Jonathan Katzy
A Qualitative Investigation into LLM-Generated Multilingual Code Comments and Automatic Evaluation Metrics
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models are essential coding assistants, yet their training is predominantly English-centric. In this study, we evaluate the performance of code language models in non-English contexts, identifying challenges in their adoption and integration into multilingual workflows. We conduct an open-coding study to analyze errors in code comments generated by five state-of-the-art code models, CodeGemma, CodeLlama, CodeQwen1.5, GraniteCode, and StarCoder2 across five natural languages: Chinese, Dutch, English, Greek, and Polish. Our study yields a dataset of 12,500 labeled generations, which we publicly release. We then assess the reliability of standard metrics in capturing comment \textit{correctness} across languages and evaluate their trustworthiness as judgment criteria. Through our open-coding investigation, we identified a taxonomy of 26 distinct error categories in model-generated code comments. They highlight variations in language cohesion, informativeness, and syntax adherence across different natural languages. Our analysis shows that, while these models frequently produce partially correct comments, modern neural metrics fail to reliably differentiate meaningful completions from random noise. Notably, the significant score overlap between expert-rated correct and incorrect comments calls into question the effectiveness of these metrics in assessing generated comments.
The Heap: A Contamination-Free Multilingual Code Dataset for Evaluating Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2025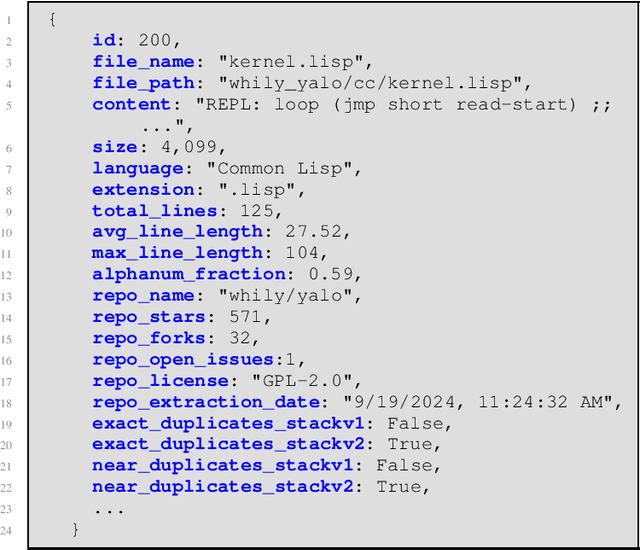
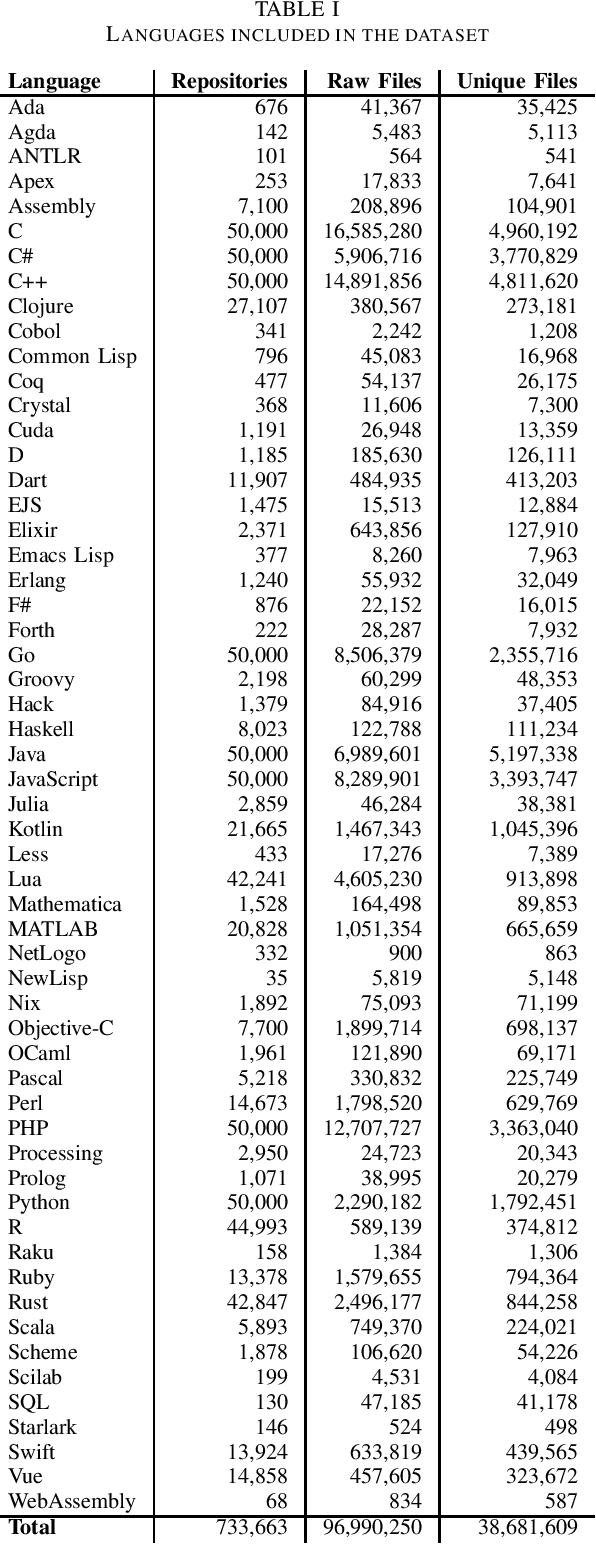
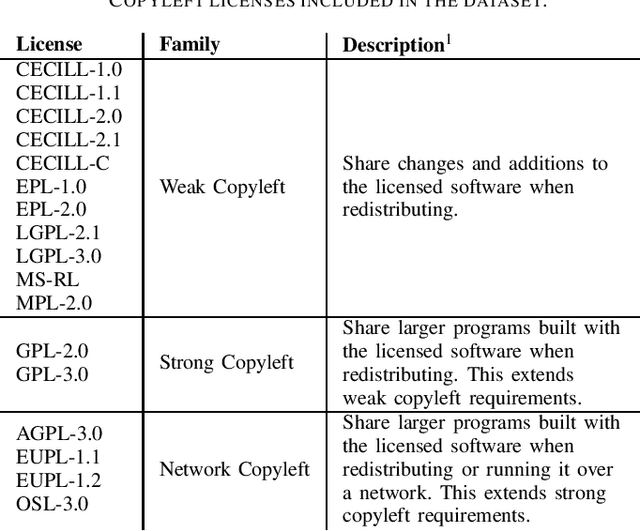
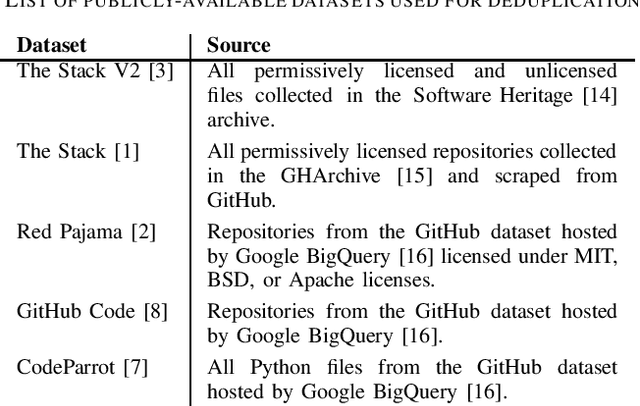
Abstract:The recent rise in the popularity of large language models has spurred the development of extensive code datasets needed to train them. This has left limited code available for collection and use in the downstream investigation of specific behaviors, or evaluation of large language models without suffering from data contamination. To address this problem, we release The Heap, a large multilingual dataset covering 57 programming languages that has been deduplicated with respect to other open datasets of code, enabling researchers to conduct fair evaluations of large language models without significant data cleaning overhead.
An Exploratory Investigation into Code License Infringements in Large Language Model Training Datasets
Mar 22, 2024

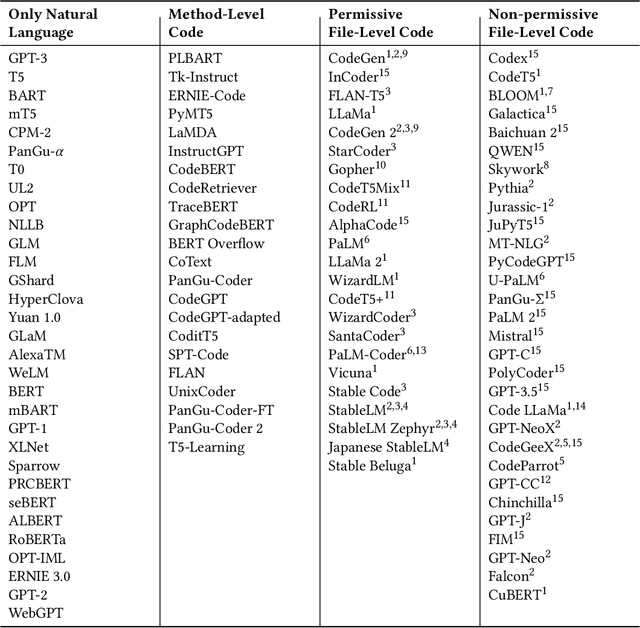
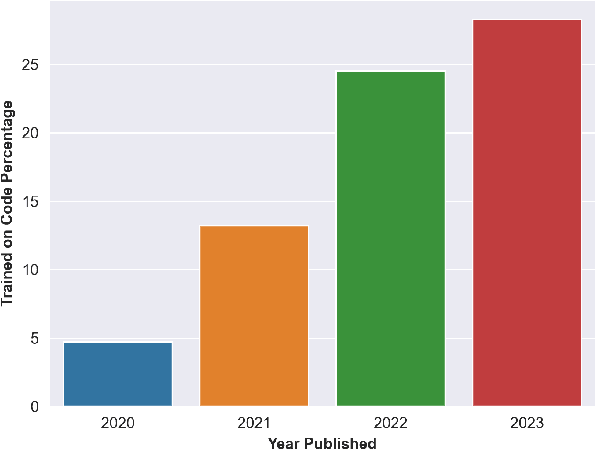
Abstract:Does the training of large language models potentially infringe upon code licenses? Furthermore, are there any datasets available that can be safely used for training these models without violating such licenses? In our study, we assess the current trends in the field and the importance of incorporating code into the training of large language models. Additionally, we examine publicly available datasets to see whether these models can be trained on them without the risk of legal issues in the future. To accomplish this, we compiled a list of 53 large language models trained on file-level code. We then extracted their datasets and analyzed how much they overlap with a dataset we created, consisting exclusively of strong copyleft code. Our analysis revealed that every dataset we examined contained license inconsistencies, despite being selected based on their associated repository licenses. We analyzed a total of 514 million code files, discovering 38 million exact duplicates present in our strong copyleft dataset. Additionally, we examined 171 million file-leading comments, identifying 16 million with strong copyleft licenses and another 11 million comments that discouraged copying without explicitly mentioning a license. Based on the findings of our study, which highlights the pervasive issue of license inconsistencies in large language models trained on code, our recommendation for both researchers and the community is to prioritize the development and adoption of best practices for dataset creation and management.
Language Models for Code Completion: A Practical Evaluation
Feb 25, 2024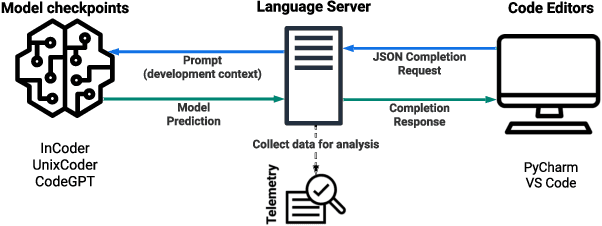
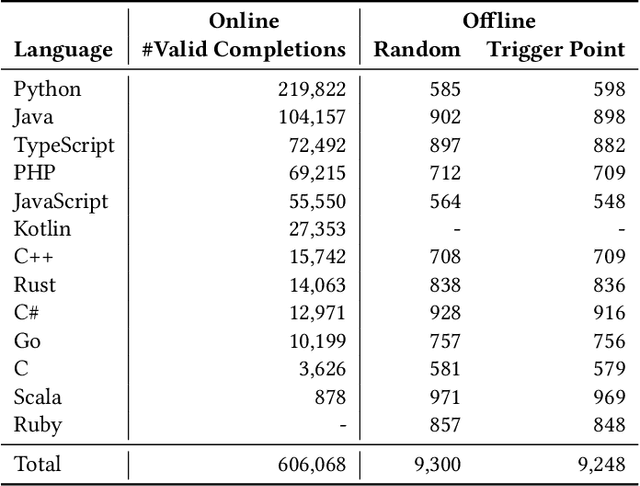
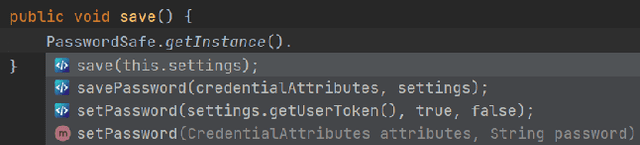
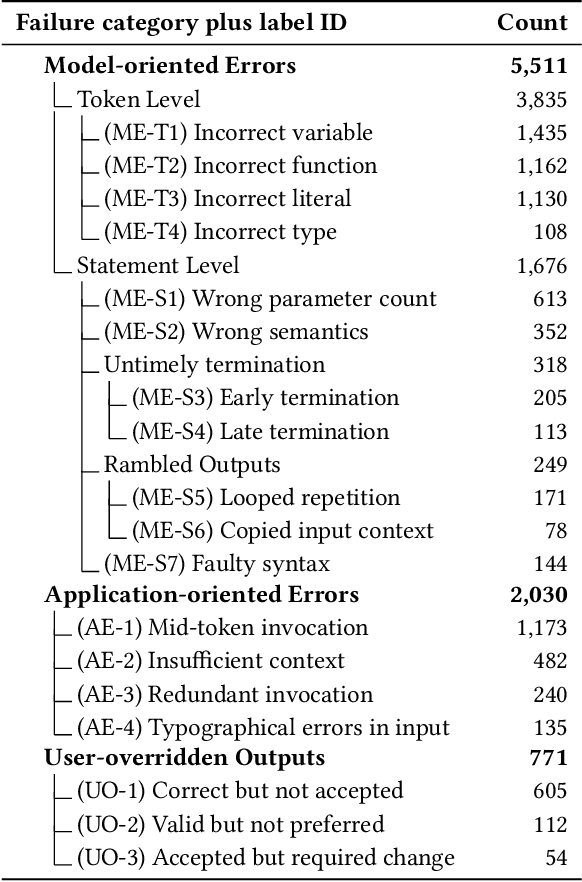
Abstract:Transformer-based language models for automatic code completion have shown great promise so far, yet the evaluation of these models rarely uses real data. This study provides both quantitative and qualitative assessments of three public code language models when completing real-world code. We first developed an open-source IDE extension, Code4Me, for the online evaluation of the models. We collected real auto-completion usage data for over a year from more than 1200 users, resulting in over 600K valid completions. These models were then evaluated using six standard metrics across twelve programming languages. Next, we conducted a qualitative study of 1690 real-world completion requests to identify the reasons behind the poor model performance. A comparative analysis of the models' performance in online and offline settings was also performed, using benchmark synthetic datasets and two masking strategies. Our findings suggest that while developers utilize code completion across various languages, the best results are achieved for mainstream languages such as Python and Java. InCoder outperformed the other models across all programming languages, highlighting the significance of training data and objectives. Our study also revealed that offline evaluations do not accurately reflect real-world scenarios. Upon qualitative analysis of the model's predictions, we found that 66.3% of failures were due to the models' limitations, 24.4% occurred due to inappropriate model usage in a development context, and 9.3% were valid requests that developers overwrote. Given these findings, we propose several strategies to overcome the current limitations. These include refining training objectives, improving resilience to typographical errors, adopting hybrid approaches, and enhancing implementations and usability.
On the Impact of Language Selection for Training and Evaluating Programming Language Models
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:The recent advancements in Transformer-based Language Models have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing the multilingual capabilities of these models. The remarkable progress made in this domain not only applies to natural language tasks but also extends to the domain of programming languages. Despite the ability of these models to learn from multiple languages, evaluations typically focus on particular combinations of the same languages. In this study, we evaluate the similarity of programming languages by analyzing their representations using a CodeBERT-based model. Our experiments reveal that token representation in languages such as C++, Python, and Java exhibit proximity to one another, whereas the same tokens in languages such as Mathematica and R display significant dissimilarity. Our findings suggest that this phenomenon can potentially result in performance challenges when dealing with diverse languages. Thus, we recommend using our similarity measure to select a diverse set of programming languages when training and evaluating future models.
A Survey on Distributed Machine Learning
Dec 20, 2019



Abstract:The demand for artificial intelligence has grown significantly over the last decade and this growth has been fueled by advances in machine learning techniques and the ability to leverage hardware acceleration. However, in order to increase the quality of predictions and render machine learning solutions feasible for more complex applications, a substantial amount of training data is required. Although small machine learning models can be trained with modest amounts of data, the input for training larger models such as neural networks grows exponentially with the number of parameters. Since the demand for processing training data has outpaced the increase in computation power of computing machinery, there is a need for distributing the machine learning workload across multiple machines, and turning the centralized into a distributed system. These distributed systems present new challenges, first and foremost the efficient parallelization of the training process and the creation of a coherent model. This article provides an extensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in the field by outlining the challenges and opportunities of distributed machine learning over conventional (centralized) machine learning, discussing the techniques used for distributed machine learning, and providing an overview of the systems that are available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge