Jonathan Morris
Introducing the Welsh Text Summarisation Dataset and Baseline Systems
May 05, 2022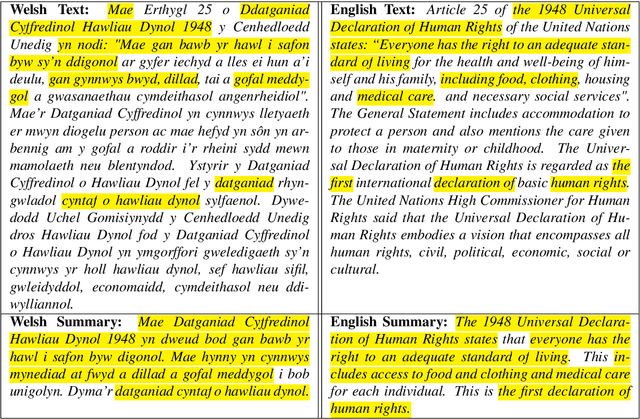
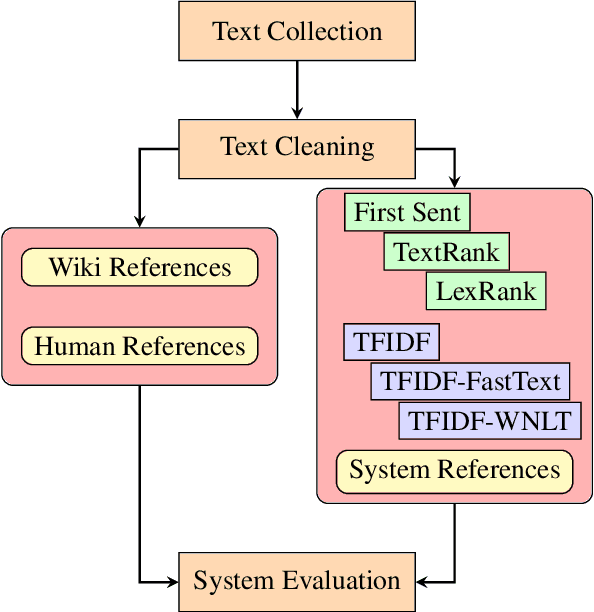
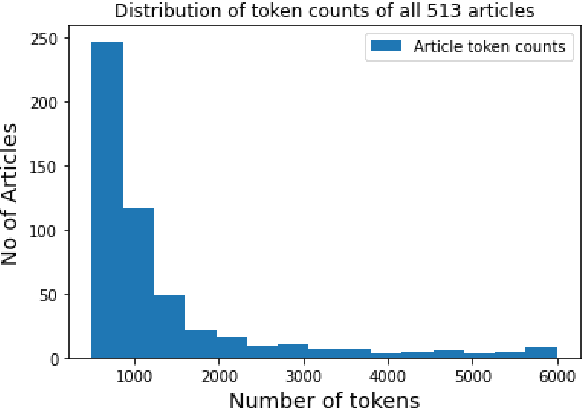
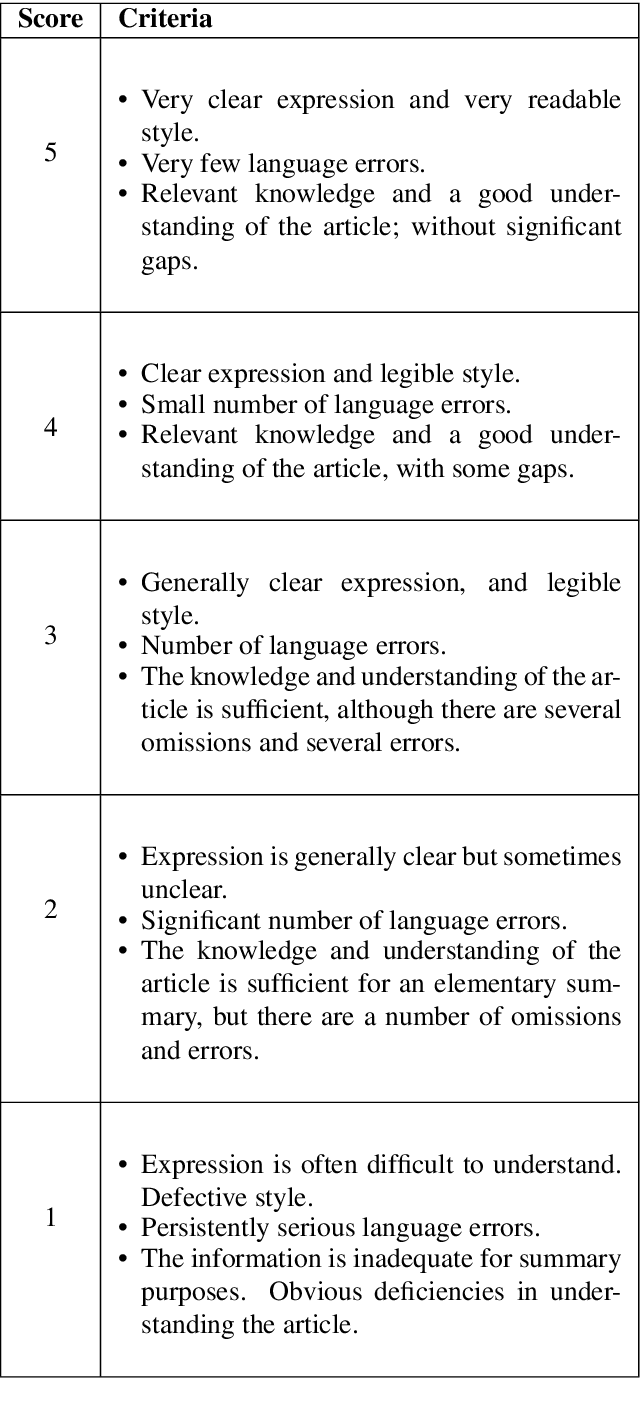
Abstract:Welsh is an official language in Wales and is spoken by an estimated 884,300 people (29.2% of the population of Wales). Despite this status and estimated increase in speaker numbers since the last (2011) census, Welsh remains a minority language undergoing revitalization and promotion by Welsh Government and relevant stakeholders. As part of the effort to increase the availability of Welsh digital technology, this paper introduces the first Welsh summarisation dataset, which we provide freely for research purposes to help advance the work on Welsh text summarization. The dataset was created by Welsh speakers by manually summarising Welsh Wikipedia articles. In addition, the paper discusses the implementation and evaluation of different summarisation systems for Welsh. The summarization systems and results will serve as benchmarks for the development of summarises in other minority language contexts.
Preterm Birth Prediction: Deriving Stable and Interpretable Rules from High Dimensional Data
Jul 28, 2016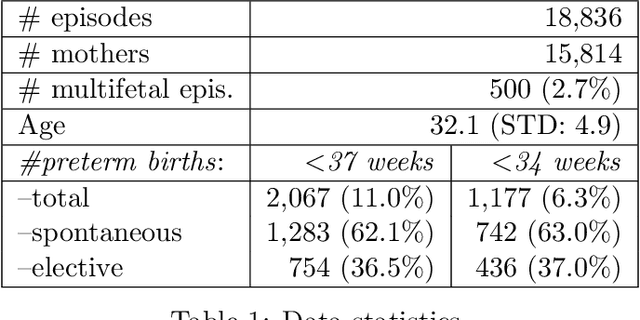

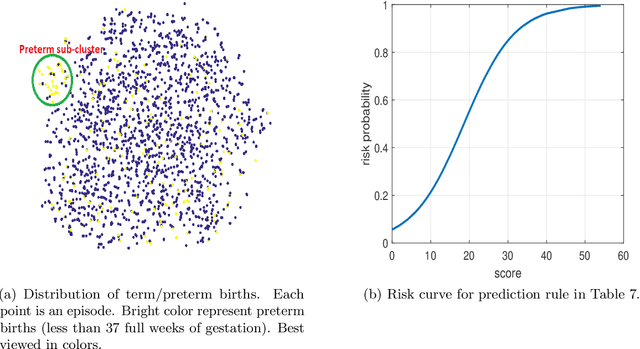
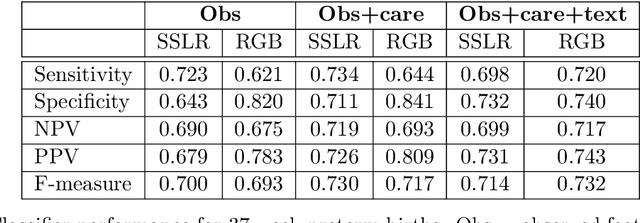
Abstract:Preterm births occur at an alarming rate of 10-15%. Preemies have a higher risk of infant mortality, developmental retardation and long-term disabilities. Predicting preterm birth is difficult, even for the most experienced clinicians. The most well-designed clinical study thus far reaches a modest sensitivity of 18.2-24.2% at specificity of 28.6-33.3%. We take a different approach by exploiting databases of normal hospital operations. We aims are twofold: (i) to derive an easy-to-use, interpretable prediction rule with quantified uncertainties, and (ii) to construct accurate classifiers for preterm birth prediction. Our approach is to automatically generate and select from hundreds (if not thousands) of possible predictors using stability-aware techniques. Derived from a large database of 15,814 women, our simplified prediction rule with only 10 items has sensitivity of 62.3% at specificity of 81.5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge