Jocelyn Grunwell
Generalist vs Specialist Time Series Foundation Models: Investigating Potential Emergent Behaviors in Assessing Human Health Using PPG Signals
Oct 16, 2025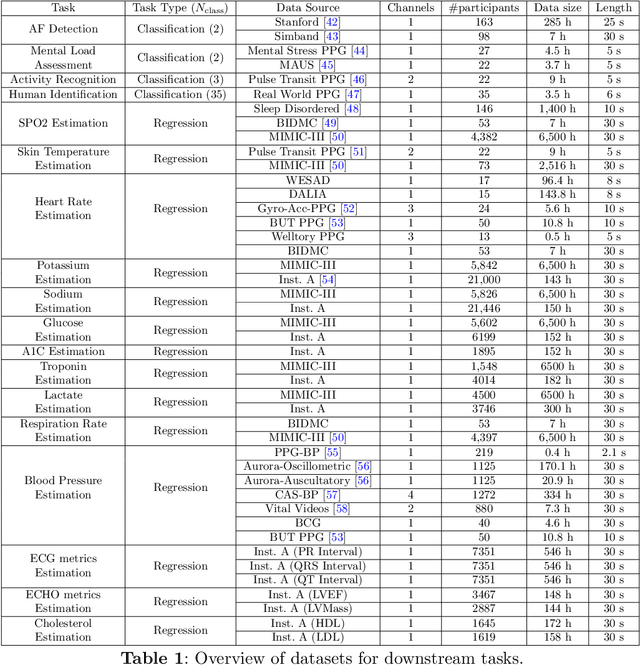
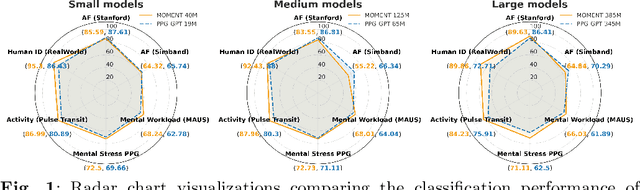
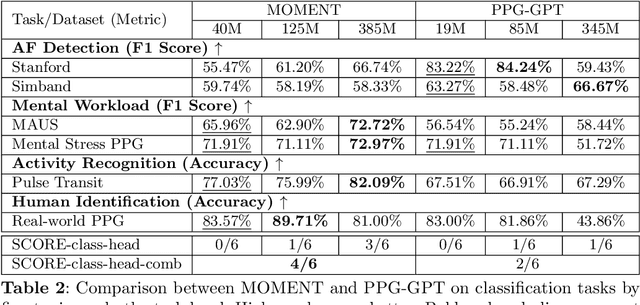
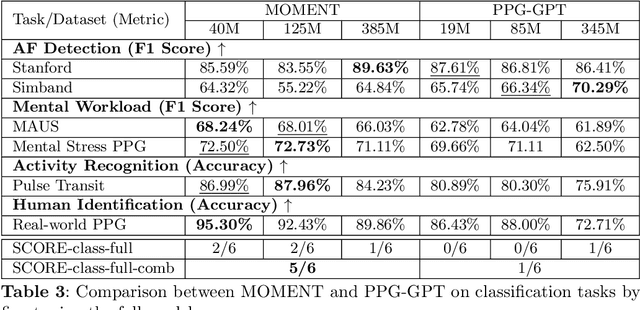
Abstract:Foundation models are large-scale machine learning models that are pre-trained on massive amounts of data and can be adapted for various downstream tasks. They have been extensively applied to tasks in Natural Language Processing and Computer Vision with models such as GPT, BERT, and CLIP. They are now also increasingly gaining attention in time-series analysis, particularly for physiological sensing. However, most time series foundation models are specialist models - with data in pre-training and testing of the same type, such as Electrocardiogram, Electroencephalogram, and Photoplethysmogram (PPG). Recent works, such as MOMENT, train a generalist time series foundation model with data from multiple domains, such as weather, traffic, and electricity. This paper aims to conduct a comprehensive benchmarking study to compare the performance of generalist and specialist models, with a focus on PPG signals. Through an extensive suite of total 51 tasks covering cardiac state assessment, laboratory value estimation, and cross-modal inference, we comprehensively evaluate both models across seven dimensions, including win score, average performance, feature quality, tuning gain, performance variance, transferability, and scalability. These metrics jointly capture not only the models' capability but also their adaptability, robustness, and efficiency under different fine-tuning strategies, providing a holistic understanding of their strengths and limitations for diverse downstream scenarios. In a full-tuning scenario, we demonstrate that the specialist model achieves a 27% higher win score. Finally, we provide further analysis on generalization, fairness, attention visualizations, and the importance of training data choice.
Continuous Cardiac Arrest Prediction in ICU using PPG Foundation Model
Feb 12, 2025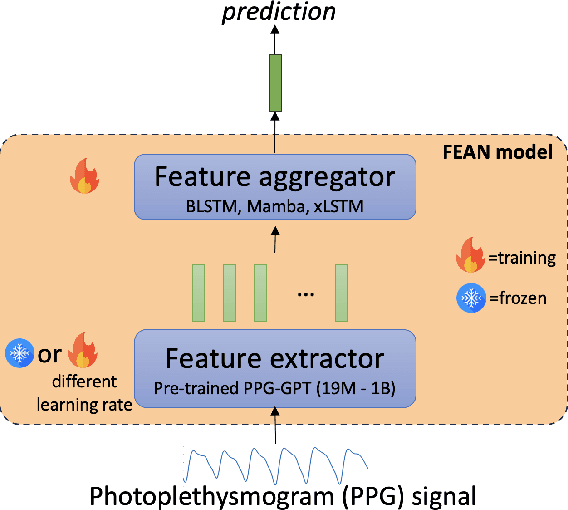
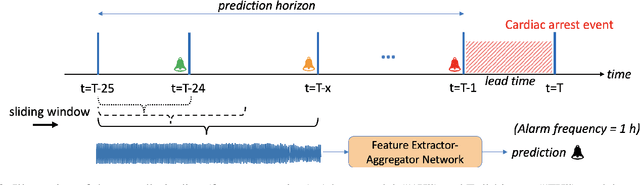
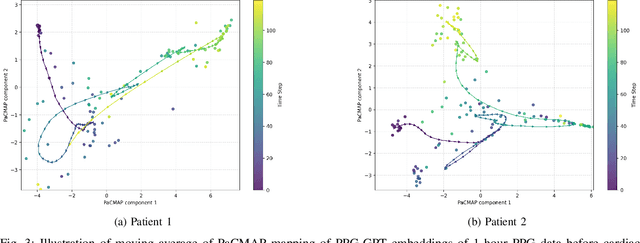
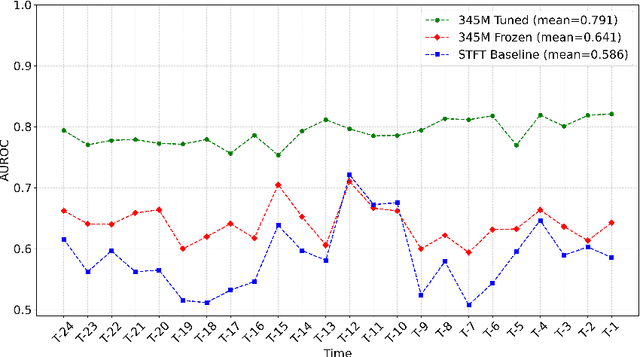
Abstract:Non-invasive patient monitoring for tracking and predicting adverse acute health events is an emerging area of research. We pursue in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA) prediction using only single-channel finger photoplethysmography (PPG) signals. Our proposed two-stage model Feature Extractor-Aggregator Network (FEAN) leverages powerful representations from pre-trained PPG foundation models (PPG-GPT of size up to 1 Billion) stacked with sequential classification models. We propose two FEAN variants ("1H", "FH") which use the latest one-hour and (max) 24-hour history to make decisions respectively. Our study is the first to present IHCA prediction results in ICU patients using only unimodal (continuous PPG signal) waveform deep representations. With our best model, we obtain an average of 0.79 AUROC over 24~h prediction window before CA event onset with our model peaking performance at 0.82 one hour before CA. We also provide a comprehensive analysis of our model through architectural tuning and PaCMAP visualization of patient health trajectory in latent space.
Early Risk Prediction of Pediatric Cardiac Arrest from Electronic Health Records via Multimodal Fused Transformer
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Early prediction of pediatric cardiac arrest (CA) is critical for timely intervention in high-risk intensive care settings. We introduce PedCA-FT, a novel transformer-based framework that fuses tabular view of EHR with the derived textual view of EHR to fully unleash the interactions of high-dimensional risk factors and their dynamics. By employing dedicated transformer modules for each modality view, PedCA-FT captures complex temporal and contextual patterns to produce robust CA risk estimates. Evaluated on a curated pediatric cohort from the CHOA-CICU database, our approach outperforms ten other artificial intelligence models across five key performance metrics and identifies clinically meaningful risk factors. These findings underscore the potential of multimodal fusion techniques to enhance early CA detection and improve patient care.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge