Karmele Lopez-de-Ipiña
Analysis of Disfluencies for automatic detection of Mild Cognitive Impartment: a deep learning approach
Mar 22, 2022
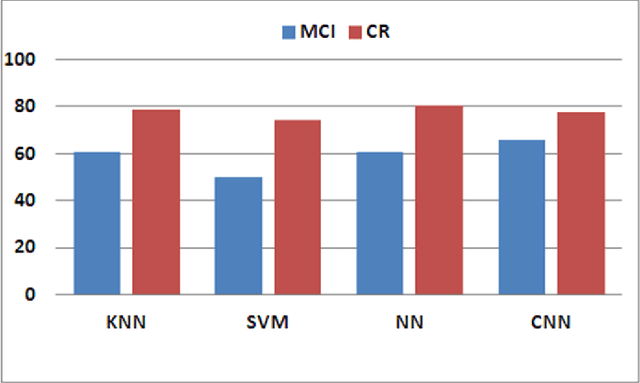
Abstract:The so-called Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or cognitive loss appears in a previous stage before Alzheimer's Disease (AD), but it does not seem sufficiently severe to interfere in independent abilities of daily life, so it usually does not receive an appropriate diagnosis. Its detection is a challenging issue to be addressed by medical specialists. This work presents a novel proposal based on automatic analysis of speech and disfluencies aimed at supporting MCI diagnosis. The approach includes deep learning by means of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and non-linear multifeature modelling. Moreover, to select the most relevant features non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-testt and Support Vector Machine Attribute (SVM) evaluation are used.
* 5 pages, published in 2017 International Conference and Workshop on Bioinspired Intelligence (IWOBI), 2017, pp. 1-4, 10-12 July Funchal (Portugal)
Assessing Progress of Parkinson s Disease Using Acoustic Analysis of Phonation
Mar 17, 2022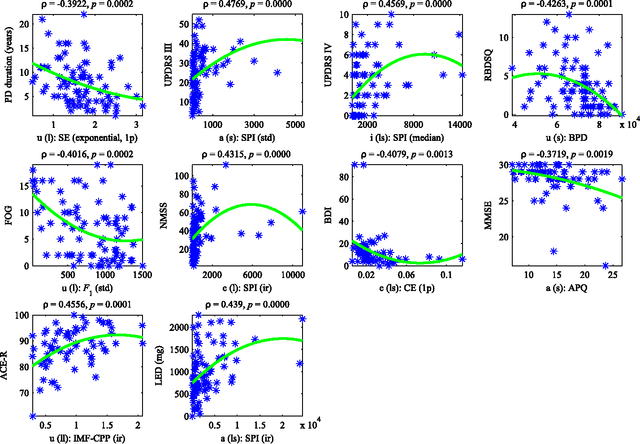
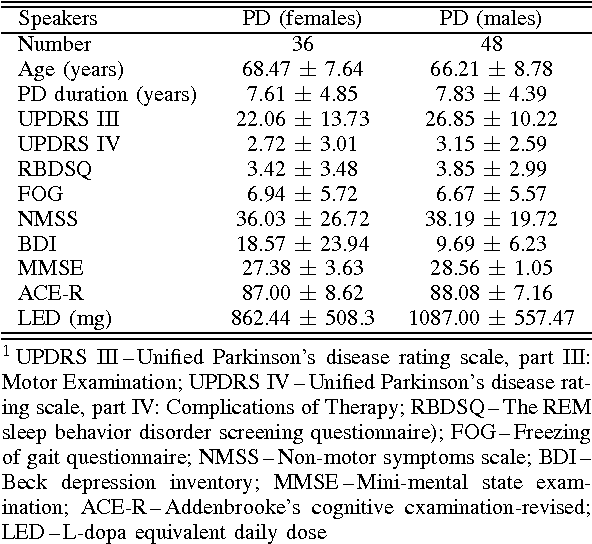
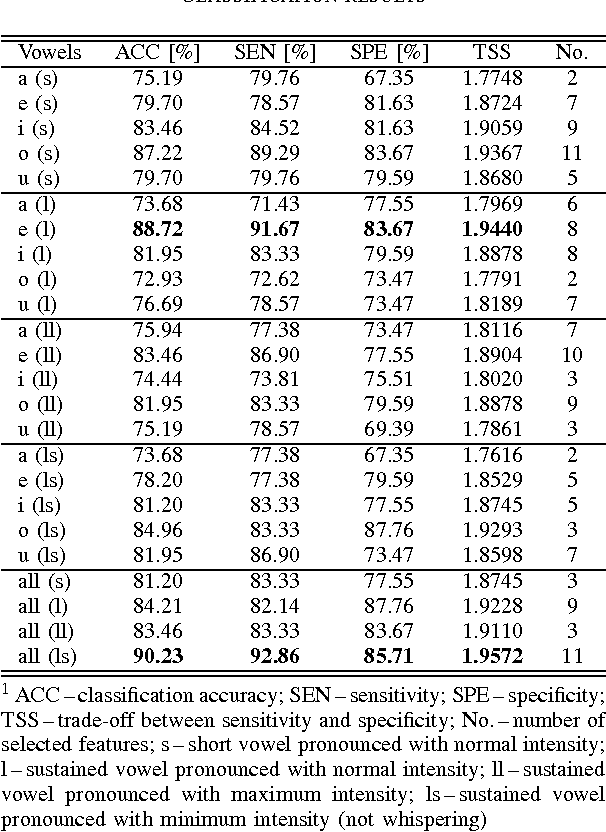
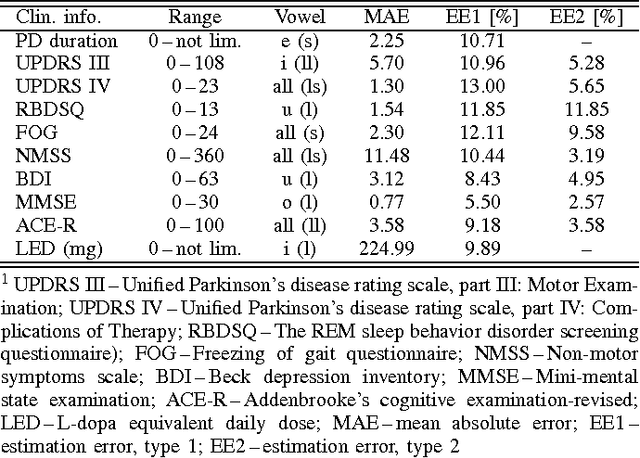
Abstract:This paper deals with a complex acoustic analysis of phonation in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) with a special focus on estimation of disease progress that is described by 7 different clinical scales ,e. g. Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale or Beck depression inventory. The analysis is based on parametrization of 5 Czech vowels pronounced by 84 PD patients. Using classification and regression trees we estimated all clinical scores with maximal error lower or equal to 13 %. Best estimation was observed in the case of Mini-mental state examination (MAE = 0.77, estimation error 5.50 %. Finally, we proposed a binary classification based on random forests that is able to identify Parkinson's disease with sensitivity SEN = 92.86 % (SPE = 85.71 %). The parametrization process was based on extraction of 107 speech features quantifying different clinical signs of hypokinetic dysarthria present in PD.
* 8 pages published in the 4th IEEE IWOBI 2015, pp. 115-122, 10-12 June, 2015 Donostia-San Sebastian. ISBN: 978-84-606-8733-7
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge