Pham Tran Anh Quang
Interpretable Reinforcement Learning for Load Balancing using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
May 20, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has been increasingly applied to network control problems, such as load balancing. However, existing RL approaches often suffer from lack of interpretability and difficulty in extracting controller equations. In this paper, we propose the use of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) for interpretable RL in network control. We employ a PPO agent with a 1-layer actor KAN model and an MLP Critic network to learn load balancing policies that maximise throughput utility, minimize loss as well as delay. Our approach allows us to extract controller equations from the learned neural networks, providing insights into the decision-making process. We evaluate our approach using different reward functions demonstrating its effectiveness in improving network performance while providing interpretable policies.
Safe Load Balancing in Software-Defined-Networking
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:High performance, reliability and safety are crucial properties of any Software-Defined-Networking (SDN) system. Although the use of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms has been widely studied to improve performance, their practical applications are still limited as they fail to ensure safe operations in exploration and decision-making. To fill this gap, we explore the design of a Control Barrier Function (CBF) on top of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms for load-balancing. We show that our DRL-CBF approach is capable of meeting safety requirements during training and testing while achieving near-optimal performance in testing. We provide results using two simulators: a flow-based simulator, which is used for proof-of-concept and benchmarking, and a packet-based simulator that implements real protocols and scheduling. Thanks to the flow-based simulator, we compared the performance against the optimal policy, solving a Non Linear Programming (NLP) problem with the SCIP solver. Furthermore, we showed that pre-trained models in the flow-based simulator, which is faster, can be transferred to the packet simulator, which is slower but more accurate, with some fine-tuning. Overall, the results suggest that near-optimal Quality-of-Service (QoS) performance in terms of end-to-end delay can be achieved while safety requirements related to link capacity constraints are guaranteed. In the packet-based simulator, we also show that our DRL-CBF algorithms outperform non-RL baseline algorithms. When the models are fine-tuned over a few episodes, we achieved smoother QoS and safety in training, and similar performance in testing compared to the case where models have been trained from scratch.
Towards Safe Load Balancing based on Control Barrier Functions and Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 10, 2024Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms have recently made significant strides in improving network performance. Nonetheless, their practical use is still limited in the absence of safe exploration and safe decision-making. In the context of commercial solutions, reliable and safe-to-operate systems are of paramount importance. Taking this problem into account, we propose a safe learning-based load balancing algorithm for Software Defined-Wide Area Network (SD-WAN), which is empowered by Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) combined with a Control Barrier Function (CBF). It safely projects unsafe actions into feasible ones during both training and testing, and it guides learning towards safe policies. We successfully implemented the solution on GPU to accelerate training by approximately 110x times and achieve model updates for on-policy methods within a few seconds, making the solution practical. We show that our approach delivers near-optimal Quality-of-Service (QoS performance in terms of end-to-end delay while respecting safety requirements related to link capacity constraints. We also demonstrated that on-policy learning based on Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) performs better than off-policy learning with Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) when both are combined with a CBF for safe load balancing.
Graph Convolutional Reinforcement Learning for Collaborative Queuing Agents
May 24, 2022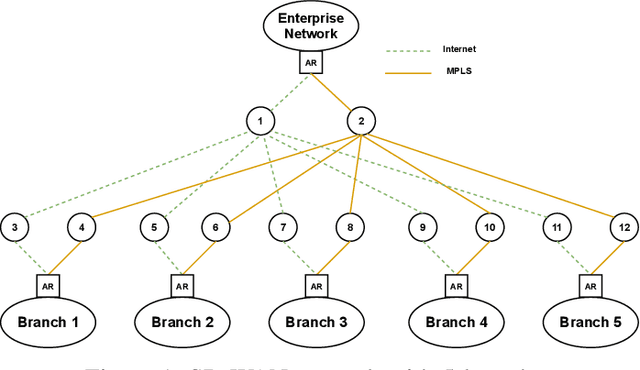
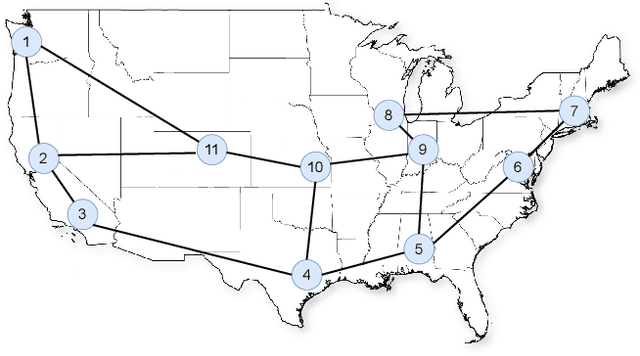
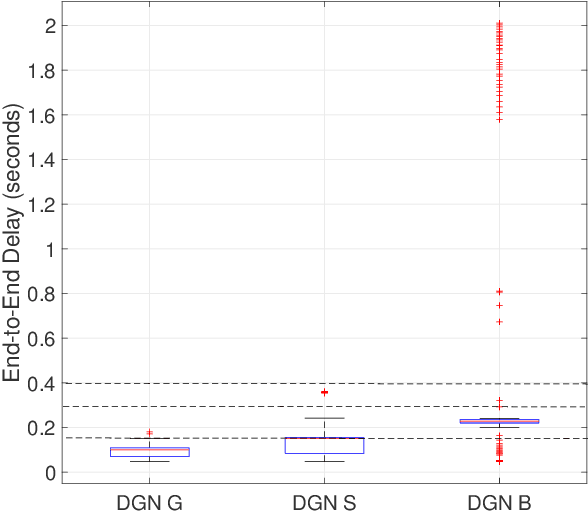
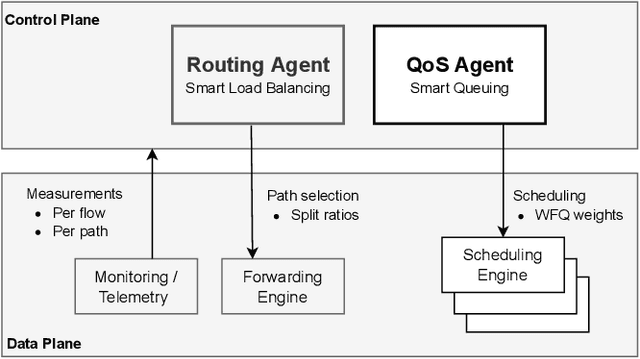
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the use of multi-agent deep learning as well as learning to cooperate principles to meet stringent service level agreements, in terms of throughput and end-to-end delay, for a set of classified network flows. We consider agents built on top of a weighted fair queuing algorithm that continuously set weights for three flow groups: gold, silver, and bronze. We rely on a novel graph-convolution based, multi-agent reinforcement learning approach known as DGN. As benchmarks, we propose centralized and distributed deep Q-network approaches and evaluate their performances in different network, traffic, and routing scenarios, highlighting the effectiveness of our proposals and the importance of agent cooperation. We show that our DGN-based approach meets stringent throughput and delay requirements across all scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge