Juhong Wang
Deep Code Search with Naming-Agnostic Contrastive Multi-View Learning
Aug 18, 2024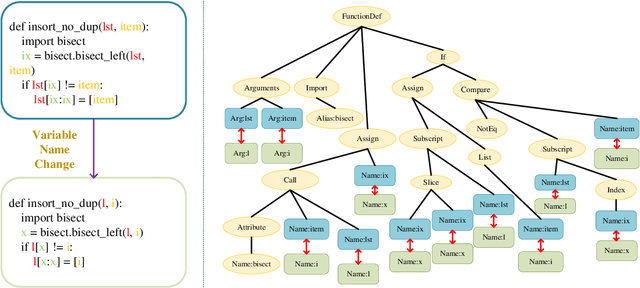
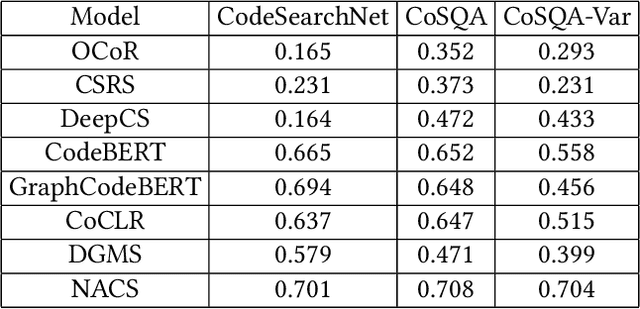
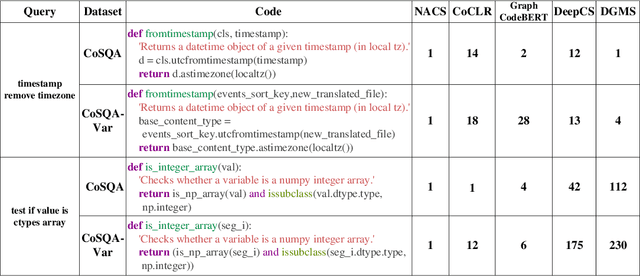
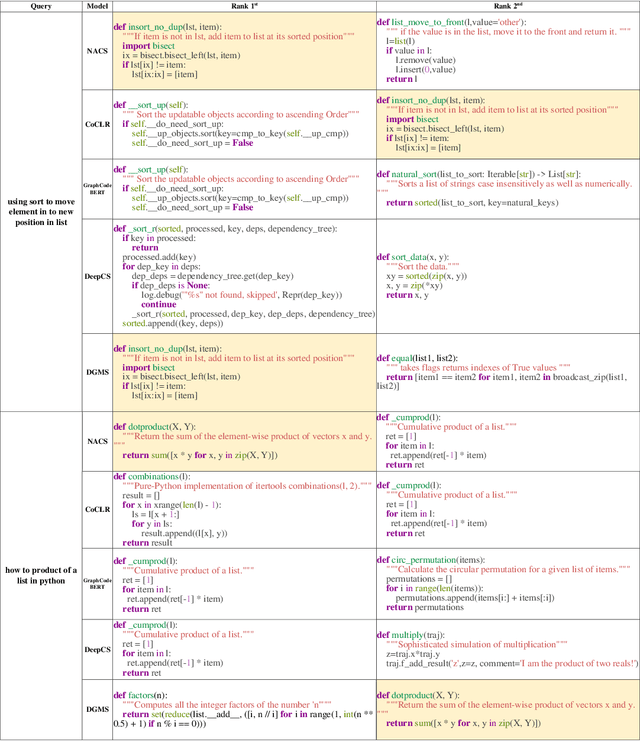
Abstract:Software development is a repetitive task, as developers usually reuse or get inspiration from existing implementations. Code search, which refers to the retrieval of relevant code snippets from a codebase according to the developer's intent that has been expressed as a query, has become increasingly important in the software development process. Due to the success of deep learning in various applications, a great number of deep learning based code search approaches have sprung up and achieved promising results. However, developers may not follow the same naming conventions and the same variable may have different variable names in different implementations, bringing a challenge to deep learning based code search methods that rely on explicit variable correspondences to understand source code. To overcome this challenge, we propose a naming-agnostic code search method (NACS) based on contrastive multi-view code representation learning. NACS strips information bound to variable names from Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), the representation of the abstract syntactic structure of source code, and focuses on capturing intrinsic properties solely from AST structures. We use semantic-level and syntax-level augmentation techniques to prepare realistically rational data and adopt contrastive learning to design a graph-view modeling component in NACS to enhance the understanding of code snippets. We further model ASTs in a path view to strengthen the graph-view modeling component through multi-view learning. Extensive experiments show that NACS provides superior code search performance compared to baselines and NACS can be adapted to help existing code search methods overcome the impact of different naming conventions.
Code Search Debiasing:Improve Search Results beyond Overall Ranking Performance
Nov 25, 2023Abstract:Code search engine is an essential tool in software development. Many code search methods have sprung up, focusing on the overall ranking performance of code search. In this paper, we study code search from another perspective by analyzing the bias of code search models. Biased code search engines provide poor user experience, even though they show promising overall performance. Due to different development conventions (e.g., prefer long queries or abbreviations), some programmers will find the engine useful, while others may find it hard to get desirable search results. To mitigate biases, we develop a general debiasing framework that employs reranking to calibrate search results. It can be easily plugged into existing engines and handle new code search biases discovered in the future. Experiments show that our framework can effectively reduce biases. Meanwhile, the overall ranking performance of code search gets improved after debiasing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge