Karim Kadry
CardioComposer: Flexible and Compositional Anatomical Structure Generation with Disentangled Geometric Guidance
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Generative models of 3D anatomy, when integrated with biophysical simulators, enable the study of structure-function relationships for clinical research and medical device design. However, current models face a trade-off between controllability and anatomical realism. We propose a programmable and compositional framework for guiding unconditional diffusion models of human anatomy using interpretable ellipsoidal primitives embedded in 3D space. Our method involves the selection of certain tissues within multi-tissue segmentation maps, upon which we apply geometric moment losses to guide the reverse diffusion process. This framework supports the independent control over size, shape, and position, as well as the composition of multi-component constraints during inference.
A Diffusion Model for Simulation Ready Coronary Anatomy with Morpho-skeletal Control
Jul 23, 2024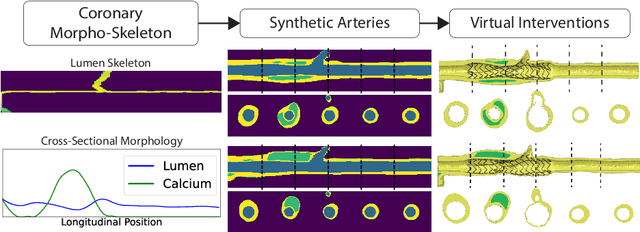
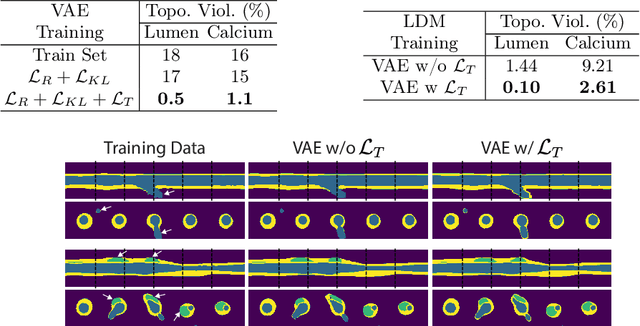
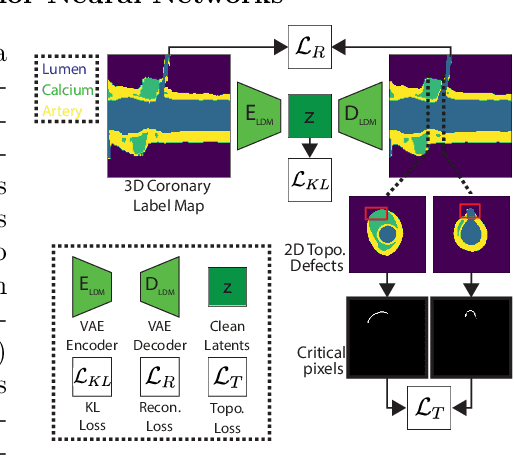
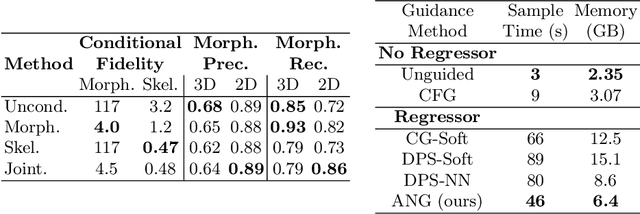
Abstract:Virtual interventions enable the physics-based simulation of device deployment within coronary arteries. This framework allows for counterfactual reasoning by deploying the same device in different arterial anatomies. However, current methods to create such counterfactual arteries face a trade-off between controllability and realism. In this study, we investigate how Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) can custom synthesize coronary anatomy for virtual intervention studies based on mid-level anatomic constraints such as topological validity, local morphological shape, and global skeletal structure. We also extend diffusion model guidance strategies to the context of morpho-skeletal conditioning and propose a novel guidance method for continuous attributes that adaptively updates the negative guiding condition throughout sampling. Our framework enables the generation and editing of coronary anatomy in a controllable manner, allowing device designers to derive mechanistic insights regarding anatomic variation and simulated device deployment.
Probing the Limits and Capabilities of Diffusion Models for the Anatomic Editing of Digital Twins
Dec 30, 2023Abstract:Numerical simulations can model the physical processes that govern cardiovascular device deployment. When such simulations incorporate digital twins; computational models of patient-specific anatomy, they can expedite and de-risk the device design process. Nonetheless, the exclusive use of patient-specific data constrains the anatomic variability which can be precisely or fully explored. In this study, we investigate the capacity of Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) to edit digital twins to create anatomic variants, which we term digital siblings. Digital twins and their corresponding siblings can serve as the basis for comparative simulations, enabling the study of how subtle anatomic variations impact the simulated deployment of cardiovascular devices, as well as the augmentation of virtual cohorts for device assessment. However, while diffusion models have been characterized in their ability to edit natural images, their capacity to anatomically edit digital twins has yet to be studied. Using a case example centered on 3D digital twins of cardiac anatomy, we implement various methods for generating digital siblings and characterize them through morphological and topological analyses. We specifically edit digital twins to introduce anatomic variation at different spatial scales and within localized regions, demonstrating the existence of bias towards common anatomic features. We further show that such anatomic bias can be leveraged for virtual cohort augmentation through selective editing, partially alleviating issues related to dataset imbalance and lack of diversity. Our experimental framework thus delineates the limits and capabilities of using latent diffusion models in synthesizing anatomic variation for in silico trials.
Morphology-based non-rigid registration of coronary computed tomography and intravascular images through virtual catheter path optimization
Dec 30, 2022



Abstract:Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) provides information on the presence, extent, and severity of obstructive coronary artery disease. Large-scale clinical studies analyzing CCTA-derived metrics typically require ground-truth validation in the form of high-fidelity 3D intravascular imaging. However, manual rigid alignment of intravascular images to corresponding CCTA images is both time consuming and user-dependent. Moreover, intravascular modalities suffer from several non-rigid motion-induced distortions arising from distortions in the imaging catheter path. To address these issues, we here present a semi-automatic segmentation-based framework for both rigid and non-rigid matching of intravascular images to CCTA images. We formulate the problem in terms of finding the optimal \emph{virtual catheter path} that samples the CCTA data to recapitulate the coronary artery morphology found in the intravascular image. We validate our co-registration framework on a cohort of $n=40$ patients using bifurcation landmarks as ground truth for longitudinal and rotational registration. Our results indicate that our non-rigid registration significantly outperforms other co-registration approaches for luminal bifurcation alignment in both longitudinal (mean mismatch: 3.3 frames) and rotational directions (mean mismatch: 28.6 degrees). By providing a differentiable framework for automatic multi-modal intravascular data fusion, our developed co-registration modules significantly reduces the manual effort required to conduct large-scale multi-modal clinical studies while also providing a solid foundation for the development of machine learning-based co-registration approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge