June Young Park
In-Context Learning for Long-Context Sentiment Analysis on Infrastructure Project Opinions
Oct 15, 2024


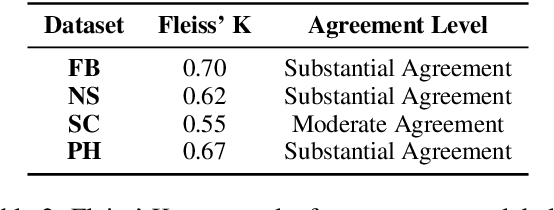
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved impressive results across various tasks. However, they still struggle with long-context documents. This study evaluates the performance of three leading LLMs: GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 1.5 Pro on lengthy, complex, and opinion-varying documents concerning infrastructure projects, under both zero-shot and few-shot scenarios. Our results indicate that GPT-4o excels in zero-shot scenarios for simpler, shorter documents, while Claude 3.5 Sonnet surpasses GPT-4o in handling more complex, sentiment-fluctuating opinions. In few-shot scenarios, Claude 3.5 Sonnet outperforms overall, while GPT-4o shows greater stability as the number of demonstrations increases.
ALDI++: Automatic and parameter-less discord and outlier detection for building energy load profiles
Mar 13, 2022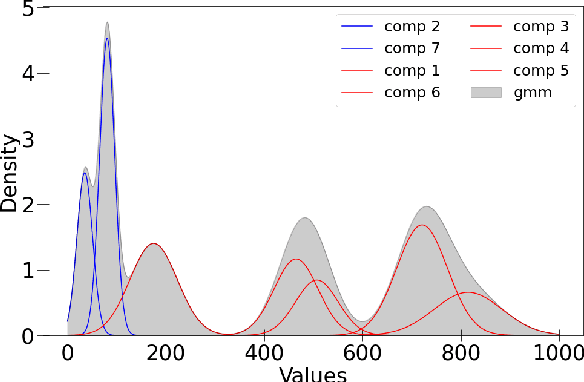
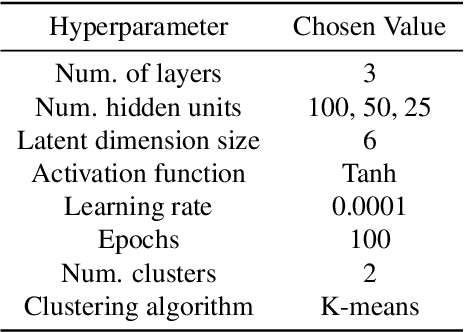
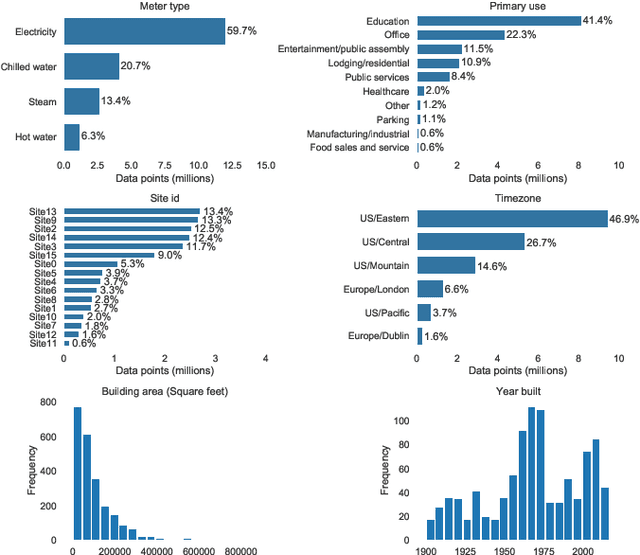
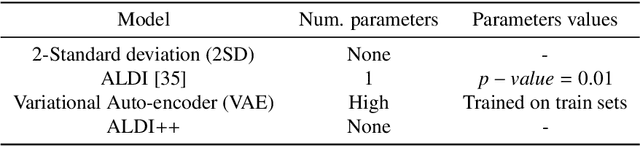
Abstract:Data-driven building energy prediction is an integral part of the process for measurement and verification, building benchmarking, and building-to-grid interaction. The ASHRAE Great Energy Predictor III (GEPIII) machine learning competition used an extensive meter data set to crowdsource the most accurate machine learning workflow for whole building energy prediction. A significant component of the winning solutions was the pre-processing phase to remove anomalous training data. Contemporary pre-processing methods focus on filtering statistical threshold values or deep learning methods requiring training data and multiple hyper-parameters. A recent method named ALDI (Automated Load profile Discord Identification) managed to identify these discords using matrix profile, but the technique still requires user-defined parameters. We develop ALDI++, a method based on the previous work that bypasses user-defined parameters and takes advantage of discord similarity. We evaluate ALDI++ against a statistical threshold, variational auto-encoder, and the original ALDI as baselines in classifying discords and energy forecasting scenarios. Our results demonstrate that while the classification performance improvement over the original method is marginal, ALDI++ helps achieve the best forecasting error improving 6% over the winning's team approach with six times less computation time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge