Zdenek Mzourek
Perceptual Features as Markers of Parkinson's Disease: The Issue of Clinical Interpretability
Mar 21, 2022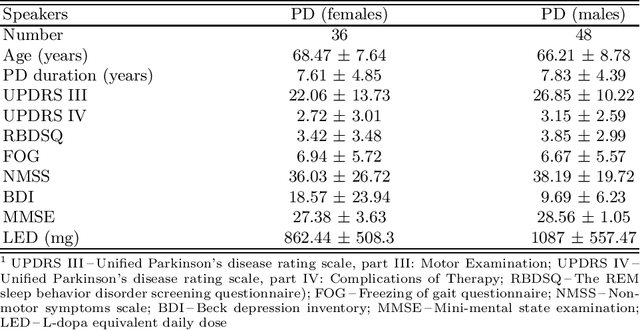
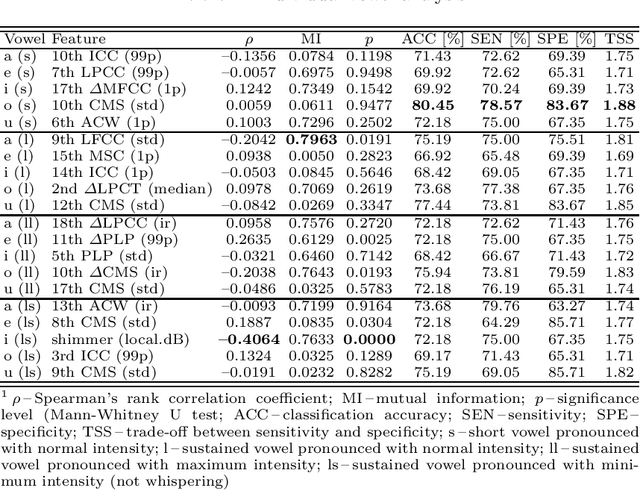
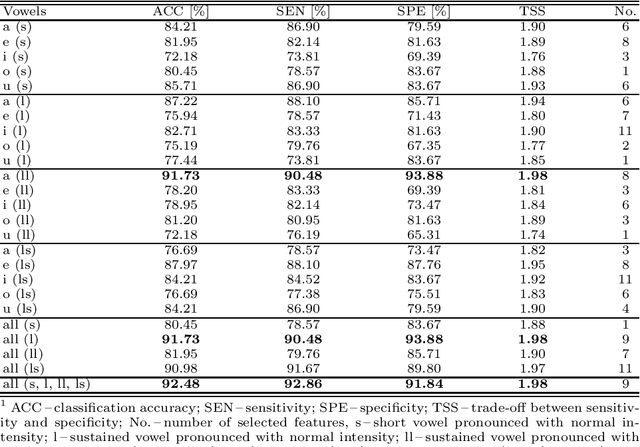

Abstract:Up to 90% of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) suffer from hypokinetic dysathria (HD) which is also manifested in the field of phonation. Clinical signs of HD like monoloudness, monopitch or hoarse voice are usually quantified by conventional clinical interpretable features (jitter, shimmer, harmonic-to-noise ratio, etc.). This paper provides large and robust insight into perceptual analysis of 5 Czech vowels of 84 PD patients and proves that despite the clinical inexplicability the perceptual features outperform the conventional ones, especially in terms of discrimination power (classification accuracy ACC = 92 %, sensitivity SEN = 93 %, specificity SPE = 92 %) and partial correlation with clinical scores like UPDRS (Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale), MMSE (Mini-mental state examination) or FOG (Freezing of gait questionnaire), where p < 0.0001.
* 8 pages, published in International Conference on NONLINEAR SPEECH PROCESSING, NOLISP 2015 jointly organized with the 25th Italian Workshop on Neural Networks, WIRN 2015, held at May 2015, Vietri sul Mare, Salerno, Italy
Assessing Progress of Parkinson s Disease Using Acoustic Analysis of Phonation
Mar 17, 2022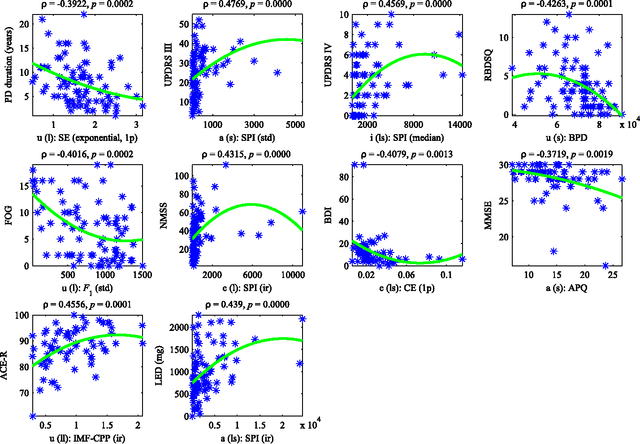
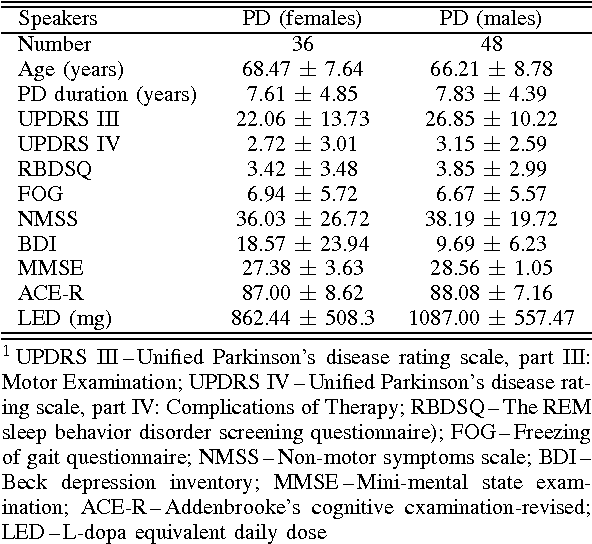
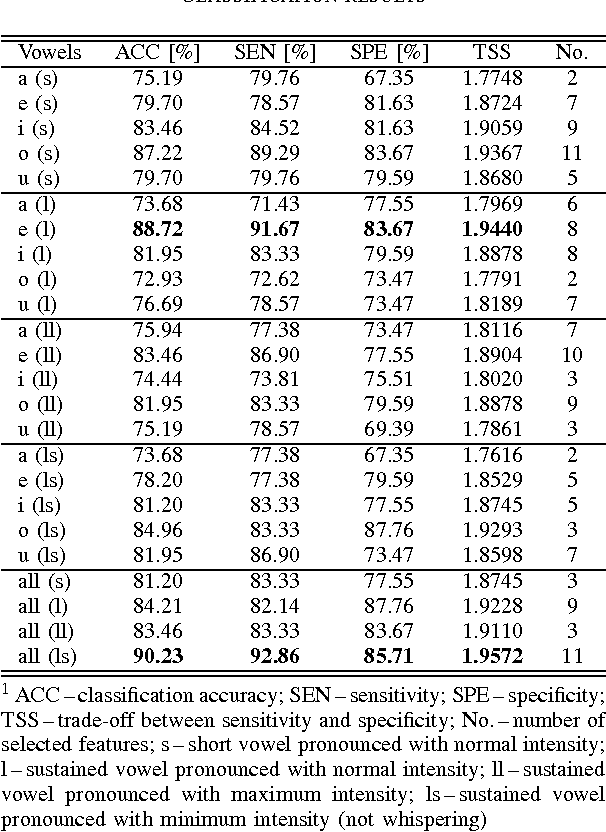
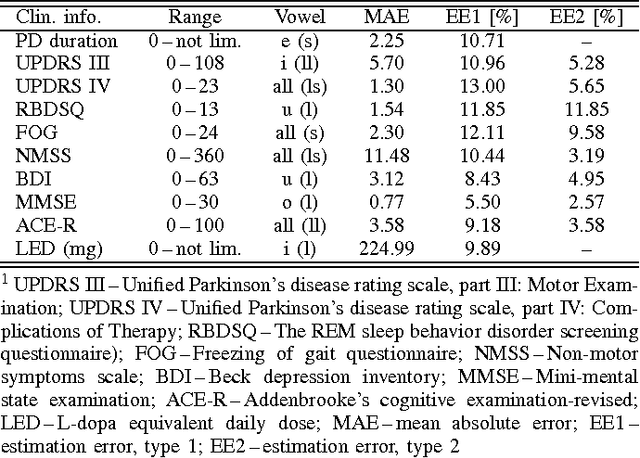
Abstract:This paper deals with a complex acoustic analysis of phonation in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) with a special focus on estimation of disease progress that is described by 7 different clinical scales ,e. g. Unified Parkinson's disease rating scale or Beck depression inventory. The analysis is based on parametrization of 5 Czech vowels pronounced by 84 PD patients. Using classification and regression trees we estimated all clinical scores with maximal error lower or equal to 13 %. Best estimation was observed in the case of Mini-mental state examination (MAE = 0.77, estimation error 5.50 %. Finally, we proposed a binary classification based on random forests that is able to identify Parkinson's disease with sensitivity SEN = 92.86 % (SPE = 85.71 %). The parametrization process was based on extraction of 107 speech features quantifying different clinical signs of hypokinetic dysarthria present in PD.
* 8 pages published in the 4th IEEE IWOBI 2015, pp. 115-122, 10-12 June, 2015 Donostia-San Sebastian. ISBN: 978-84-606-8733-7
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge