Pilar Calvo
Analysis of Disfluencies for automatic detection of Mild Cognitive Impartment: a deep learning approach
Mar 22, 2022
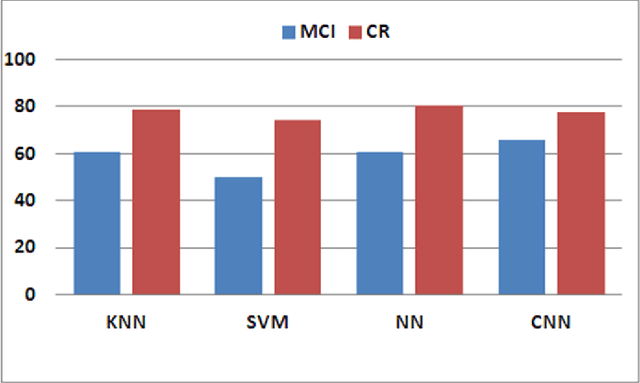
Abstract:The so-called Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or cognitive loss appears in a previous stage before Alzheimer's Disease (AD), but it does not seem sufficiently severe to interfere in independent abilities of daily life, so it usually does not receive an appropriate diagnosis. Its detection is a challenging issue to be addressed by medical specialists. This work presents a novel proposal based on automatic analysis of speech and disfluencies aimed at supporting MCI diagnosis. The approach includes deep learning by means of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and non-linear multifeature modelling. Moreover, to select the most relevant features non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-testt and Support Vector Machine Attribute (SVM) evaluation are used.
* 5 pages, published in 2017 International Conference and Workshop on Bioinspired Intelligence (IWOBI), 2017, pp. 1-4, 10-12 July Funchal (Portugal)
Multi-class versus One-class classifier in spontaneous speech analysis oriented to Alzheimer Disease diagnosis
Mar 21, 2022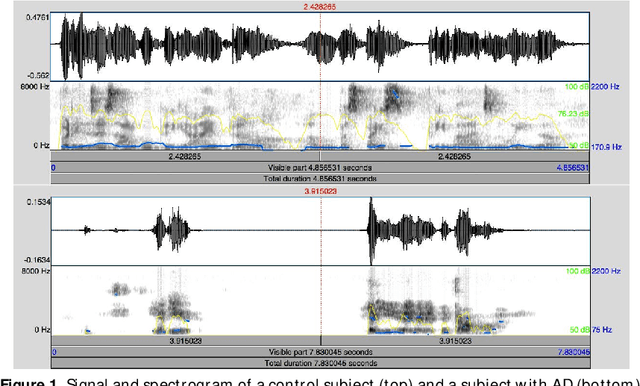
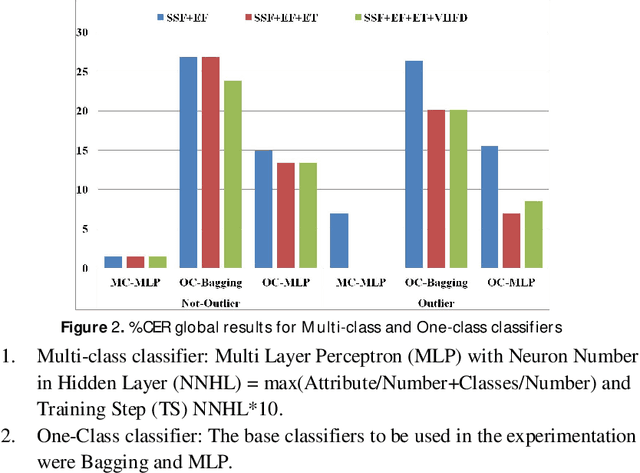
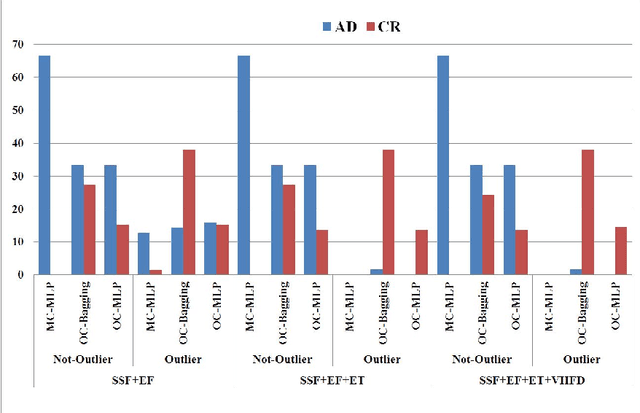
Abstract:Most of medical developments require the ability to identify samples that are anomalous with respect to a target group or control group, in the sense they could belong to a new, previously unseen class or are not class data. In this case when there are not enough data to train two-class One-class classification appear like an available solution. On the other hand non-linear approaches could give very useful information. The aim of our project is to contribute to earlier diagnosis of AD and better estimates of its severity by using automatic analysis performed through new biomarkers extracted from speech signal. The methods selected in this case are speech biomarkers oriented to Spontaneous Speech and Emotional Response Analysis. In this approach One-class classifiers and two-class classifiers are analyzed. The use of information about outlier and Fractal Dimension features improves the system performance.
* 10 pages, published in International Conference on NONLINEAR SPEECH PROCESSING, NOLISP 2015 jointly organized with the 25th Italian Workshop on Neural Networks, WIRN 2015, held at May 2015, Vietri sul Mare, Salerno, Italy
Selection of entropy based features for the analysis of the Archimedes' spiral applied to essential tremor
Mar 18, 2022


Abstract:Biomedical systems are regulated by interacting mechanisms that operate across multiple spatial and temporal scales and produce biosignals with linear and non-linear information inside. In this sense entropy could provide a useful measure about disorder in the system, lack of information in time-series and/or irregularity of the signals. Essential tremor (ET) is the most common movement disorder, being 20 times more common than Parkinson's disease, and 50-70% of this disease cases are estimated to be genetic in origin. Archimedes spiral drawing is one of the most used standard tests for clinical diagnosis. This work, on selection of nonlinear biomarkers from drawings and handwriting, is part of a wide-ranging cross study for the diagnosis of essential tremor in BioDonostia Health Institute. Several entropy algorithms are used to generate nonlinear feayures. The automatic analysis system consists of several Machine Learning paradigms.
* 5 pages, published in 2015 4th International Work Conference on Bioinspired Intelligence ,IWOBI, 2015, pp. 157-162
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge