Katelyn Lee
ReactEMG Stroke: Healthy-to-Stroke Few-shot Adaptation for sEMG-Based Intent Detection
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a promising control signal for assist-as-needed hand rehabilitation after stroke, but detecting intent from paretic muscles often requires lengthy, subject-specific calibration and remains brittle to variability. We propose a healthy-to-stroke adaptation pipeline that initializes an intent detector from a model pretrained on large-scale able-bodied sEMG, then fine-tunes it for each stroke participant using only a small amount of subject-specific data. Using a newly collected dataset from three individuals with chronic stroke, we compare adaptation strategies (head-only tuning, parameter-efficient LoRA adapters, and full end-to-end fine-tuning) and evaluate on held-out test sets that include realistic distribution shifts such as within-session drift, posture changes, and armband repositioning. Across conditions, healthy-pretrained adaptation consistently improves stroke intent detection relative to both zero-shot transfer and stroke-only training under the same data budget; the best adaptation methods improve average transition accuracy from 0.42 to 0.61 and raw accuracy from 0.69 to 0.78. These results suggest that transferring a reusable healthy-domain EMG representation can reduce calibration burden while improving robustness for real-time post-stroke intent detection.
Volitional Control of the Paretic Hand Post-Stroke Increases Finger Stiffness and Resistance to Robot-Assisted Movement
Feb 12, 2024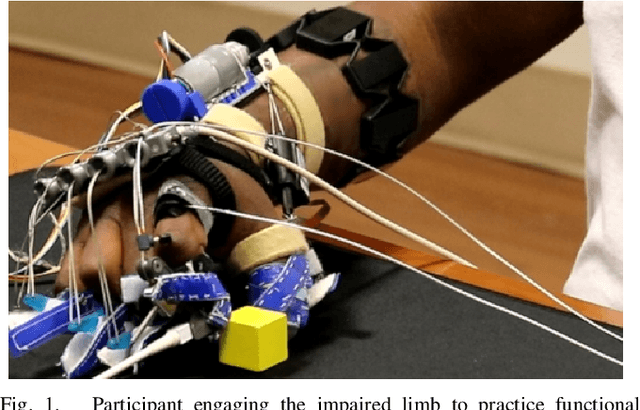
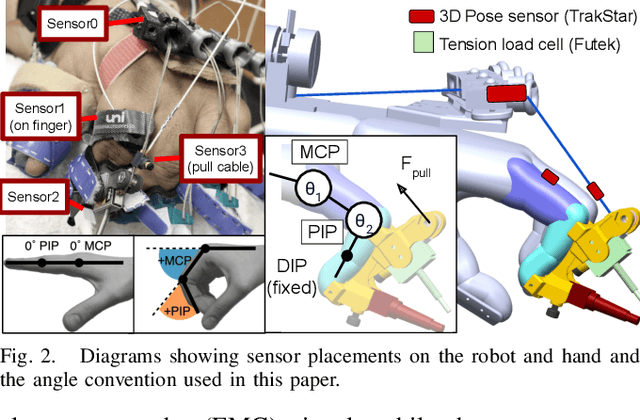
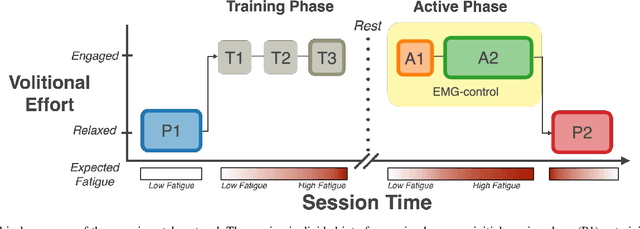
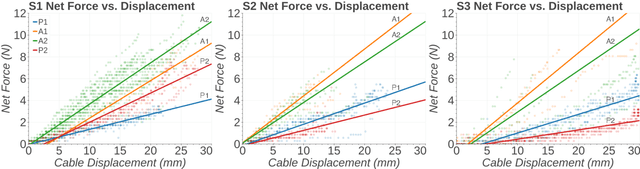
Abstract:Increased effort during use of the paretic arm and hand can provoke involuntary abnormal synergy patterns and amplify stiffness effects of muscle tone for individuals after stroke, which can add difficulty for user-controlled devices to assist hand movement during functional tasks. We study how volitional effort, exerted in an attempt to open or close the hand, affects resistance to robot-assisted movement at the finger level. We perform experiments with three chronic stroke survivors to measure changes in stiffness when the user is actively exerting effort to activate ipsilateral EMG-controlled robot-assisted hand movements, compared with when the fingers are passively stretched, as well as overall effects from sustained active engagement and use. Our results suggest that active engagement of the upper extremity increases muscle tone in the finger to a much greater degree than through passive-stretch or sustained exertion over time. Potential design implications of this work suggest that developers should anticipate higher levels of finger stiffness when relying on user-driven ipsilateral control methods for assistive or rehabilitative devices for stroke.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge