Jo Eidsvik
Latent Diffusion Model for Conditional Reservoir Facies Generation
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:Creating accurate and geologically realistic reservoir facies based on limited measurements is crucial for field development and reservoir management, especially in the oil and gas sector. Traditional two-point geostatistics, while foundational, often struggle to capture complex geological patterns. Multi-point statistics offers more flexibility, but comes with its own challenges. With the rise of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and their success in various fields, there has been a shift towards using them for facies generation. However, recent advances in the computer vision domain have shown the superiority of diffusion models over GANs. Motivated by this, a novel Latent Diffusion Model is proposed, which is specifically designed for conditional generation of reservoir facies. The proposed model produces high-fidelity facies realizations that rigorously preserve conditioning data. It significantly outperforms a GAN-based alternative.
VNIbCReg: VICReg with Neighboring-Invariance and better-Covariance Evaluated on Non-stationary Seismic Signal Time Series
Apr 08, 2022



Abstract:One of the latest self-supervised learning (SSL) methods, VICReg, showed a great performance both in the linear evaluation and the fine-tuning evaluation. However, VICReg is proposed in computer vision and it learns by pulling representations of random crops of an image while maintaining the representation space by the variance and covariance loss. However, VICReg would be ineffective on non-stationary time series where different parts/crops of input should be differently encoded to consider the non-stationarity. Another recent SSL proposal, Temporal Neighborhood Coding (TNC) is effective for encoding non-stationary time series. This study shows that a combination of a VICReg-style method and TNC is very effective for SSL on non-stationary time series, where a non-stationary seismic signal time series is used as an evaluation dataset.
Learning excursion sets of vector-valued Gaussian random fields for autonomous ocean sampling
Jul 07, 2020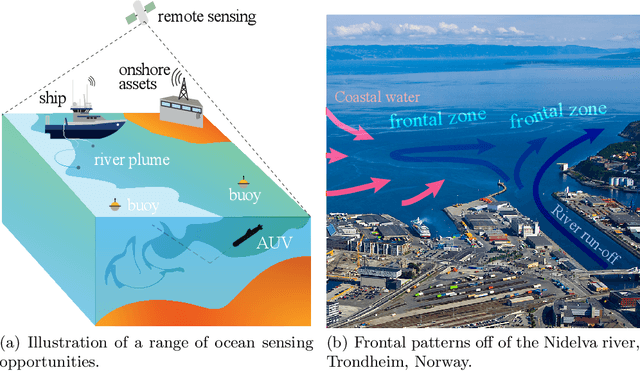

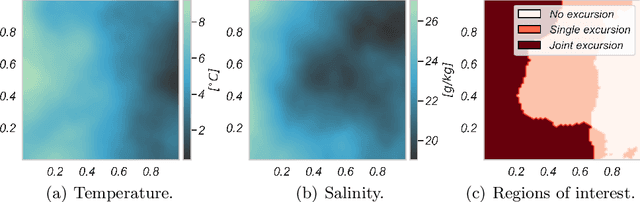
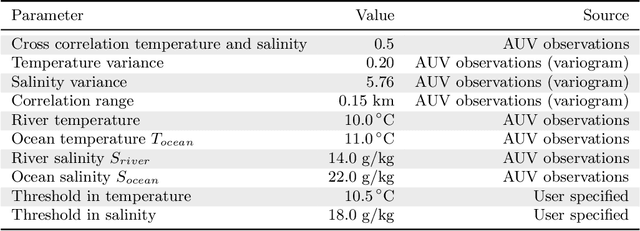
Abstract:Improving and optimizing oceanographic sampling is a crucial task for marine science and maritime resource management. Faced with limited resources in understanding processes in the water-column, the combination of statistics and autonomous systems provide new opportunities for experimental design. In this work we develop efficient spatial sampling methods for characterizing regions defined by simultaneous exceedances above prescribed thresholds of several responses, with an application focus on mapping coastal ocean phenomena based on temperature and salinity measurements. Specifically, we define a design criterion based on uncertainty in the excursions of vector-valued Gaussian random fields, and derive tractable expressions for the expected integrated Bernoulli variance reduction in such a framework. We demonstrate how this criterion can be used to prioritize sampling efforts at locations that are ambiguous, making exploration more effective. We use simulations to study and compare properties of the considered approaches, followed by results from field deployments with an autonomous underwater vehicle as part of a study mapping the boundary of a river plume. The results demonstrate the potential of combining statistical methods and robotic platforms to effectively inform and execute data-driven environmental sampling.
Dynamic Decision Making for Graphical Models Applied to Oil Exploration
Jun 28, 2013



Abstract:This paper has been withdrawn by the authors. We present a framework for sequential decision making in problems described by graphical models. The setting is given by dependent discrete random variables with associated costs or revenues. In our examples, the dependent variables are the potential outcomes (oil, gas or dry) when drilling a petroleum well. The goal is to develop an optimal selection strategy that incorporates a chosen utility function within an approximated dynamic programming scheme. We propose and compare different approximations, from simple heuristics to more complex iterative schemes, and we discuss their computational properties. We apply our strategies to oil exploration over multiple prospects modeled by a directed acyclic graph, and to a reservoir drilling decision problem modeled by a Markov random field. The results show that the suggested strategies clearly improve the simpler intuitive constructions, and this is useful when selecting exploration policies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge