Kai-Xin Gao
Eigenvalue-corrected Natural Gradient Based on a New Approximation
Nov 27, 2020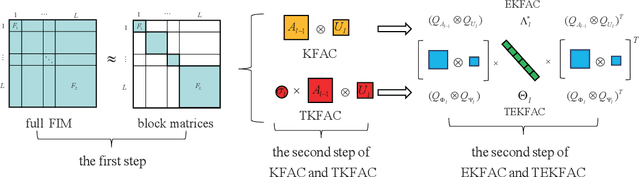
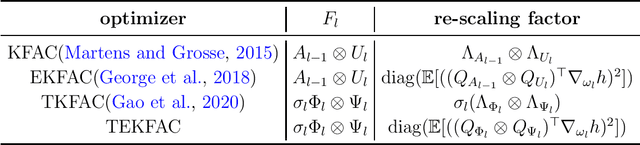
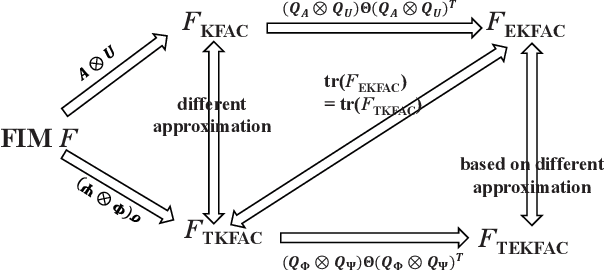
Abstract:Using second-order optimization methods for training deep neural networks (DNNs) has attracted many researchers. A recently proposed method, Eigenvalue-corrected Kronecker Factorization (EKFAC) (George et al., 2018), proposes an interpretation of viewing natural gradient update as a diagonal method, and corrects the inaccurate re-scaling factor in the Kronecker-factored eigenbasis. Gao et al. (2020) considers a new approximation to the natural gradient, which approximates the Fisher information matrix (FIM) to a constant multiplied by the Kronecker product of two matrices and keeps the trace equal before and after the approximation. In this work, we combine the ideas of these two methods and propose Trace-restricted Eigenvalue-corrected Kronecker Factorization (TEKFAC). The proposed method not only corrects the inexact re-scaling factor under the Kronecker-factored eigenbasis, but also considers the new approximation method and the effective damping technique proposed in Gao et al. (2020). We also discuss the differences and relationships among the Kronecker-factored approximations. Empirically, our method outperforms SGD with momentum, Adam, EKFAC and TKFAC on several DNNs.
A Trace-restricted Kronecker-Factored Approximation to Natural Gradient
Nov 21, 2020
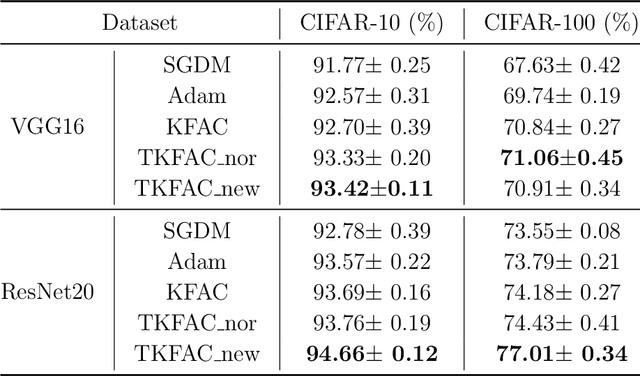
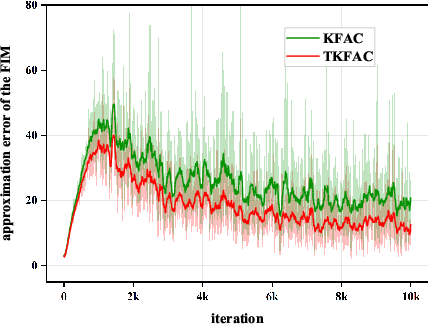
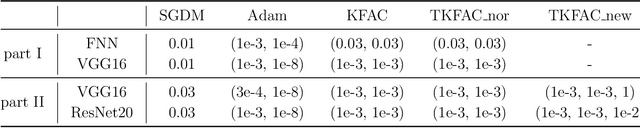
Abstract:Second-order optimization methods have the ability to accelerate convergence by modifying the gradient through the curvature matrix. There have been many attempts to use second-order optimization methods for training deep neural networks. Inspired by diagonal approximations and factored approximations such as Kronecker-Factored Approximate Curvature (KFAC), we propose a new approximation to the Fisher information matrix (FIM) called Trace-restricted Kronecker-factored Approximate Curvature (TKFAC) in this work, which can hold the certain trace relationship between the exact and the approximate FIM. In TKFAC, we decompose each block of the approximate FIM as a Kronecker product of two smaller matrices and scaled by a coefficient related to trace. We theoretically analyze TKFAC's approximation error and give an upper bound of it. We also propose a new damping technique for TKFAC on convolutional neural networks to maintain the superiority of second-order optimization methods during training. Experiments show that our method has better performance compared with several state-of-the-art algorithms on some deep network architectures.
EAdam Optimizer: How $ε$ Impact Adam
Nov 04, 2020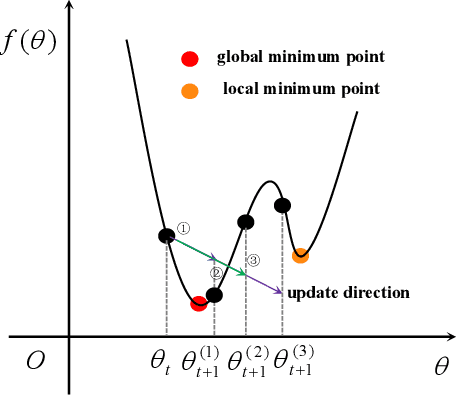
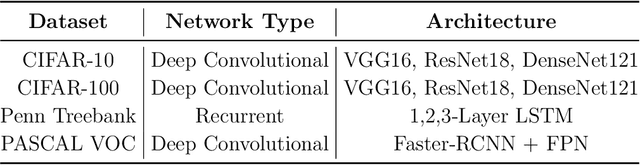
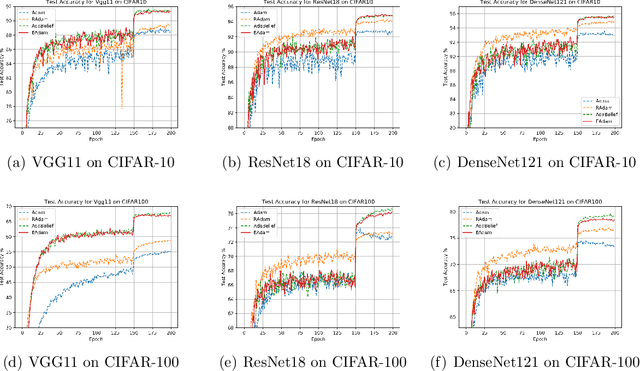
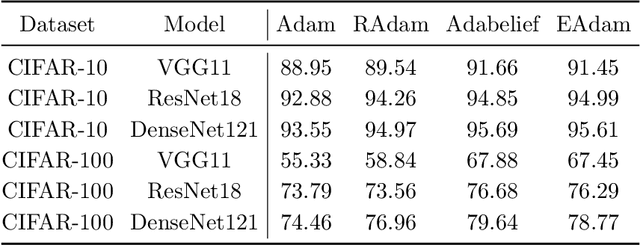
Abstract:Many adaptive optimization methods have been proposed and used in deep learning, in which Adam is regarded as the default algorithm and widely used in many deep learning frameworks. Recently, many variants of Adam, such as Adabound, RAdam and Adabelief, have been proposed and show better performance than Adam. However, these variants mainly focus on changing the stepsize by making differences on the gradient or the square of it. Motivated by the fact that suitable damping is important for the success of powerful second-order optimizers, we discuss the impact of the constant $\epsilon$ for Adam in this paper. Surprisingly, we can obtain better performance than Adam simply changing the position of $\epsilon$. Based on this finding, we propose a new variant of Adam called EAdam, which doesn't need extra hyper-parameters or computational costs. We also discuss the relationships and differences between our method and Adam. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on various popular tasks and models. Experimental results show that our method can bring significant improvement compared with Adam. Our code is available at https://github.com/yuanwei2019/EAdam-optimizer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge