Jochen S. Utikal
Clinical Melanoma Diagnosis with Artificial Intelligence: Insights from a Prospective Multicenter Study
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Early detection of melanoma, a potentially lethal type of skin cancer with high prevalence worldwide, improves patient prognosis. In retrospective studies, artificial intelligence (AI) has proven to be helpful for enhancing melanoma detection. However, there are few prospective studies confirming these promising results. Existing studies are limited by low sample sizes, too homogenous datasets, or lack of inclusion of rare melanoma subtypes, preventing a fair and thorough evaluation of AI and its generalizability, a crucial aspect for its application in the clinical setting. Therefore, we assessed 'All Data are Ext' (ADAE), an established open-source ensemble algorithm for detecting melanomas, by comparing its diagnostic accuracy to that of dermatologists on a prospectively collected, external, heterogeneous test set comprising eight distinct hospitals, four different camera setups, rare melanoma subtypes, and special anatomical sites. We advanced the algorithm with real test-time augmentation (R-TTA, i.e. providing real photographs of lesions taken from multiple angles and averaging the predictions), and evaluated its generalization capabilities. Overall, the AI showed higher balanced accuracy than dermatologists (0.798, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.779-0.814 vs. 0.781, 95% CI 0.760-0.802; p<0.001), obtaining a higher sensitivity (0.921, 95% CI 0.900- 0.942 vs. 0.734, 95% CI 0.701-0.770; p<0.001) at the cost of a lower specificity (0.673, 95% CI 0.641-0.702 vs. 0.828, 95% CI 0.804-0.852; p<0.001). As the algorithm exhibited a significant performance advantage on our heterogeneous dataset exclusively comprising melanoma-suspicious lesions, AI may offer the potential to support dermatologists particularly in diagnosing challenging cases.
Using Multiple Dermoscopic Photographs of One Lesion Improves Melanoma Classification via Deep Learning: A Prognostic Diagnostic Accuracy Study
Jun 05, 2023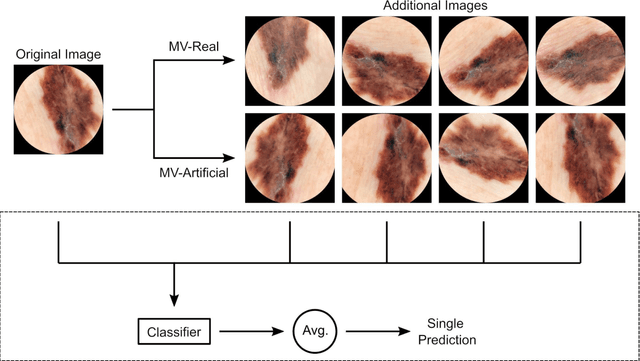
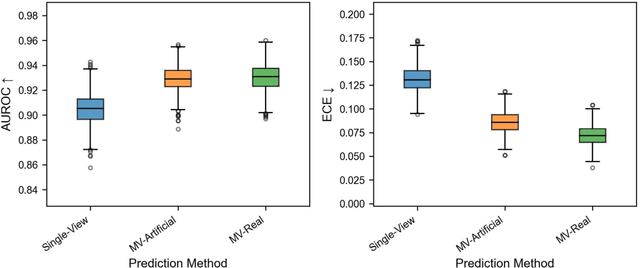
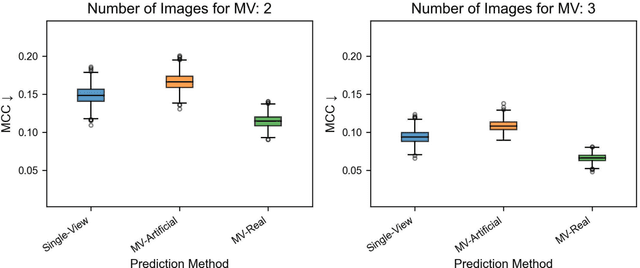
Abstract:Background: Convolutional neural network (CNN)-based melanoma classifiers face several challenges that limit their usefulness in clinical practice. Objective: To investigate the impact of multiple real-world dermoscopic views of a single lesion of interest on a CNN-based melanoma classifier. Methods: This study evaluated 656 suspected melanoma lesions. Classifier performance was measured using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), expected calibration error (ECE) and maximum confidence change (MCC) for (I) a single-view scenario, (II) a multiview scenario using multiple artificially modified images per lesion and (III) a multiview scenario with multiple real-world images per lesion. Results: The multiview approach with real-world images significantly increased the AUROC from 0.905 (95% CI, 0.879-0.929) in the single-view approach to 0.930 (95% CI, 0.909-0.951). ECE and MCC also improved significantly from 0.131 (95% CI, 0.105-0.159) to 0.072 (95% CI: 0.052-0.093) and from 0.149 (95% CI, 0.125-0.171) to 0.115 (95% CI: 0.099-0.131), respectively. Comparing multiview real-world to artificially modified images showed comparable diagnostic accuracy and uncertainty estimation, but significantly worse robustness for the latter. Conclusion: Using multiple real-world images is an inexpensive method to positively impact the performance of a CNN-based melanoma classifier.
Dermatologist-like explainable AI enhances trust and confidence in diagnosing melanoma
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Although artificial intelligence (AI) systems have been shown to improve the accuracy of initial melanoma diagnosis, the lack of transparency in how these systems identify melanoma poses severe obstacles to user acceptance. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) methods can help to increase transparency, but most XAI methods are unable to produce precisely located domain-specific explanations, making the explanations difficult to interpret. Moreover, the impact of XAI methods on dermatologists has not yet been evaluated. Extending on two existing classifiers, we developed an XAI system that produces text and region based explanations that are easily interpretable by dermatologists alongside its differential diagnoses of melanomas and nevi. To evaluate this system, we conducted a three-part reader study to assess its impact on clinicians' diagnostic accuracy, confidence, and trust in the XAI-support. We showed that our XAI's explanations were highly aligned with clinicians' explanations and that both the clinicians' trust in the support system and their confidence in their diagnoses were significantly increased when using our XAI compared to using a conventional AI system. The clinicians' diagnostic accuracy was numerically, albeit not significantly, increased. This work demonstrates that clinicians are willing to adopt such an XAI system, motivating their future use in the clinic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge