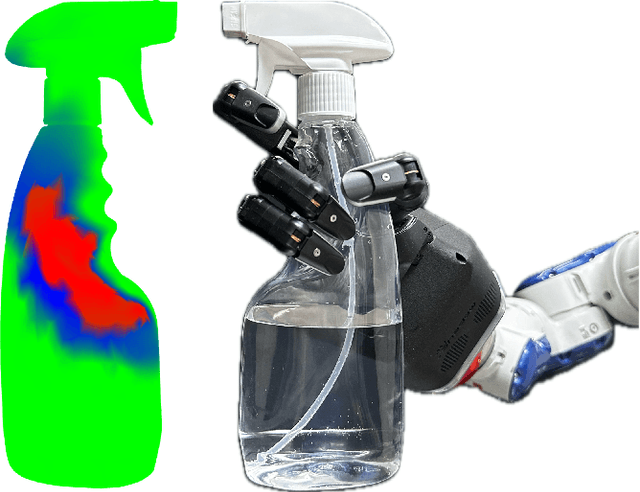
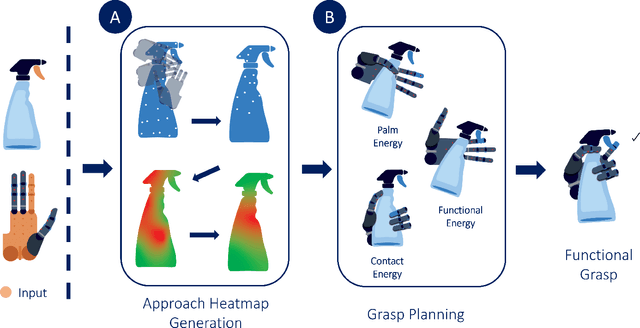
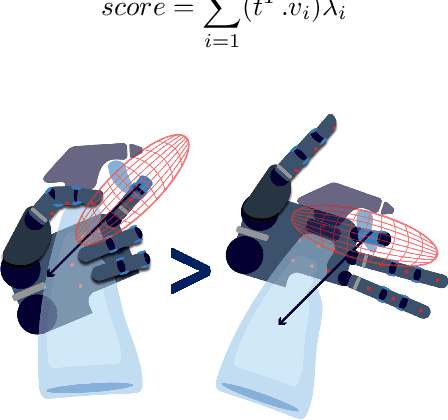
Abstract:This work presents a framework for a robot with a multi-fingered hand to freely utilize daily tools, including functional parts like buttons and triggers. An approach heatmap is generated by selecting a functional finger, indicating optimal palm positions on the object's surface that enable the functional finger to contact the tool's functional part. Once the palm position is identified through the heatmap, achieving the functional grasp becomes a straightforward process where the fingers stably grasp the object with low-dimensional inputs using the eigengrasp. As our approach does not need human demonstrations, it can easily adapt to various sizes and designs, extending its applicability to different objects. In our approach, we use directional manipulability to obtain the approach heatmap. In addition, we add two kinds of energy functions, i.e., palm energy and functional energy functions, to realize the eigengrasp. Using this method, each robotic gripper can autonomously identify its optimal workspace for functional grasping, extending its applicability to non-anthropomorphic robotic hands. We show that several daily tools like spray, drill, and remotes can be efficiently used by not only an anthropomorphic Shadow hand but also a non-anthropomorphic Barrett hand.
Functionally Divided Manipulation Synergy for Controlling Multi-fingered Hands
Mar 26, 2020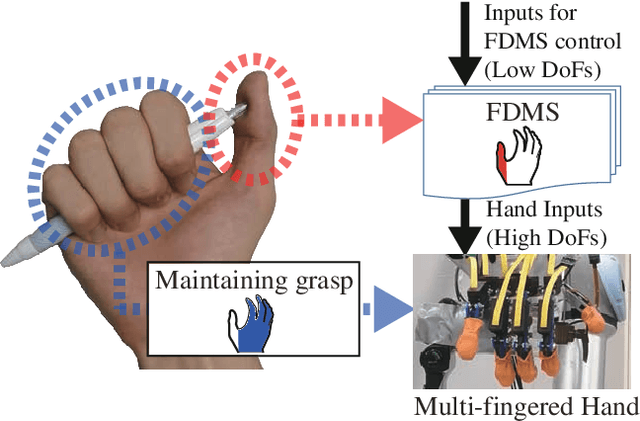
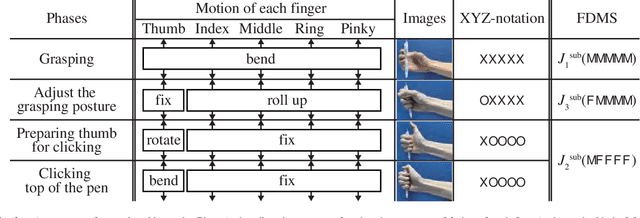
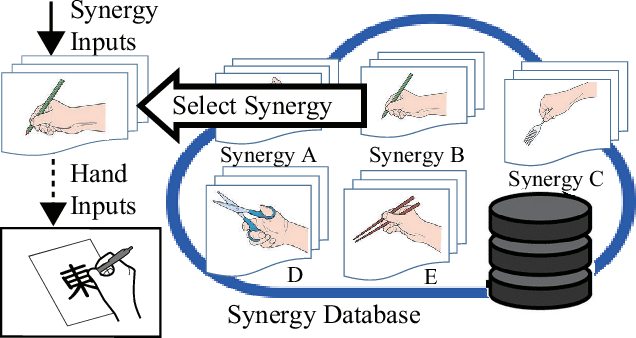
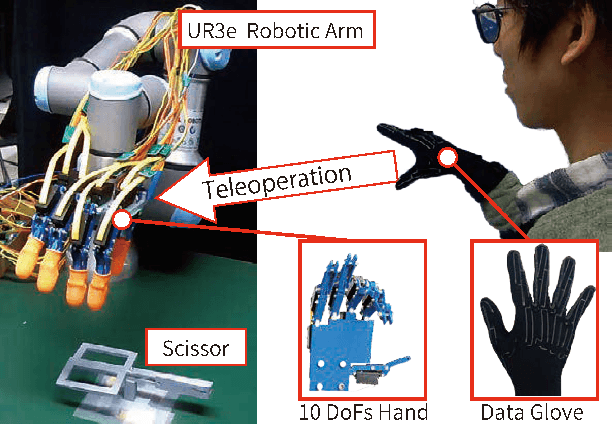
Abstract:Synergy supplies a practical approach for expressing various postures of a multi-fingered hand. However, a conventional synergy defined for reproducing grasping postures cannot perform general-purpose tasks expected for a multi-fingered hand. Locking the position of particular fingers is essential for a multi-fingered hand to manipulate an object. When using conventional synergy based control to manipulate an object, which requires locking some fingers, the coordination of joints is heavily restricted, decreasing the dexterity of the hand. We propose a functionally divided manipulation synergy (FDMS) method, which provides a synergy-based control to achieves both dimensionality reduction and in-hand manipulation. In FDMS, first, we define the function of each finger of the hand as either "manipulation" or "fixed." Then, we apply synergy control only to the fingers having the manipulation function, so that dexterous manipulations can be realized with few control inputs. The effectiveness of our proposed approach is experimentally verified.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge