Johannes Oberreuter
Weakly-supervised Biomechanically-constrained CT/MRI Registration of the Spine
May 16, 2022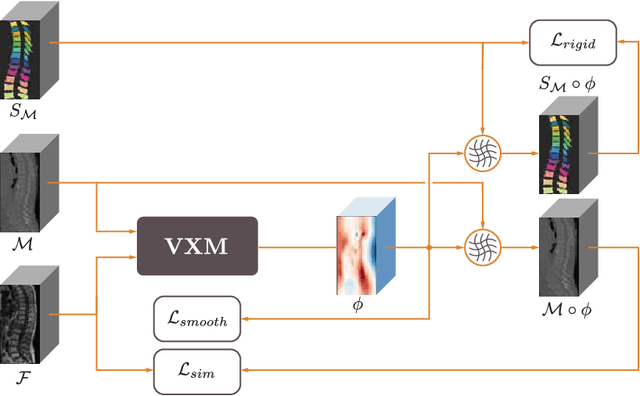
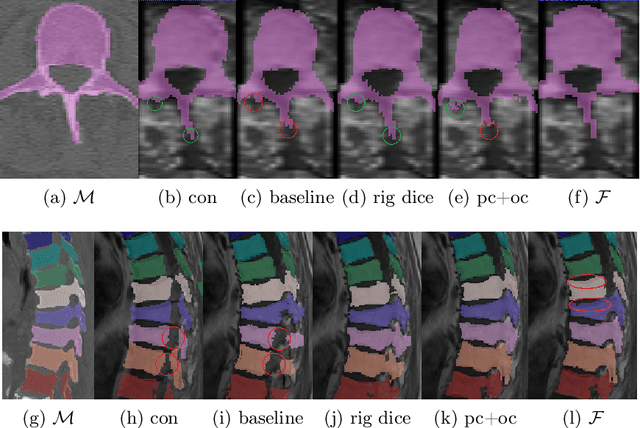
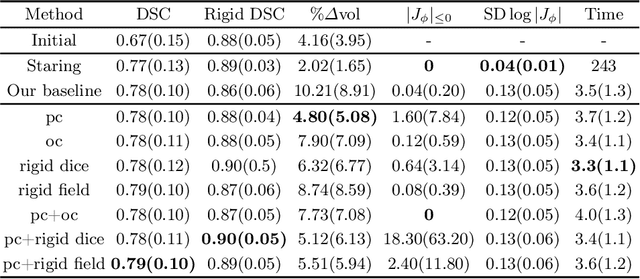
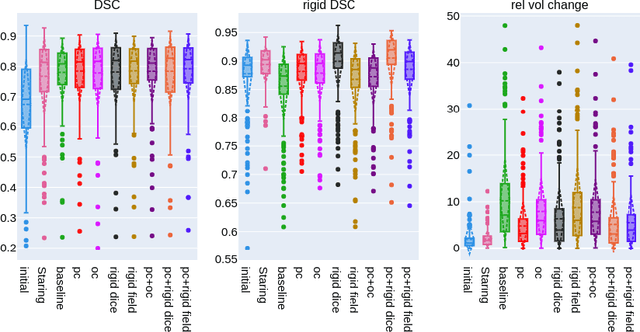

Abstract:CT and MRI are two of the most informative modalities in spinal diagnostics and treatment planning. CT is useful when analysing bony structures, while MRI gives information about the soft tissue. Thus, fusing the information of both modalities can be very beneficial. Registration is the first step for this fusion. While the soft tissues around the vertebra are deformable, each vertebral body is constrained to move rigidly. We propose a weakly-supervised deep learning framework that preserves the rigidity and the volume of each vertebra while maximizing the accuracy of the registration. To achieve this goal, we introduce anatomy-aware losses for training the network. We specifically design these losses to depend only on the CT label maps since automatic vertebra segmentation in CT gives more accurate results contrary to MRI. We evaluate our method on an in-house dataset of 167 patients. Our results show that adding the anatomy-aware losses increases the plausibility of the inferred transformation while keeping the accuracy untouched.
Patient-specific virtual spine straightening and vertebra inpainting: An automatic framework for osteoplasty planning
Mar 23, 2021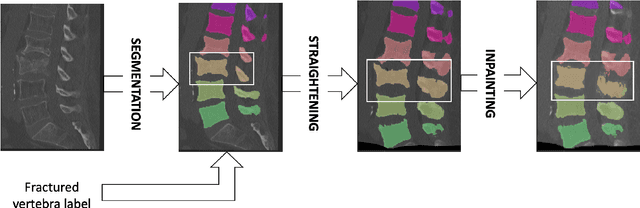

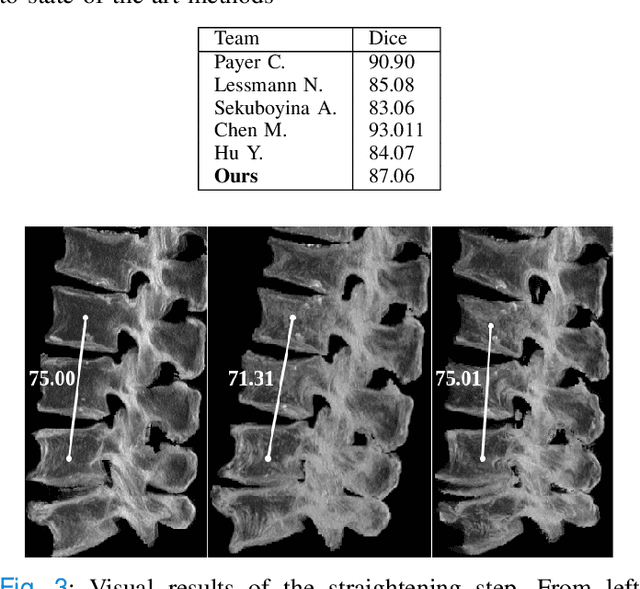
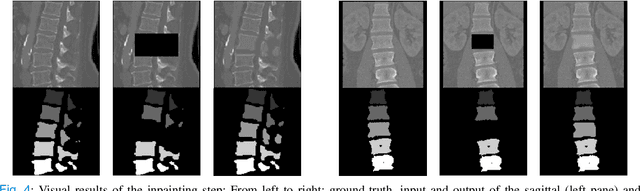
Abstract:Symptomatic spinal vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) often require osteoplasty treatment. A cement-like material is injected into the bone to stabilize the fracture, restore the vertebral body height and alleviate pain. Leakage is a common complication and may occur due to too much cement being injected. In this work, we propose an automated patient-specific framework that can allow physicians to calculate an upper bound of cement for the injection and estimate the optimal outcome of osteoplasty. The framework uses the patient CT scan and the fractured vertebra label to build a virtual healthy spine using a high-level approach. Firstly, the fractured spine is segmented with a three-step Convolution Neural Network (CNN) architecture. Next, a per-vertebra rigid registration to a healthy spine atlas restores its curvature. Finally, a GAN-based inpainting approach replaces the fractured vertebra with an estimation of its original shape. Based on this outcome, we then estimate the maximum amount of bone cement for injection. We evaluate our framework by comparing the virtual vertebrae volumes of ten patients to their healthy equivalent and report an average error of 3.88$\pm$7.63\%. The presented pipeline offers a first approach to a personalized automatic high-level framework for planning osteoplasty procedures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge