Kamiar Alaei
Development of Interactive Nomograms for Predicting Short-Term Survival in ICU Patients with Aplastic Anemia
May 23, 2025Abstract:Aplastic anemia is a rare, life-threatening hematologic disorder characterized by pancytopenia and bone marrow failure. ICU admission in these patients often signals critical complications or disease progression, making early risk assessment crucial for clinical decision-making and resource allocation. In this study, we used the MIMIC-IV database to identify ICU patients diagnosed with aplastic anemia and extracted clinical features from five domains: demographics, synthetic indicators, laboratory results, comorbidities, and medications. Over 400 variables were reduced to seven key predictors through machine learning-based feature selection. Logistic regression and Cox regression models were constructed to predict 7-, 14-, and 28-day mortality, and their performance was evaluated using AUROC. External validation was conducted using the eICU Collaborative Research Database to assess model generalizability. Among 1,662 included patients, the logistic regression model demonstrated superior performance, with AUROC values of 0.8227, 0.8311, and 0.8298 for 7-, 14-, and 28-day mortality, respectively, compared to the Cox model. External validation yielded AUROCs of 0.7391, 0.7119, and 0.7093. Interactive nomograms were developed based on the logistic regression model to visually estimate individual patient risk. In conclusion, we identified a concise set of seven predictors, led by APS III, to build validated and generalizable nomograms that accurately estimate short-term mortality in ICU patients with aplastic anemia. These tools may aid clinicians in personalized risk stratification and decision-making at the point of care.
Machine Learning-Based Model for Postoperative Stroke Prediction in Coronary Artery Disease
Mar 15, 2025


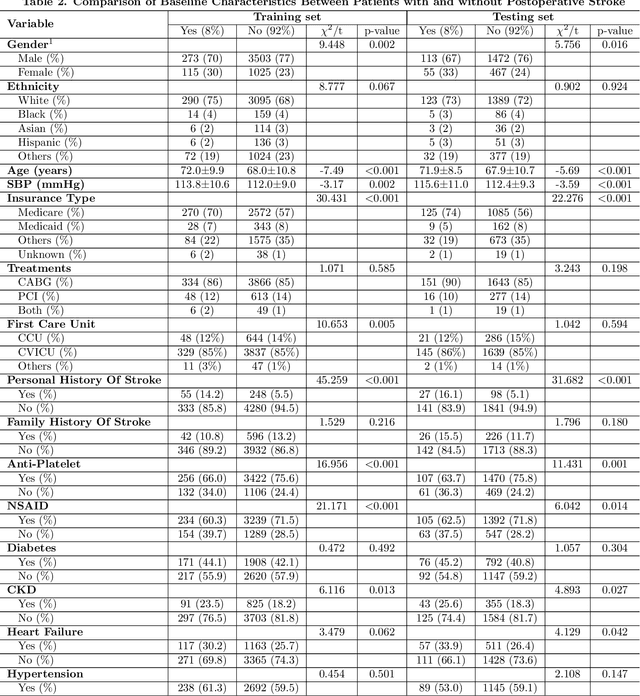
Abstract:Coronary artery disease remains one of the leading causes of mortality globally. Despite advances in revascularization treatments like PCI and CABG, postoperative stroke is inevitable. This study aims to develop and evaluate a sophisticated machine learning prediction model to assess postoperative stroke risk in coronary revascularization patients.This research employed data from the MIMIC-IV database, consisting of a cohort of 7023 individuals. Study data included clinical, laboratory, and comorbidity variables. To reduce multicollinearity, variables with over 30% missing values and features with a correlation coefficient larger than 0.9 were deleted. The dataset has 70% training and 30% test. The Random Forest technique interpolated residual dataset missing values. Numerical values were normalized, whereas categorical variables were one-hot encoded. LASSO regularization selected features, and grid search found model hyperparameters. Finally, Logistic Regression, XGBoost, SVM, and CatBoost were employed for predictive modeling, and SHAP analysis assessed stroke risk for each variable. AUC of 0.855 (0.829-0.878) showed that SVM model outperformed logistic regression and CatBoost models in prior research. SHAP research showed that the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure are significant prognostic factors for postoperative stroke. This study shows that improved machine learning reduces overfitting and improves model predictive accuracy. Models using the CCI alone cannot predict postoperative stroke risk as accurately as those using independent comorbidity variables. The suggested technique provides a more thorough and individualized risk assessment by encompassing a wider range of clinically relevant characteristics, making it a better reference for preoperative risk assessments and targeted intervention.
XGBoost-Based Prediction of ICU Mortality in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Patients Using MIMIC-IV Database with Validation from eICU Database
Feb 25, 2025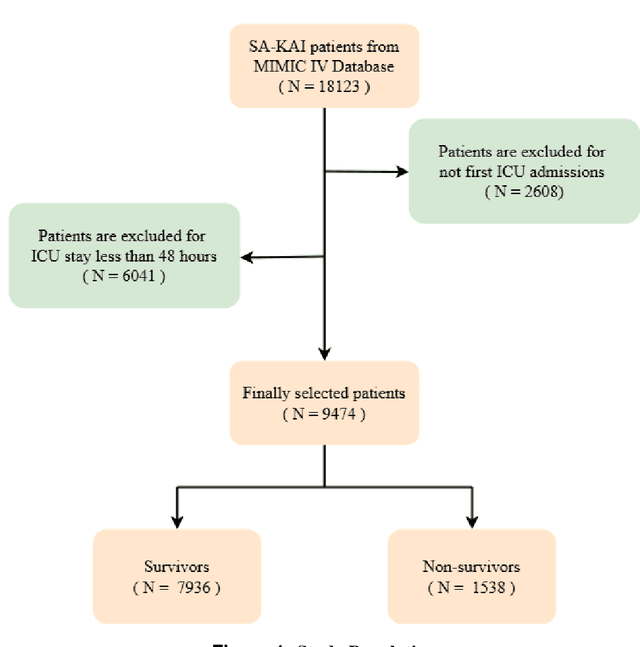
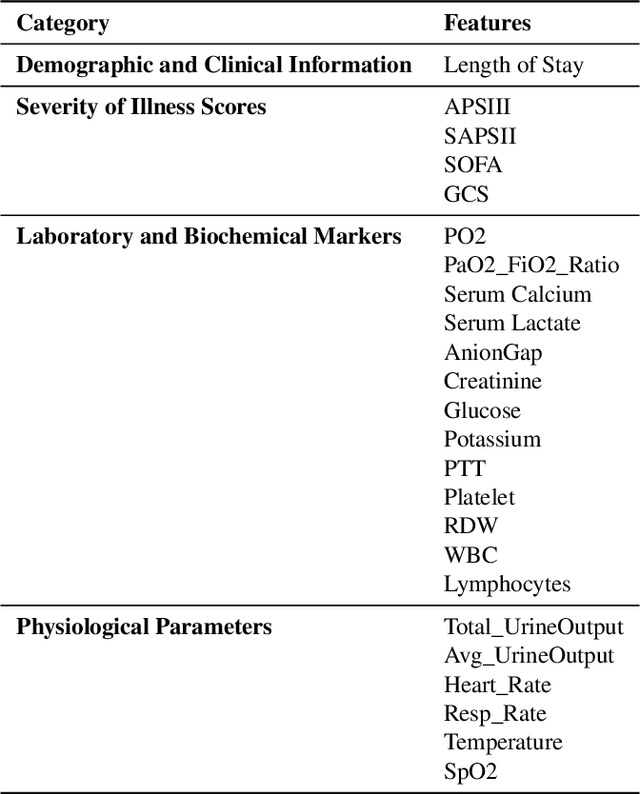
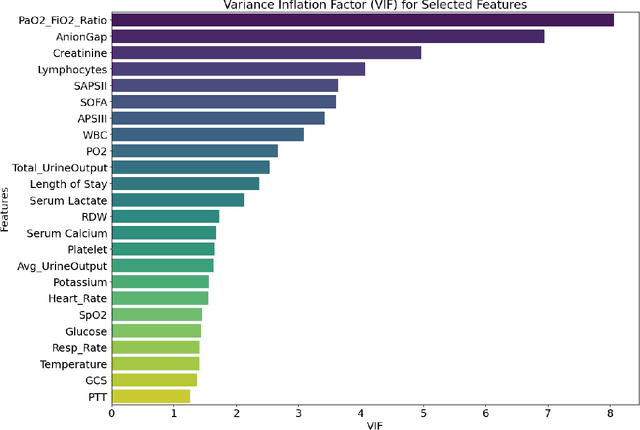
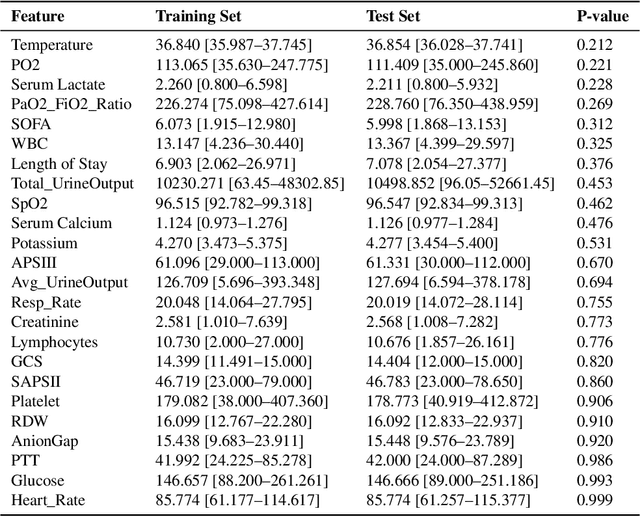
Abstract:Background: Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury (SA-AKI) leads to high mortality in intensive care. This study develops machine learning models using the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care IV (MIMIC-IV) database to predict Intensive Care Unit (ICU) mortality in SA-AKI patients. External validation is conducted using the eICU Collaborative Research Database. Methods: For 9,474 identified SA-AKI patients in MIMIC-IV, key features like lab results, vital signs, and comorbidities were selected using Variance Inflation Factor (VIF), Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE), and expert input, narrowing to 24 predictive variables. An Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model was built for in-hospital mortality prediction, with hyperparameters optimized using GridSearch. Model interpretability was enhanced with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME). External validation was conducted using the eICU database. Results: The proposed XGBoost model achieved an internal Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.878 (95% Confidence Interval: 0.859-0.897). SHAP identified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), serum lactate, and respiratory rate as key mortality predictors. LIME highlighted serum lactate, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, total urine output, and serum calcium as critical features. Conclusions: The integration of advanced techniques with the XGBoost algorithm yielded a highly accurate and interpretable model for predicting SA-AKI mortality across diverse populations. It supports early identification of high-risk patients, enhancing clinical decision-making in intensive care. Future work needs to focus on enhancing adaptability, versatility, and real-world applications.
A Novel Multi-Task Teacher-Student Architecture with Self-Supervised Pretraining for 48-Hour Vasoactive-Inotropic Trend Analysis in Sepsis Mortality Prediction
Feb 24, 2025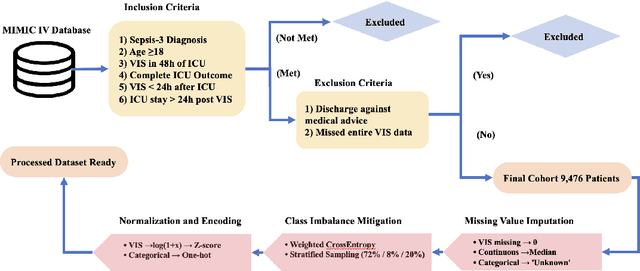
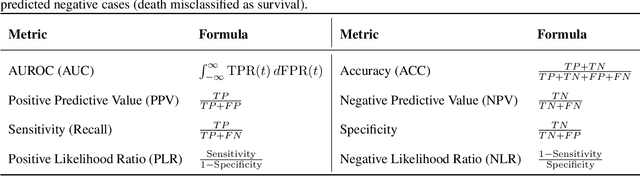
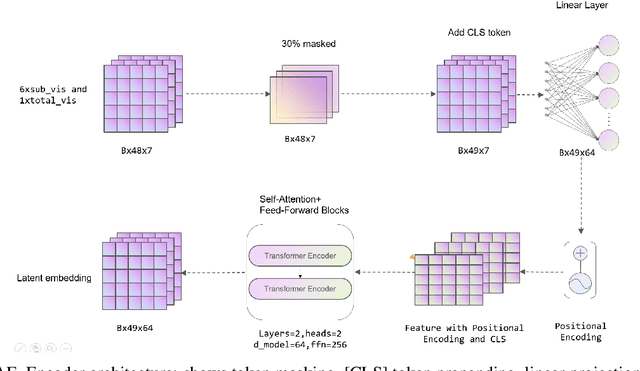
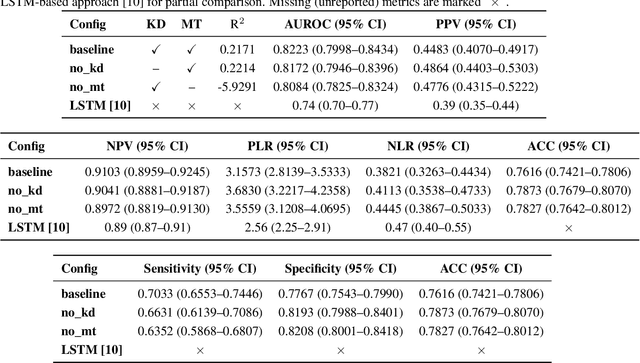
Abstract:Sepsis is a major cause of ICU mortality, where early recognition and effective interventions are essential for improving patient outcomes. However, the vasoactive-inotropic score (VIS) varies dynamically with a patient's hemodynamic status, complicated by irregular medication patterns, missing data, and confounders, making sepsis prediction challenging. To address this, we propose a novel Teacher-Student multitask framework with self-supervised VIS pretraining via a Masked Autoencoder (MAE). The teacher model performs mortality classification and severity-score regression, while the student distills robust time-series representations, enhancing adaptation to heterogeneous VIS data. Compared to LSTM-based methods, our approach achieves an AUROC of 0.82 on MIMIC-IV 3.0 (9,476 patients), outperforming the baseline (0.74). SHAP analysis revealed that SOFA score (0.147) had the greatest impact on ICU mortality, followed by LODS (0.033), single marital status (0.031), and Medicaid insurance (0.023), highlighting the role of sociodemographic factors. SAPSII (0.020) also contributed significantly. These findings suggest that both clinical and social factors should be considered in ICU decision-making. Our novel multitask and distillation strategies enable earlier identification of high-risk patients, improving prediction accuracy and disease management, offering new tools for ICU decision support.
Machine Learning-Based Prediction of ICU Readmissions in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Patients: Insights from the MIMIC Databases
Jan 02, 2025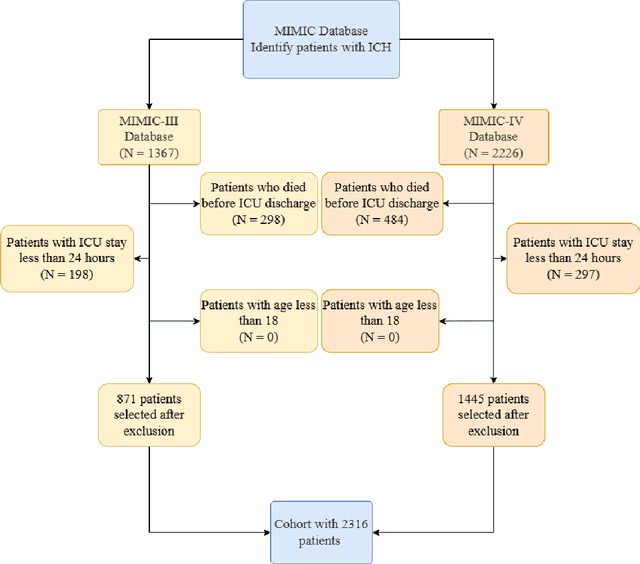
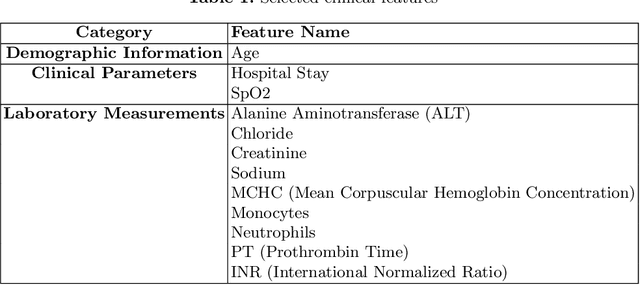
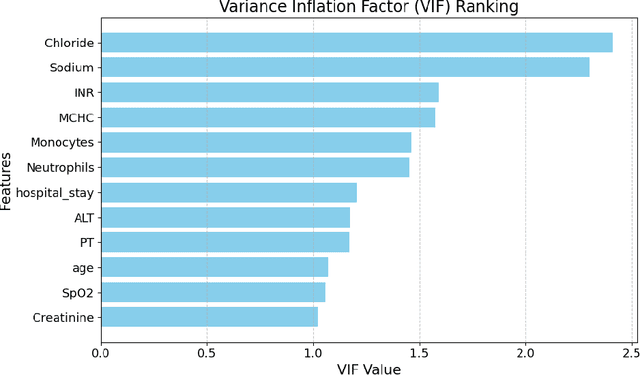
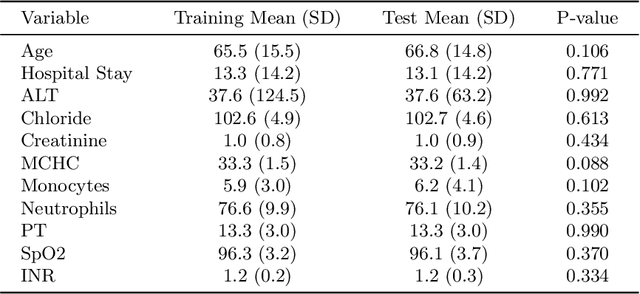
Abstract:Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a life-risking condition characterized by bleeding within the brain parenchyma. ICU readmission in ICH patients is a critical outcome, reflecting both clinical severity and resource utilization. Accurate prediction of ICU readmission risk is crucial for guiding clinical decision-making and optimizing healthcare resources. This study utilized the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV) databases, which contain comprehensive clinical and demographic data on ICU patients. Patients with ICH were identified from both databases. Various clinical, laboratory, and demographic features were extracted for analysis based on both overview literature and experts' opinions. Preprocessing methods like imputing and sampling were applied to improve the performance of our models. Machine learning techniques, such as Artificial Neural Network (ANN), XGBoost, and Random Forest, were employed to develop predictive models for ICU readmission risk. Model performance was evaluated using metrics such as AUROC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity. The developed models demonstrated robust predictive accuracy for ICU readmission in ICH patients, with key predictors including demographic information, clinical parameters, and laboratory measurements. Our study provides a predictive framework for ICU readmission risk in ICH patients, which can aid in clinical decision-making and improve resource allocation in intensive care settings.
Utilizing Machine Learning Models to Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Septic Patients from MIMIC-III Database
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:Sepsis is a severe condition that causes the body to respond incorrectly to an infection. This reaction can subsequently cause organ failure, a major one being acute kidney injury (AKI). For septic patients, approximately 50% develop AKI, with a mortality rate above 40%. Creating models that can accurately predict AKI based on specific qualities of septic patients is crucial for early detection and intervention. Using medical data from septic patients during intensive care unit (ICU) admission from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care 3 (MIMIC-III) database, we extracted 3301 patients with sepsis, with 73% of patients developing AKI. The data was randomly divided into a training set (n = 1980, 40%), a test set (n = 661, 10%), and a validation set (n = 660, 50%). The proposed model was logistic regression, and it was compared against five baseline models: XGBoost, K Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forest (RF), and LightGBM. Area Under the Curve (AUC), Accuracy, F1-Score, and Recall were calculated for each model. After analysis, we were able to select 23 features to include in our model, the top features being urine output, maximum bilirubin, minimum bilirubin, weight, maximum blood urea nitrogen, and minimum estimated glomerular filtration rate. The logistic regression model performed the best, achieving an AUC score of 0.887 (95% CI: [0.861-0.915]), an accuracy of 0.817, an F1 score of 0.866, a recall score of 0.827, and a Brier score of 0.13. Compared to the best existing literature in this field, our model achieved an 8.57% improvement in AUC while using 13 fewer variables, showcasing its effectiveness in determining AKI in septic patients. While the features selected for predicting AKI in septic patients are similar to previous literature, the top features that influenced our model's performance differ.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge