Jordi Sole-Casals
Selection of entropy based features for the analysis of the Archimedes' spiral applied to essential tremor
Mar 18, 2022


Abstract:Biomedical systems are regulated by interacting mechanisms that operate across multiple spatial and temporal scales and produce biosignals with linear and non-linear information inside. In this sense entropy could provide a useful measure about disorder in the system, lack of information in time-series and/or irregularity of the signals. Essential tremor (ET) is the most common movement disorder, being 20 times more common than Parkinson's disease, and 50-70% of this disease cases are estimated to be genetic in origin. Archimedes spiral drawing is one of the most used standard tests for clinical diagnosis. This work, on selection of nonlinear biomarkers from drawings and handwriting, is part of a wide-ranging cross study for the diagnosis of essential tremor in BioDonostia Health Institute. Several entropy algorithms are used to generate nonlinear feayures. The automatic analysis system consists of several Machine Learning paradigms.
* 5 pages, published in 2015 4th International Work Conference on Bioinspired Intelligence ,IWOBI, 2015, pp. 157-162
HAIDA: Biometric technological therapy tools for neurorehabilitation of Cognitive Impairment
Mar 09, 2022
Abstract:Dementia, and specially Alzheimer s disease (AD) and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) are one of the most important diseases suffered by elderly population. Music therapy is one of the most widely used non-pharmacological treatment in the field of cognitive impairments, given that music influences their mood, behavior, the decrease of anxiety, as well as facilitating reminiscence, emotional expressions and movement. In this work we present HAIDA, a multi-platform support system for Musical Therapy oriented to cognitive impairment, which includes not only therapy tools but also non-invasive biometric analysis, speech, activity and hand activity. At this moment the system is on use and recording the first sets of data.
* 2 pages
Speaker recognition improvement using blind inversion of distortions
Feb 23, 2022



Abstract:In this paper we propose the inversion of nonlinear distortions in order to improve the recognition rates of a speaker recognizer system. We study the effect of saturations on the test signals, trying to take into account real situations where the training material has been recorded in a controlled situation but the testing signals present some mismatch with the input signal level (saturations). The experimental results shows that a combination of data fusion with and without nonlinear distortion compensation can improve the recognition rates with saturated test sentences from 80% to 88.57%, while the results with clean speech (without saturation) is 87.76% for one microphone.
* 4 pages
Brain-Computer Interface with Corrupted EEG Data: A Tensor Completion Approach
Jul 26, 2018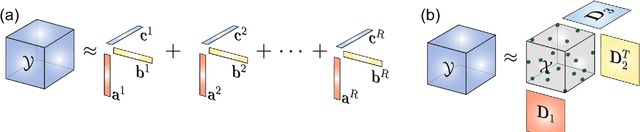

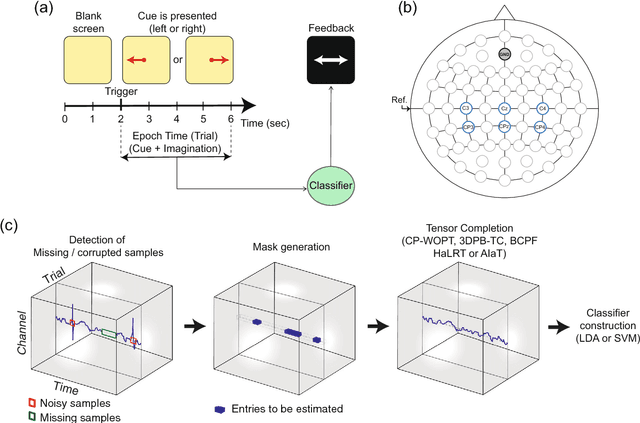
Abstract:One of the current issues in Brain-Computer Interface is how to deal with noisy Electroencephalography measurements organized as multidimensional datasets. On the other hand, recently, significant advances have been made in multidimensional signal completion algorithms that exploit tensor decomposition models to capture the intricate relationship among entries in a multidimensional signal. We propose to use tensor completion applied to EEG data for improving the classification performance in a motor imagery BCI system with corrupted measurements. Noisy measurements are considered as unknowns that are inferred from a tensor decomposition model. We evaluate the performance of four recently proposed tensor completion algorithms plus a simple interpolation strategy, first with random missing entries and then with missing samples constrained to have a specific structure (random missing channels), which is a more realistic assumption in BCI Applications. We measured the ability of these algorithms to reconstruct the tensor from observed data. Then, we tested the classification accuracy of imagined movement in a BCI experiment with missing samples. We show that for random missing entries, all tensor completion algorithms can recover missing samples increasing the classification performance compared to a simple interpolation approach. For the random missing channels case, we show that tensor completion algorithms help to reconstruct missing channels, significantly improving the accuracy in the classification of motor imagery, however, not at the same level as clean data. Tensor completion algorithms are useful in real BCI applications. The proposed strategy could allow using motor imagery BCI systems even when EEG data is highly affected by missing channels and/or samples, avoiding the need of new acquisitions in the calibration stage.
* 21 pages, 3 tables, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge