Kamal Singh
From GNNs to Symbolic Surrogates via Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Delay Prediction
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Accurate prediction of flow delay is essential for optimizing and managing modern communication networks. We investigate three levels of modeling for this task. First, we implement a heterogeneous GNN with attention-based message passing, establishing a strong neural baseline. Second, we propose FlowKANet in which Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks replace standard MLP layers, reducing trainable parameters while maintaining competitive predictive performance. FlowKANet integrates KAMP-Attn (Kolmogorov-Arnold Message Passing with Attention), embedding KAN operators directly into message-passing and attention computation. Finally, we distill the model into symbolic surrogate models using block-wise regression, producing closed-form equations that eliminate trainable weights while preserving graph-structured dependencies. The results show that KAN layers provide a favorable trade-off between efficiency and accuracy and that symbolic surrogates emphasize the potential for lightweight deployment and enhanced transparency.
Interpretable Reinforcement Learning for Load Balancing using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
May 20, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has been increasingly applied to network control problems, such as load balancing. However, existing RL approaches often suffer from lack of interpretability and difficulty in extracting controller equations. In this paper, we propose the use of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) for interpretable RL in network control. We employ a PPO agent with a 1-layer actor KAN model and an MLP Critic network to learn load balancing policies that maximise throughput utility, minimize loss as well as delay. Our approach allows us to extract controller equations from the learned neural networks, providing insights into the decision-making process. We evaluate our approach using different reward functions demonstrating its effectiveness in improving network performance while providing interpretable policies.
A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing Antibiotic Discovery Using Machine Learning Derived Bio-computation
Nov 08, 2024

Abstract:Traditional drug discovery is a long, expensive, and complex process. Advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are beginning to change this narrative. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of different AI and ML tools that can be used to streamline and accelerate the drug discovery process. By using data sets to train ML algorithms, it is possible to discover drugs or drug-like compounds relatively quickly, and efficiently. Additionally, we address limitations in AI-based drug discovery and development, including the scarcity of high-quality data to train AI models and ethical considerations. The growing impact of AI on the pharmaceutical industry is also highlighted. Finally, we discuss how AI and ML can expedite the discovery of new antibiotics to combat the problem of worldwide antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Unified Capacity Results for Free-Space Optical Communication Systems Over Gamma-Gamma Atmospheric Turbulence Channels
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:In terrestrial free-space optical (FSO) communication systems, adaptive power control at the optical laser transmitters is crucial not only to prolong the life span of the laser sources, but more importantly to maintain robust and spectrally efficient communication through atmospheric turbulence. However, a comprehensive study of dynamic power adaptation in existing FSO systems is lacking in the literature. In this paper, we investigate FSO communication systems capable of adaptive laser power control with heterodyne detection (HD) and direct detection (DD) based receivers operating under shot-noise-limited conditions. Under these FSO systems considerations, we derive unified exact and asymptotic formulas for the capacities of Gamma-Gamma atmospheric turbulence channels with and without pointing errors; these novel closed-form capacity expressions are much simpler and provide new insights into the impact of varying turbulence conditions and pointing errors. Finally, the numerical results highlight the intricate relations of atmospheric fading, pointing error, and large-scale channel parameters in a typical terrestrial FSO channel setting, followed up by an accurate assessment of the key parameters determining the capacity performances of the aforementioned FSO systems revealing several interesting characteristics.
Capacity and Performance Analysis of RIS-Assisted Communication Over Rician Fading Channels
Nov 08, 2021
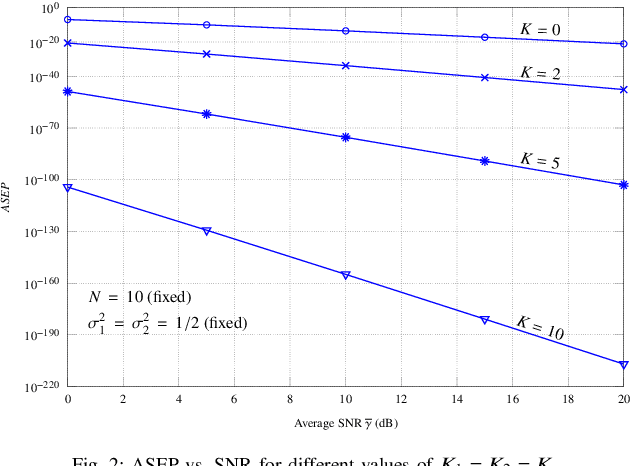
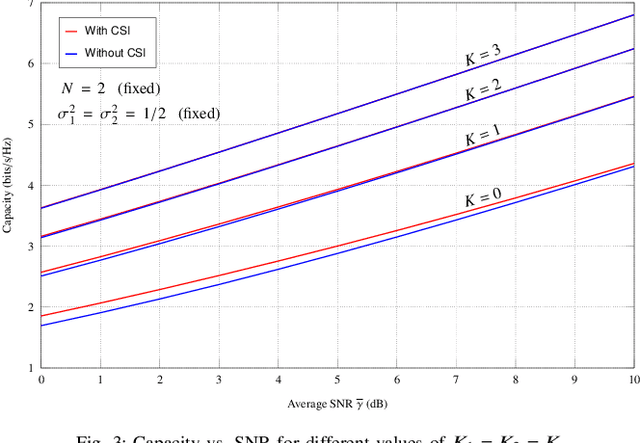
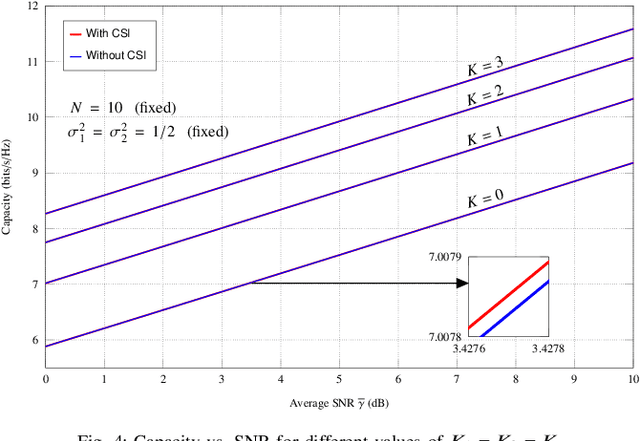
Abstract:This paper investigates two performance metrics, namely ergodic capacity and symbol error rate, of mmWave communication system assisted by a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS). We assume independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) Rician fadings between user-RIS-Access Point (AP), with RIS surface consisting of passive reflecting elements. First, we derive a new unified closed-form formula for the average symbol error probability of generalised M-QAM/M-PSK signalling over this mmWave link. We then obtain new closed-form expressions for the ergodic capacity with and without channel state information (CSI) at the AP.
Low SNR Capacity of Keyhole MIMO Channel in Nakagami-m Fading With Full CSI
Sep 07, 2021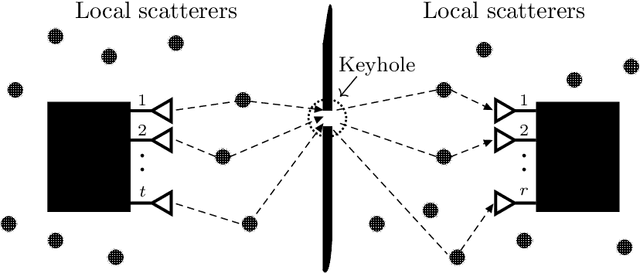
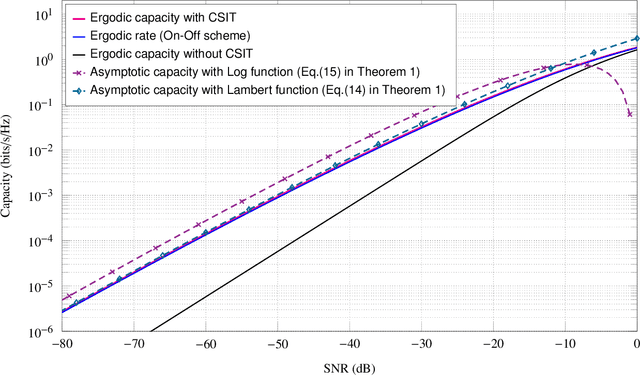
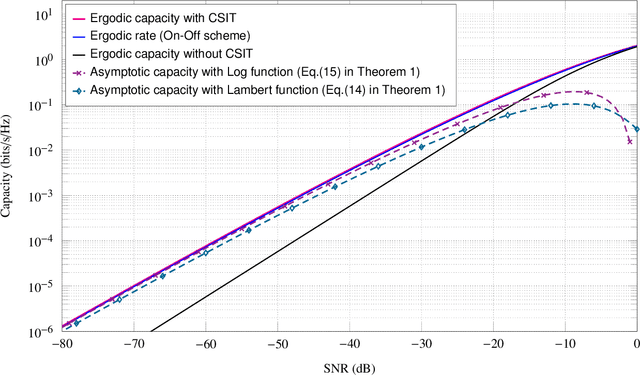
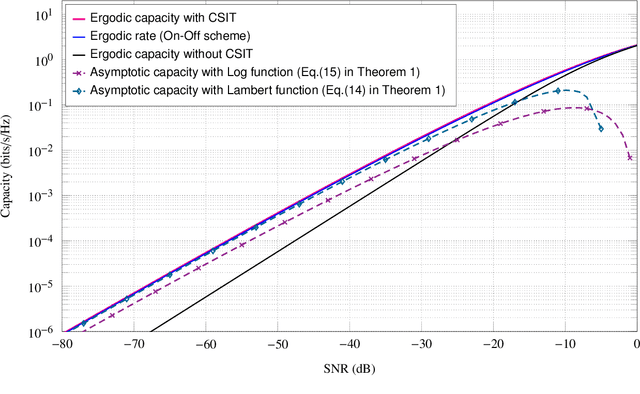
Abstract:In this paper, we derive asymptotic expressions for the ergodic capacity of the multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) keyhole channel at low SNR in independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) Nakagami-$m$ fading conditions with perfect channel state information available at both the transmitter (CSI-T) and the receiver (CSI-R). We show that the low-SNR capacity of this keyhole channel scales proportionally as $\frac{\textrm{SNR}}{4} \log^2 \left(1/{\textrm{SNR}}\right)$. Further, we develop a practically appealing On-Off transmission scheme that is aymptotically capacity achieving at low SNR; it requires only one-bit CSI-T feedback and is robust against both mild and severe Nakagami-$m$ fadings for a very wide range of low-SNR values. These results also extend to the Rayleigh keyhole MIMO channel as a special case.
Fast Beam Training for RIS-Assisted Uplink Communication
Jul 23, 2021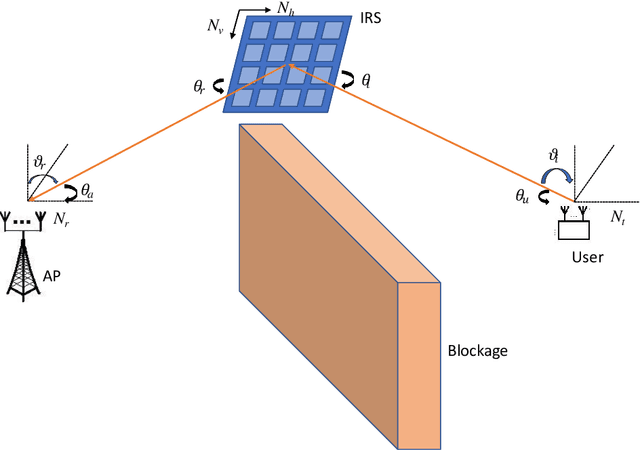
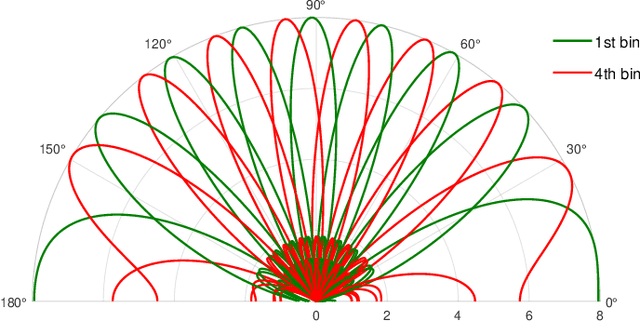
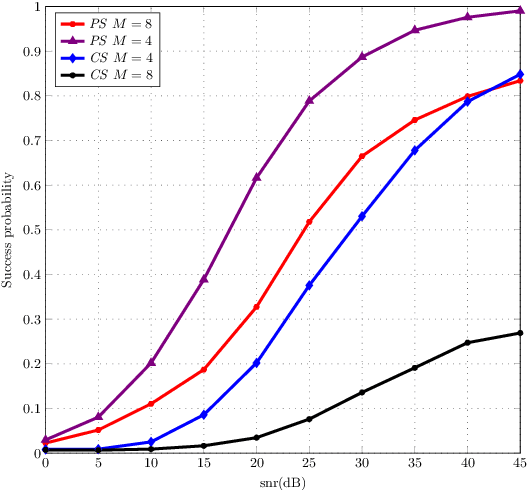
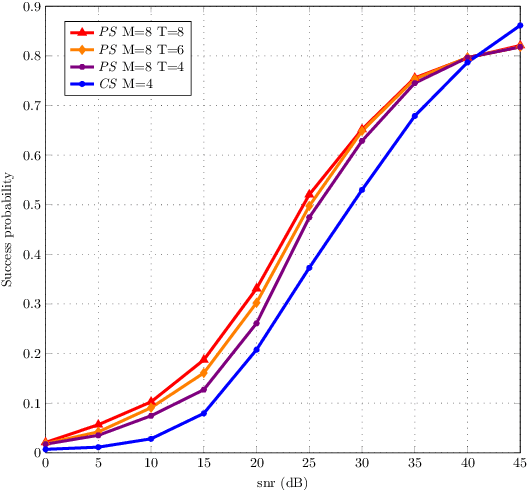
Abstract:In this work, we propose a beam training codebook for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) assisted mmWave uplink communication. Beam training procedure is important to establish a reliable link between user node and Access point (AP). A codebook based training procedure reduces the search time to obtain best possible phase shift by RIS controller to align incident beam at RIS in the direction of receiving node. We consider a semi passive RIS to assist RIS controller with a feedback of minimum overhead. It is shown that the procedure detects a mobile node with high probability in a short interval of time. Further we use the same codebook at user node to know the desired direction of communication via RIS.
Towards a Question Answering System over the Semantic Web
Mar 02, 2018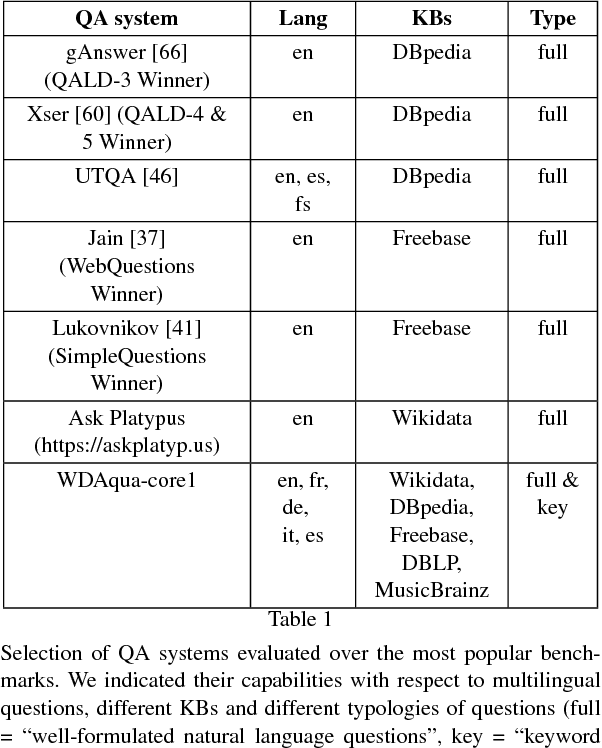
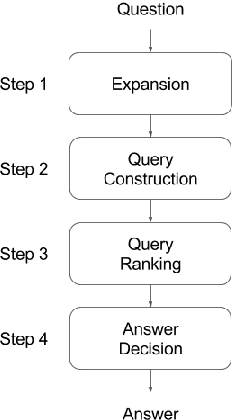
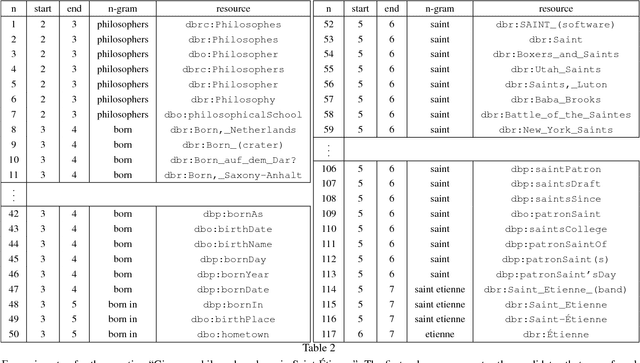
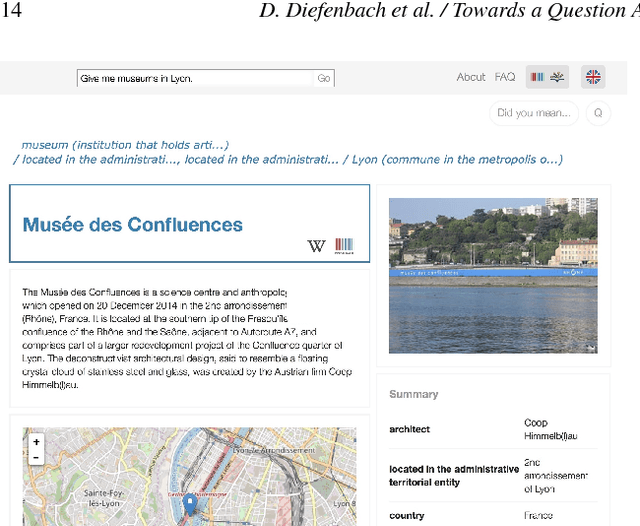
Abstract:Thanks to the development of the Semantic Web, a lot of new structured data has become available on the Web in the form of knowledge bases (KBs). Making this valuable data accessible and usable for end-users is one of the main goals of Question Answering (QA) over KBs. Most current QA systems query one KB, in one language (namely English). The existing approaches are not designed to be easily adaptable to new KBs and languages. We first introduce a new approach for translating natural language questions to SPARQL queries. It is able to query several KBs simultaneously, in different languages, and can easily be ported to other KBs and languages. In our evaluation, the impact of our approach is proven using 5 different well-known and large KBs: Wikidata, DBpedia, MusicBrainz, DBLP and Freebase as well as 5 different languages namely English, German, French, Italian and Spanish. Second, we show how we integrated our approach, to make it easily accessible by the research community and by end-users. To summarize, we provided a conceptional solution for multilingual, KB-agnostic Question Answering over the Semantic Web. The provided first approximation validates this concept.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge