Juan Alonso
Latent Space Explorations of Singing Voice Synthesis using DDSP
Mar 12, 2021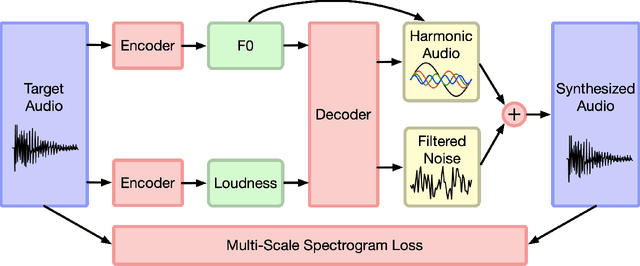

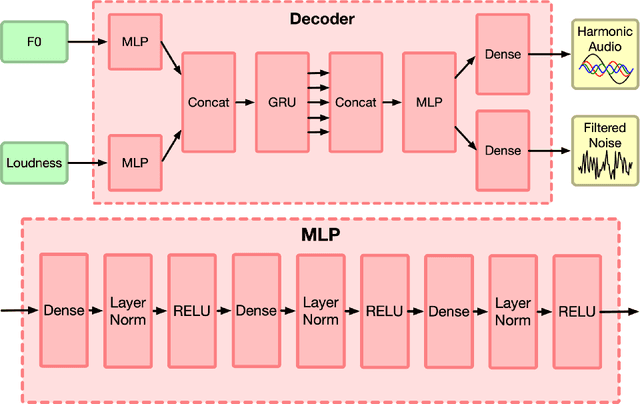

Abstract:Machine learning based singing voice models require large datasets and lengthy training times. In this work we present a lightweight architecture, based on the Differentiable Digital Signal Processing (DDSP) library, that is able to output song-like utterances conditioned only on pitch and amplitude, after twelve hours of training using small datasets of unprocessed audio. The results are promising, as both the melody and the singer's voice are recognizable. In addition, we present two zero-configuration tools to train new models and experiment with them. Currently we are exploring the latent space representation, which is included in the DDSP library, but not in the original DDSP examples. Our results indicate that the latent space improves both the identification of the singer as well as the comprehension of the lyrics. Our code is available at https://github.com/juanalonso/DDSP-singing-experiments with links to the zero-configuration notebooks, and our sound examples are at https://juanalonso.github.io/DDSP-singing-experiments/ .
Aspects of Terminological and Named Entity Knowledge within Rule-Based Machine Translation Models for Under-Resourced Neural Machine Translation Scenarios
Sep 28, 2020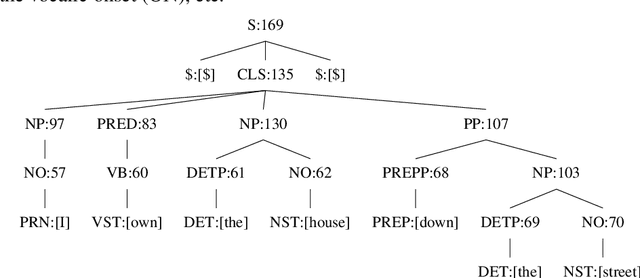
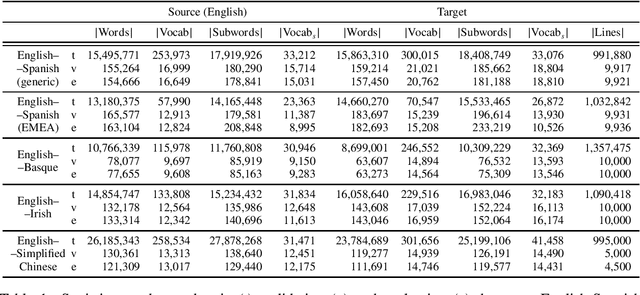
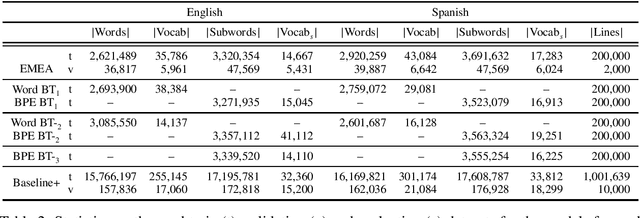
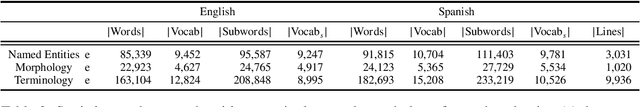
Abstract:Rule-based machine translation is a machine translation paradigm where linguistic knowledge is encoded by an expert in the form of rules that translate text from source to target language. While this approach grants extensive control over the output of the system, the cost of formalising the needed linguistic knowledge is much higher than training a corpus-based system, where a machine learning approach is used to automatically learn to translate from examples. In this paper, we describe different approaches to leverage the information contained in rule-based machine translation systems to improve a corpus-based one, namely, a neural machine translation model, with a focus on a low-resource scenario. Three different kinds of information were used: morphological information, named entities and terminology. In addition to evaluating the general performance of the system, we systematically analysed the performance of the proposed approaches when dealing with the targeted phenomena. Our results suggest that the proposed models have limited ability to learn from external information, and most approaches do not significantly alter the results of the automatic evaluation, but our preliminary qualitative evaluation shows that in certain cases the hypothesis generated by our system exhibit favourable behaviour such as keeping the use of passive voice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge