K S Shriram
Task-driven Prompt Evolution for Foundation Models
Oct 26, 2023Abstract:Promptable foundation models, particularly Segment Anything Model (SAM), have emerged as a promising alternative to the traditional task-specific supervised learning for image segmentation. However, many evaluation studies have found that their performance on medical imaging modalities to be underwhelming compared to conventional deep learning methods. In the world of large pre-trained language and vision-language models, learning prompt from downstream tasks has achieved considerable success in improving performance. In this work, we propose a plug-and-play Prompt Optimization Technique for foundation models like SAM (SAMPOT) that utilizes the downstream segmentation task to optimize the human-provided prompt to obtain improved performance. We demonstrate the utility of SAMPOT on lung segmentation in chest X-ray images and obtain an improvement on a significant number of cases ($\sim75\%$) over human-provided initial prompts. We hope this work will lead to further investigations in the nascent field of automatic visual prompt-tuning.
Pristine annotations-based multi-modal trained artificial intelligence solution to triage chest X-ray for COVID-19
Nov 10, 2020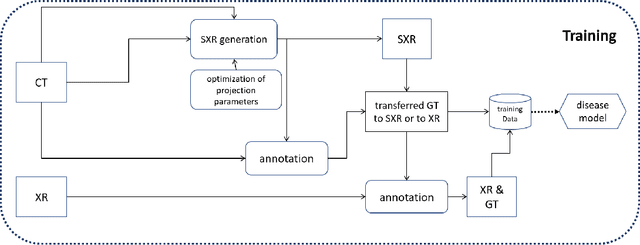



Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread and impact the well-being of the global population. The front-line modalities including computed tomography (CT) and X-ray play an important role for triaging COVID patients. Considering the limited access of resources (both hardware and trained personnel) and decontamination considerations, CT may not be ideal for triaging suspected subjects. Artificial intelligence (AI) assisted X-ray based applications for triaging and monitoring require experienced radiologists to identify COVID patients in a timely manner and to further delineate the disease region boundary are seen as a promising solution. Our proposed solution differs from existing solutions by industry and academic communities, and demonstrates a functional AI model to triage by inferencing using a single x-ray image, while the deep-learning model is trained using both X-ray and CT data. We report on how such a multi-modal training improves the solution compared to X-ray only training. The multi-modal solution increases the AUC (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve) from 0.89 to 0.93 and also positively impacts the Dice coefficient (0.59 to 0.62) for localizing the pathology. To the best our knowledge, it is the first X-ray solution by leveraging multi-modal information for the development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge