Jorge Andres Quintero Serna
Debate Dynamics for Human-comprehensible Fact-checking on Knowledge Graphs
Jan 09, 2020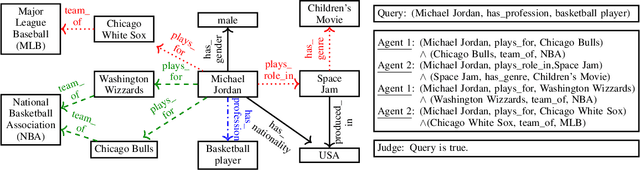


Abstract:We propose a novel method for fact-checking on knowledge graphs based on debate dynamics. The underlying idea is to frame the task of triple classification as a debate game between two reinforcement learning agents which extract arguments -- paths in the knowledge graph -- with the goal to justify the fact being true (thesis) or the fact being false (antithesis), respectively. Based on these arguments, a binary classifier, referred to as the judge, decides whether the fact is true or false. The two agents can be considered as sparse feature extractors that present interpretable evidence for either the thesis or the antithesis. In contrast to black-box methods, the arguments enable the user to gain an understanding for the decision of the judge. Moreover, our method allows for interactive reasoning on knowledge graphs where the users can raise additional arguments or evaluate the debate taking common sense reasoning and external information into account. Such interactive systems can increase the acceptance of various AI applications based on knowledge graphs and can further lead to higher efficiency, robustness, and fairness.
Reasoning on Knowledge Graphs with Debate Dynamics
Jan 02, 2020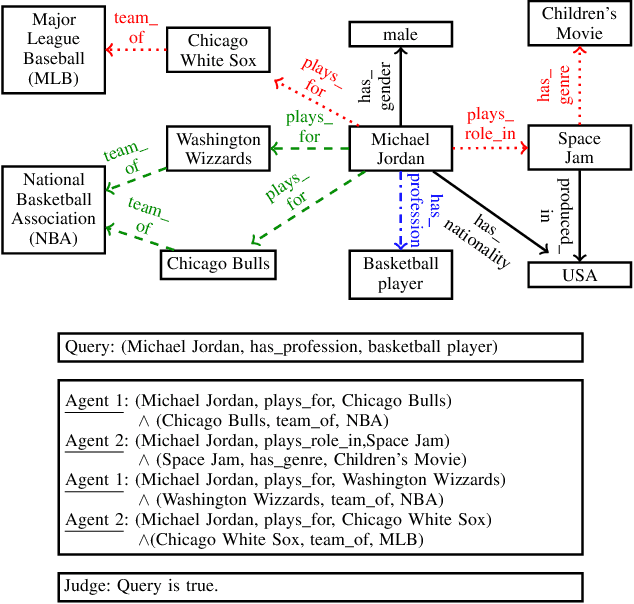

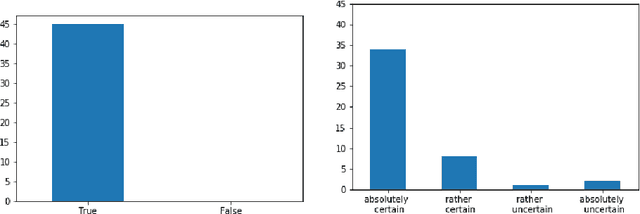
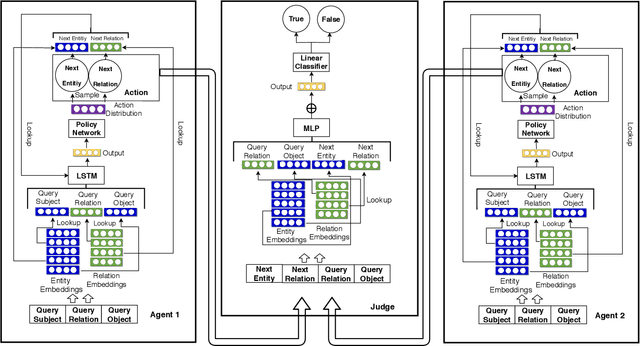
Abstract:We propose a novel method for automatic reasoning on knowledge graphs based on debate dynamics. The main idea is to frame the task of triple classification as a debate game between two reinforcement learning agents which extract arguments -- paths in the knowledge graph -- with the goal to promote the fact being true (thesis) or the fact being false (antithesis), respectively. Based on these arguments, a binary classifier, called the judge, decides whether the fact is true or false. The two agents can be considered as sparse, adversarial feature generators that present interpretable evidence for either the thesis or the antithesis. In contrast to other black-box methods, the arguments allow users to get an understanding of the decision of the judge. Since the focus of this work is to create an explainable method that maintains a competitive predictive accuracy, we benchmark our method on the triple classification and link prediction task. Thereby, we find that our method outperforms several baselines on the benchmark datasets FB15k-237, WN18RR, and Hetionet. We also conduct a survey and find that the extracted arguments are informative for users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge