Julian Zimmerlin
Hidden Biases of End-to-End Driving Datasets
Dec 12, 2024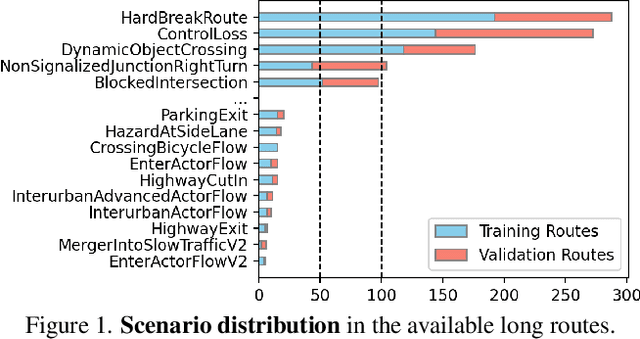
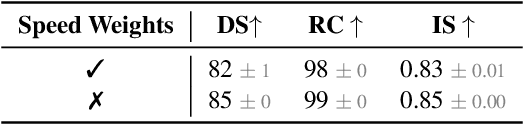
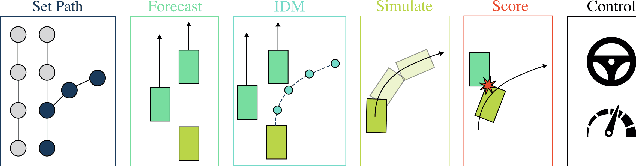
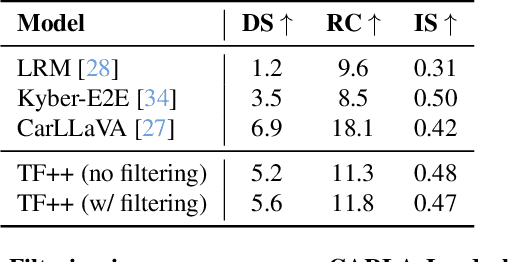
Abstract:End-to-end driving systems have made rapid progress, but have so far not been applied to the challenging new CARLA Leaderboard 2.0. Further, while there is a large body of literature on end-to-end architectures and training strategies, the impact of the training dataset is often overlooked. In this work, we make a first attempt at end-to-end driving for Leaderboard 2.0. Instead of investigating architectures, we systematically analyze the training dataset, leading to new insights: (1) Expert style significantly affects downstream policy performance. (2) In complex data sets, the frames should not be weighted on the basis of simplistic criteria such as class frequencies. (3) Instead, estimating whether a frame changes the target labels compared to previous frames can reduce the size of the dataset without removing important information. By incorporating these findings, our model ranks first and second respectively on the map and sensors tracks of the 2024 CARLA Challenge, and sets a new state-of-the-art on the Bench2Drive test routes. Finally, we uncover a design flaw in the current evaluation metrics and propose a modification for future challenges. Our dataset, code, and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/autonomousvision/carla_garage.
GINA: Neural Relational Inference From Independent Snapshots
May 29, 2021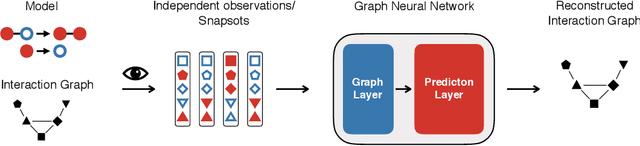
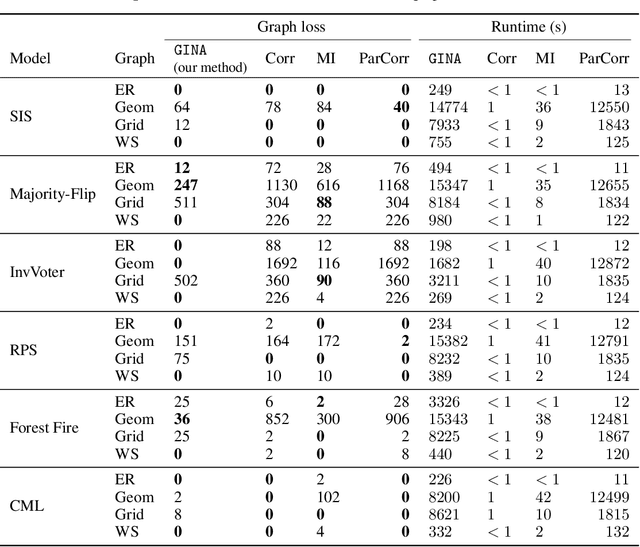
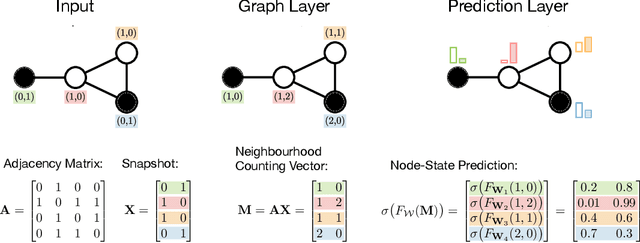
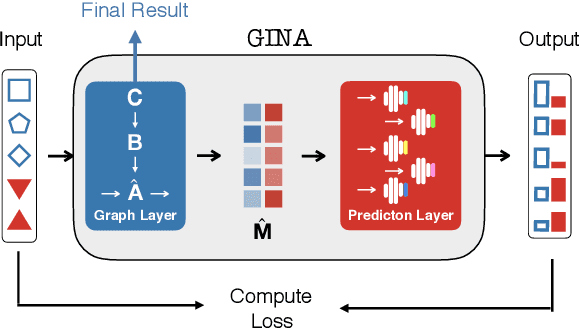
Abstract:Dynamical systems in which local interactions among agents give rise to complex emerging phenomena are ubiquitous in nature and society. This work explores the problem of inferring the unknown interaction structure (represented as a graph) of such a system from measurements of its constituent agents or individual components (represented as nodes). We consider a setting where the underlying dynamical model is unknown and where different measurements (i.e., snapshots) may be independent (e.g., may stem from different experiments). We propose GINA (Graph Inference Network Architecture), a graph neural network (GNN) to simultaneously learn the latent interaction graph and, conditioned on the interaction graph, the prediction of a node's observable state based on adjacent vertices. GINA is based on the hypothesis that the ground truth interaction graph -- among all other potential graphs -- allows to predict the state of a node, given the states of its neighbors, with the highest accuracy. We test this hypothesis and demonstrate GINA's effectiveness on a wide range of interaction graphs and dynamical processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge