Joachim Groeger
Inverse Reinforcement Learning with Explicit Policy Estimates
Mar 04, 2021
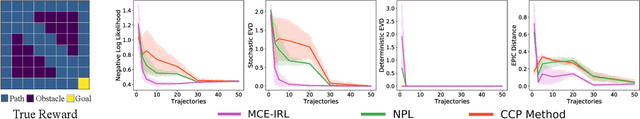
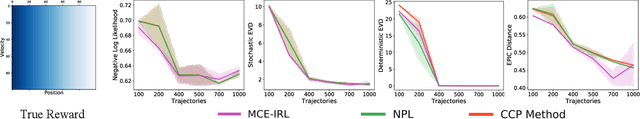
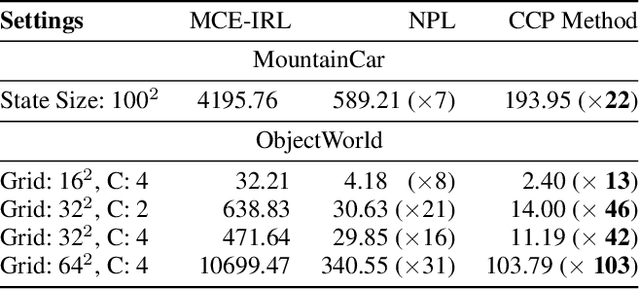
Abstract:Various methods for solving the inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) problem have been developed independently in machine learning and economics. In particular, the method of Maximum Causal Entropy IRL is based on the perspective of entropy maximization, while related advances in the field of economics instead assume the existence of unobserved action shocks to explain expert behavior (Nested Fixed Point Algorithm, Conditional Choice Probability method, Nested Pseudo-Likelihood Algorithm). In this work, we make previously unknown connections between these related methods from both fields. We achieve this by showing that they all belong to a class of optimization problems, characterized by a common form of the objective, the associated policy and the objective gradient. We demonstrate key computational and algorithmic differences which arise between the methods due to an approximation of the optimal soft value function, and describe how this leads to more efficient algorithms. Using insights which emerge from our study of this class of optimization problems, we identify various problem scenarios and investigate each method's suitability for these problems.
Inverse Reinforcement Learning with Conditional Choice Probabilities
Sep 22, 2017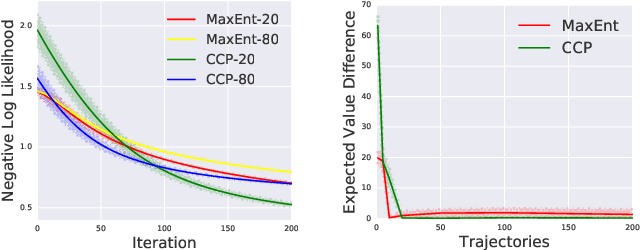
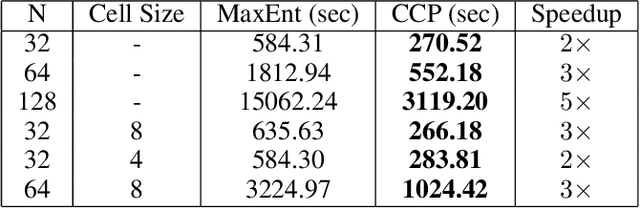

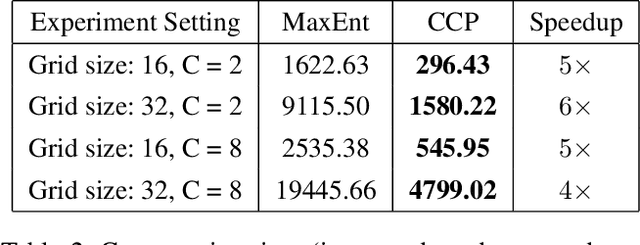
Abstract:We make an important connection to existing results in econometrics to describe an alternative formulation of inverse reinforcement learning (IRL). In particular, we describe an algorithm using Conditional Choice Probabilities (CCP), which are maximum likelihood estimates of the policy estimated from expert demonstrations, to solve the IRL problem. Using the language of structural econometrics, we re-frame the optimal decision problem and introduce an alternative representation of value functions due to (Hotz and Miller 1993). In addition to presenting the theoretical connections that bridge the IRL literature between Economics and Robotics, the use of CCPs also has the practical benefit of reducing the computational cost of solving the IRL problem. Specifically, under the CCP representation, we show how one can avoid repeated calls to the dynamic programming subroutine typically used in IRL. We show via extensive experimentation on standard IRL benchmarks that CCP-IRL is able to outperform MaxEnt-IRL, with as much as a 5x speedup and without compromising on the quality of the recovered reward function.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge