Josh Joseph
The Dataset Nutrition Label (2nd Gen): Leveraging Context to Mitigate Harms in Artificial Intelligence
Jan 10, 2022
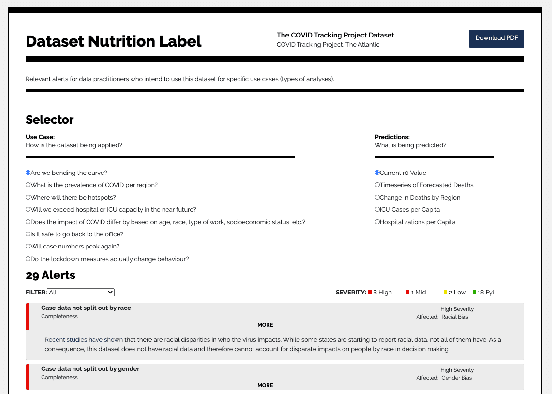
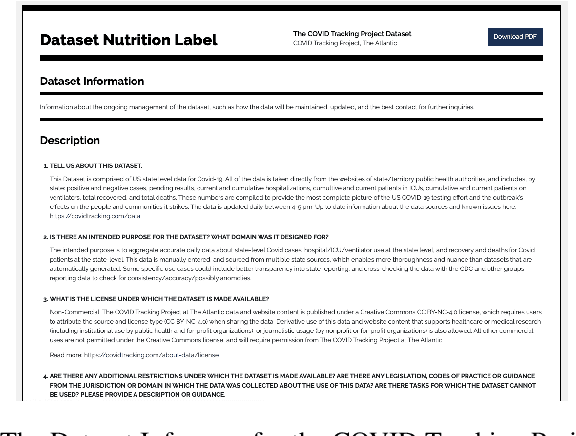
Abstract:As the production of and reliance on datasets to produce automated decision-making systems (ADS) increases, so does the need for processes for evaluating and interrogating the underlying data. After launching the Dataset Nutrition Label in 2018, the Data Nutrition Project has made significant updates to the design and purpose of the Label, and is launching an updated Label in late 2020, which is previewed in this paper. The new Label includes context-specific Use Cases &Alerts presented through an updated design and user interface targeted towards the data scientist profile. This paper discusses the harm and bias from underlying training data that the Label is intended to mitigate, the current state of the work including new datasets being labeled, new and existing challenges, and further directions of the work, as well as Figures previewing the new label.
A Study of Compositional Generalization in Neural Models
Jul 08, 2020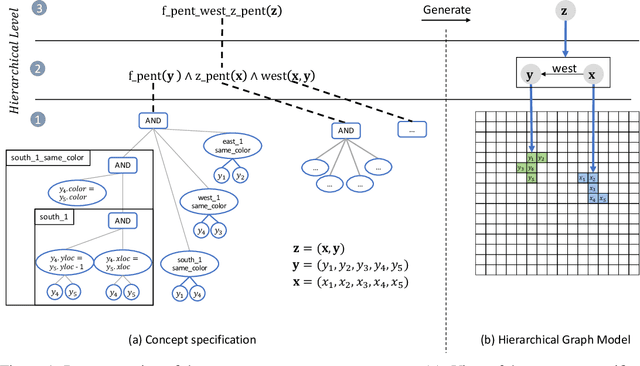
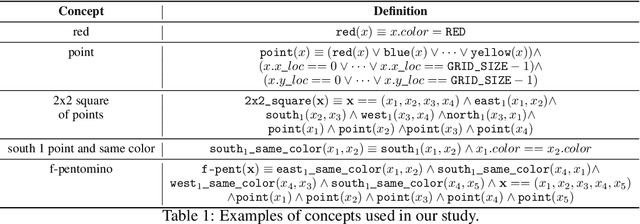
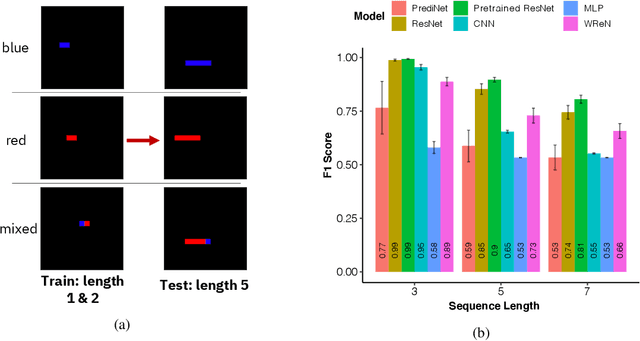
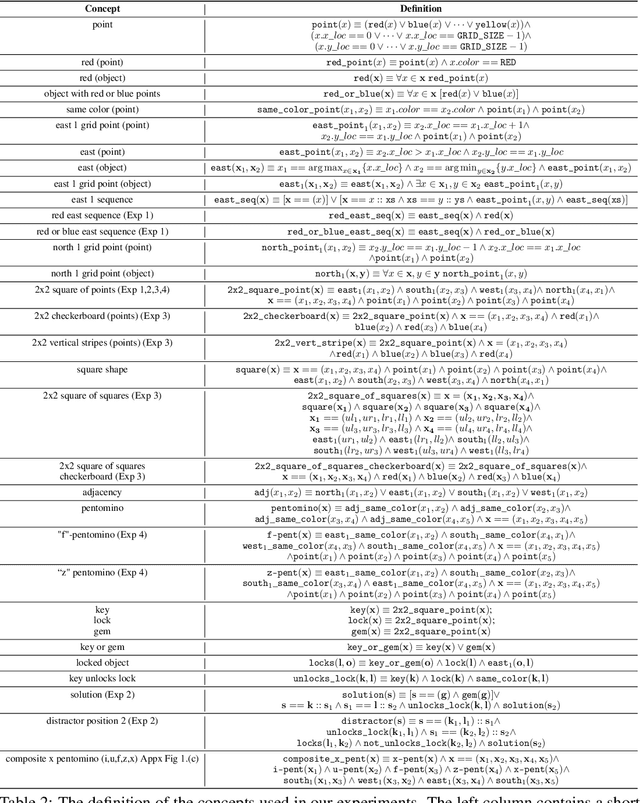
Abstract:Compositional and relational learning is a hallmark of human intelligence, but one which presents challenges for neural models. One difficulty in the development of such models is the lack of benchmarks with clear compositional and relational task structure on which to systematically evaluate them. In this paper, we introduce an environment called ConceptWorld, which enables the generation of images from compositional and relational concepts, defined using a logical domain specific language. We use it to generate images for a variety of compositional structures: 2x2 squares, pentominoes, sequences, scenes involving these objects, and other more complex concepts. We perform experiments to test the ability of standard neural architectures to generalize on relations with compositional arguments as the compositional depth of those arguments increases and under substitution. We compare standard neural networks such as MLP, CNN and ResNet, as well as state-of-the-art relational networks including WReN and PrediNet in a multi-class image classification setting. For simple problems, all models generalize well to close concepts but struggle with longer compositional chains. For more complex tests involving substitutivity, all models struggle, even with short chains. In highlighting these difficulties and providing an environment for further experimentation, we hope to encourage the development of models which are able to generalize effectively in compositional, relational domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge