Jitendra Bhandari
VeriLoC: Line-of-Code Level Prediction of Hardware Design Quality from Verilog Code
Jun 08, 2025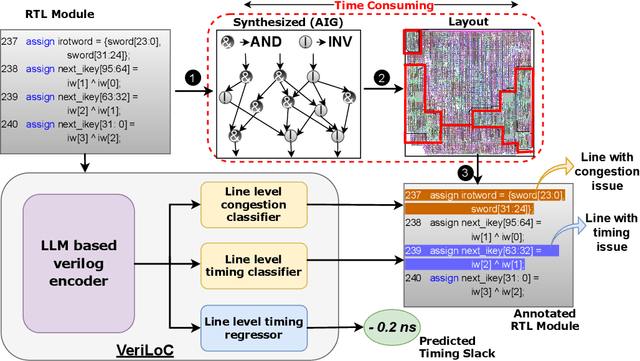
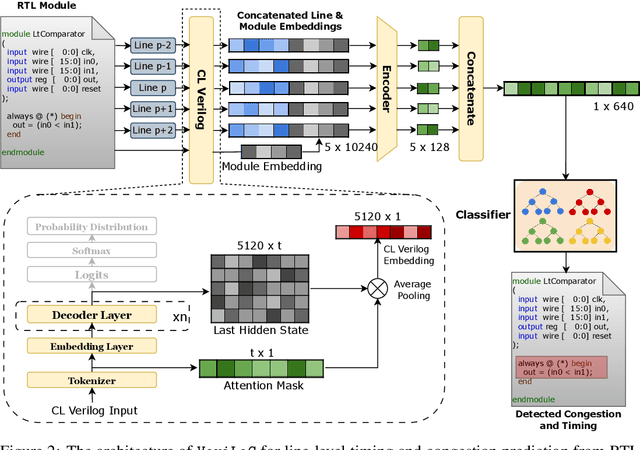
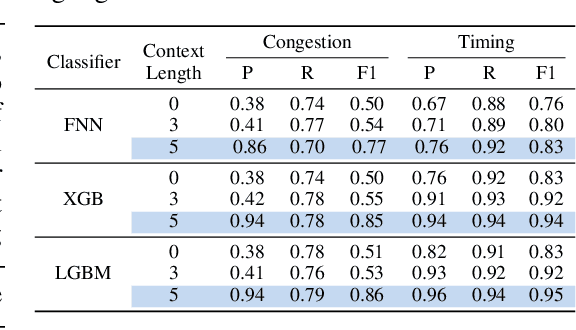
Abstract:Modern chip design is complex, and there is a crucial need for early-stage prediction of key design-quality metrics like timing and routing congestion directly from Verilog code (a commonly used programming language for hardware design). It is especially important yet complex to predict individual lines of code that cause timing violations or downstream routing congestion. Prior works have tried approaches like converting Verilog into an intermediate graph representation and using LLM embeddings alongside other features to predict module-level quality, but did not consider line-level quality prediction. We propose VeriLoC, the first method that predicts design quality directly from Verilog at both the line- and module-level. To this end, VeriLoC leverages recent Verilog code-generation LLMs to extract local line-level and module-level embeddings, and train downstream classifiers/regressors on concatenations of these embeddings. VeriLoC achieves high F1-scores of 0.86-0.95 for line-level congestion and timing prediction, and reduces the mean average percentage error from 14% - 18% for SOTA methods down to only 4%. We believe that VeriLoC embeddings and insights from our work will also be of value for other predictive and optimization tasks for complex hardware design.
VeriContaminated: Assessing LLM-Driven Verilog Coding for Data Contamination
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized code generation, achieving exceptional results on various established benchmarking frameworks. However, concerns about data contamination - where benchmark data inadvertently leaks into pre-training or fine-tuning datasets - raise questions about the validity of these evaluations. While this issue is known, limiting the industrial adoption of LLM-driven software engineering, hardware coding has received little to no attention regarding these risks. For the first time, we analyze state-of-the-art (SOTA) evaluation frameworks for Verilog code generation (VerilogEval and RTLLM), using established methods for contamination detection (CCD and Min-K% Prob). We cover SOTA commercial and open-source LLMs (CodeGen2.5, Minitron 4b, Mistral 7b, phi-4 mini, LLaMA-{1,2,3.1}, GPT-{2,3.5,4o}, Deepseek-Coder, and CodeQwen 1.5), in baseline and fine-tuned models (RTLCoder and Verigen). Our study confirms that data contamination is a critical concern. We explore mitigations and the resulting trade-offs for code quality vs fairness (i.e., reducing contamination toward unbiased benchmarking).
VeriLeaky: Navigating IP Protection vs Utility in Fine-Tuning for LLM-Driven Verilog Coding
Mar 17, 2025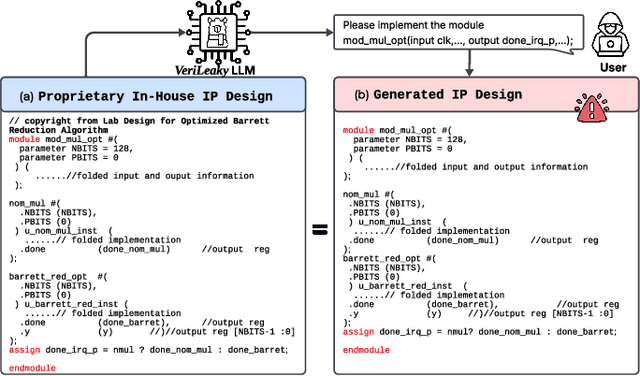
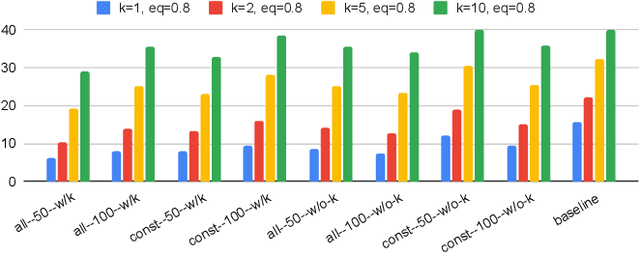
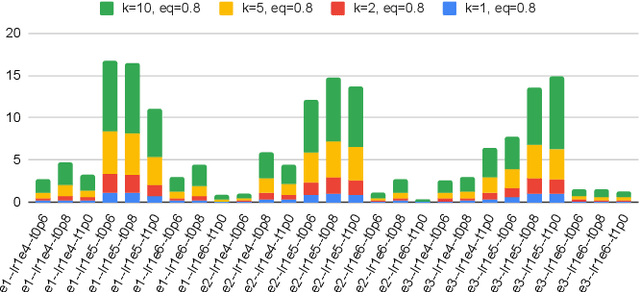
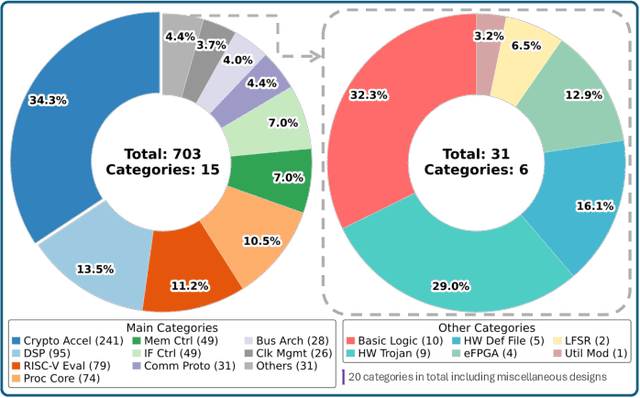
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer significant potential for coding, yet fine-tuning (FT) with curated data is essential for niche languages like Verilog. Using proprietary intellectual property (IP) for FT presents a serious risk, as FT data can be leaked through LLM inference. This leads to a critical dilemma for design houses: seeking to build externally accessible LLMs offering competitive Verilog coding, how can they leverage in-house IP to enhance FT utility while ensuring IP protection? For the first time in the literature, we study this dilemma. Using LLaMA 3.1-8B, we conduct in-house FT on a baseline Verilog dataset (RTLCoder) supplemented with our own in-house IP, which is validated through multiple tape-outs. To rigorously assess IP leakage, we quantify structural similarity (AST/Dolos) and functional equivalence (Synopsys Formality) between generated codes and our in-house IP. We show that our IP can indeed be leaked, confirming the threat. As defense, we evaluate logic locking of Verilog codes (ASSURE). This offers some level of protection, yet reduces the IP's utility for FT and degrades the LLM's performance. Our study shows the need for novel strategies that are both effective and minimally disruptive to FT, an essential effort for enabling design houses to fully utilize their proprietary IP toward LLM-driven Verilog coding.
SENTAUR: Security EnhaNced Trojan Assessment Using LLMs Against Undesirable Revisions
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:A globally distributed IC supply chain brings risks due to untrusted third parties. The risks span inadvertent use of hardware Trojan (HT), inserted Intellectual Property (3P-IP) or Electronic Design Automation (EDA) flows. HT can introduce stealthy HT behavior, prevent an IC work as intended, or leak sensitive data via side channels. To counter HTs, rapidly examining HT scenarios is a key requirement. While Trust-Hub benchmarks are a good starting point to assess defenses, they encompass a small subset of manually created HTs within the expanse of HT designs. Further, the HTs may disappear during synthesis. We propose a large language model (LLM) framework SENTAUR to generate a suite of legitimate HTs for a Register Transfer Level (RTL) design by learning its specifications, descriptions, and natural language descriptions of HT effects. Existing tools and benchmarks are limited; they need a learning period to construct an ML model to mimic the threat model and are difficult to reproduce. SENTAUR can swiftly produce HT instances by leveraging LLMs without any learning period and sanitizing the HTs facilitating their rapid assessment. Evaluation of SENTAUR involved generating effective, synthesizable, and practical HTs from TrustHub and elsewhere, investigating impacts of payloads/triggers at the RTL. While our evaluation focused on HT insertion, SENTAUR can generalize to automatically transform an RTL code to have defined functional modifications.
ASCENT: Amplifying Power Side-Channel Resilience via Learning & Monte-Carlo Tree Search
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Power side-channel (PSC) analysis is pivotal for securing cryptographic hardware. Prior art focused on securing gate-level netlists obtained as-is from chip design automation, neglecting all the complexities and potential side-effects for security arising from the design automation process. That is, automation traditionally prioritizes power, performance, and area (PPA), sidelining security. We propose a "security-first" approach, refining the logic synthesis stage to enhance the overall resilience of PSC countermeasures. We introduce ASCENT, a learning-and-search-based framework that (i) drastically reduces the time for post-design PSC evaluation and (ii) explores the security-vs-PPA design space. Thus, ASCENT enables an efficient exploration of a large number of candidate netlists, leading to an improvement in PSC resilience compared to regular PPA-optimized netlists. ASCENT is up to 120x faster than traditional PSC analysis and yields a 3.11x improvement for PSC resilience of state-of-the-art PSC countermeasures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge